Process Modeling - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
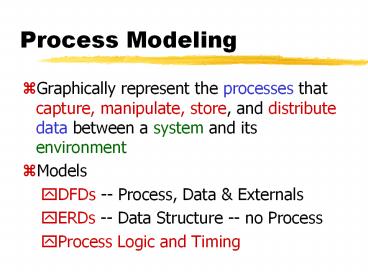
Process Modeling
Description:
Process Modeling. Graphically represent the processes that capture, manipulate, ... Explode a single process into subprocesses. Balancing (the Great Circle Rule) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:47
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Process Modeling
1
Process Modeling
- Graphically represent the processes that capture,
manipulate, store, and distribute data between a
system and its environment - Models
- DFDs -- Process, Data Externals
- ERDs -- Data Structure -- no Process
- Process Logic and Timing
2
Process Modeling Deliverables
- Context DFD (Not in D/2000)
- DFD of current physical system
- DFD of current logical system
- DFD of new logical system
- Adequate descriptions of each DFD component
(Oracle Repository)
3
DFD Mechanics
4
Context Level DFD
Figure 8.4, p284
5
Level Zero (First Level) Diagram
Figure 8.5, p285
6
DFD Rules -- Process
- A. No process can have only outputs
- B. No process can have only inputs
- Every Process has Input Output
- C. (1) Use Verb phrase labels for the lowest
level (Basic Function Module - a BFM has no
explosion) (2) Use xxx Process for the others
7
DFD Rules -- Process
Incorrect Correct
A. B.
8
DFD Rules -- Data Store
- D. Data cannot move directly from one data store
to another data store - E. Data cannot move directly from an outside
source to a data store - F. Data cannot move directly to an outside sink
from a data store - One end of a Data Flow must be a Process
- G. Use a Noun phrase label (Entity Name)
9
DFD Rules -- Source / Sink
- H. Data cannot move directly from a source to a
sink. It must be moved by a process. - I. Noun phrase label. (External)
- Contents are Entities - one Primary
10
DFD Rules -- Data Flow
- J. A data flow has only one direction of flow
between symbols a data flow may flow in both
directions to and from a data store (usually
two symbols) - K. A fork in a data flow means that exactly the
same data goes to two different processes or
data stores. - L. A join in a data flow means that exactly the
same data comes from two different processes
and data stores.
11
DFD Rules -- Data Flow
Incorrect Correct
J. K. L.
12
DFD Rules -- Data Flow
- M. A data flow cannot go directly back to the
same process it leaves - N. A data flow to a data store means create,
update or delete - O. A data flow from a data store means retrieve
or use - P. Use a Noun phrase label. Contents are
attributes of entities and data items
13
Other DFD Issues
- Decomposition (Explosion)
- Explode a single process into subprocesses
- Balancing (the Great Circle Rule)
- Conserve all process inputs and outputs when
decomposing a process
14
Decomposition of 4.0
Figure 8.8 and 8.7, p289
15
Decomposition of 4.3
Figure 8.9, p290
16
Balance - Context Level
0
System
B
A
Sink 1
Source 1
17
Unbalanced DFD
1
A
Source 1
C
Formatted A
Formatted C
Source 2
2
Sink 1
B
18
DFD Rules -- Advanced Rules
- R. The inputs to a process must be sufficient to
produce the outputs - S. At the lowest level of DFDs, new data flows
may be added to represent data that are
transmitted under exceptional conditions (e.g.,
error messages). - T. To avoid having data flow lines cross each
other, you may repeat data stores or sources /
sinks on a DFD.
19
DFD Guidelines
- Completeness
- Consistency
- Timing
- Iterative Development
20
Primitive DFDs -- BFM Level
- Single database operation - update, retrieve,
create, delete - Single other process function -- input or output
data calculate decision - Process for each option or choice
- Data flow split to each use set
- User and Analyst are satisfied
- Element of Personal Choice