Nuclear Processes PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title: Nuclear Processes
1
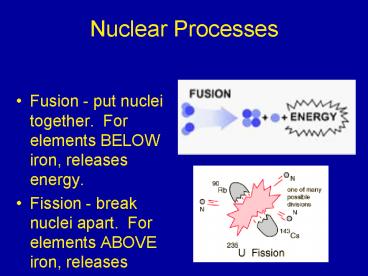
Nuclear Processes
- Fusion - put nuclei together. For elements BELOW
iron, releases energy. - Fission - break nuclei apart. For elements ABOVE
iron, releases energy.
2
Warmup
- What is the atomic number of Oxygen?
- What element has 32 protons?
- 8
- Germanium
3
Power Generation
- Uranium fission - 108 J / kg. Leaves behind
radioactive waste Currently known ore deposits
could supply our energy needs for about 50 years. - Hydrogen fusion - 1015 J / kg. Very little
radioactive waste. Hydrogen can be produced from
water, so the supply is practically limitless.
Not yet feasible, but close. - For comparison, oil produces about 105 J / kg,
and will last, at most, another 100 years.
4
Radioactive Decay
- Radioisotope - an unstable isotope that will
naturally decay, producing a new element and some
radiation - Half-life - the amount of time it takes for half
of the atoms of a radioisotope to decay
5
Radioactive Decay example
- For example, Uranium-239 has a half-life of 23
minutes, and decays into Neptunium - 239.
6
Practice
- Plutonium - 239 has a half life of about 20,000
years. If you started with 2 kg of Pu-239, how
long would you need to wait to have less than 0.5
kg?
- 40,000 years!
- After 20,000 years, you would have 1 kg.
- After 40,000 years, you would have 0.5 kg.
7
Why Does Decay Happen?
- The answer is the fourth and final of the four
fundamental forces of nature that we have been
studying. It is called the Weak Force. - The Weak Force causes particles to interact in
the nucleus and transmutate (change into) a
different kind of particle. Those particles are
then emitted (shot out of) the nucleus of the
atom at high speed. This turns the atom into a
different kind of atom!
8
Radioactivity
- Radioactivity - the energetic particles emitted
by elements when they decay. These particles can
be dangerous to living things. They can harm
genetic material and living tissue. - Important Measure - how much energy received per
kilogram of body mass. Unit is the sievert,
which is 1 Joule / kg of body mass.
9
Types of Radioactivity
- Alpha - a nucleus emits a Helium nucleus (2
protons and 2 neutrons). Not very penetrating. - Beta - a neutron becomes a proton and emits an
electron with lots of energy. So-so penetrating. - Gamma - the nucleus changes shape and emits a
very high energy photon of light. Very
penetrating - Which of these would change the element and the
mass? Which of these would change the element
but not the mass?
10
Practice
- Iodine is collected by the thyroid gland in the
body. To study how well the thyroid is working,
doctors inject a patient with radioactive iodine
and watch for how quickly the radioactivity
starts emitting from the thyroid. Which type of
radioactivity do they use?
- Gamma, because it is most penetrating. More
alpha and beta would be absorbed by the body.
11
Background Radiation
- In the US, the average person is exposed to about
3.5 milliSieverts of radiation each year. 50
milliSieverts per year is the legally allowed
limit (past this, no more x-rays or working with
radiation sources) - Some surprising sources are radon gas that seeps
up from the ground radioactive isotopes that are
part of our food and thousands of particles that
stream through our bodies each second, generated
by cosmic rays hitting the upper atmosphere!
12
(No Transcript)
13
Practice
- Measurements have shown that living within 50
miles of a nuclear power plant will increase your
yearly radiation dosage by 90 nanoSievert - Measurements have shown that living within 50
miles of a coal burning power plant increases
your yearly radiation dosage by 300 nanoSievert - How could living near a coal plant increase your
exposure by more than living near a nuclear power
plant?!
14
- Nuclear power plants have many measures in place
to block IN the radiation - The radioactivity in coal comes from
radioisotopes such as Carbon-14 that are
naturally present in the coal. - These radioisotopes are then present in the smoke
that is released by the power plant. - Exposure is also increased when you BREATHE the
smoke - that allows the radiation direct access
to unprotected tissues in your lungs!