Monophyletic groups PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Monophyletic groups
1
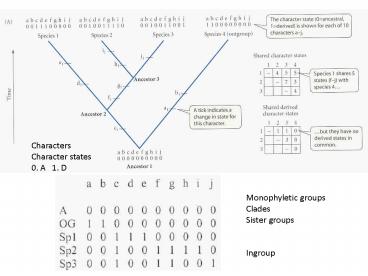
Characters Character states 0. A 1. D
Monophyletic groups Clades Sister groups Ingroup
2
autapomorphies
Synapomorphy shared DCSs
3
No
Homoplasy Independently derived
character states and reversals
A a b c d e f g h I j OG 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Sp1 0 1 1 0
0 0 1 1 0 1 Sp2 0 1 1 1 1 1
0 1 0 0 Sp3 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
1
4
- Most phylogenetic analyses use the principle of
parsimony. - Best phylogenetic depiction is the one
requiring the fewest evolutionary changes.
5
Principle of parsimony
Convergence
6
An example of phylogenetic analysis relationship
of whales to other mammals. Principle of
parsimony. Why is this a bad example?
7
Artiodactyl hypothesis
Whale-hippo hypothesis
Whale phylogeny
Competing hypotheses
10,395 trees
8
Perissodactyla
Artiodactyla
9
Gain of artiodactyl astragalus
Perissodactyl astragalus
10
Genetic resolution?
A sequence of 60 bases from the beta-casein gene
60 characters
- Characters
- (a) informative
- Character 166
- (b) uninformative
- no variation
- e.g., character 142
- 2. occur only once
- autapomorphy
- e.g., character 192
- (c) conflicting
- phylogenetic
- signals
- e.g., 162 and 177
- Homoplasy
11
Resolution of whale phylogeny
SINES and LINES Retrotransposable interspersed
elements RNA intermediate Contains info
for reverse transcriptase
12
Example of a phylogeny a globin pseudogene
13
A few difficulties Different genes may give
different results gene trees
14
A difficulty dataset could not resolve all
relationships
Polytomy
15
You hope for congruence
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.