The Structure of a nucleotide PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title: The Structure of a nucleotide
1
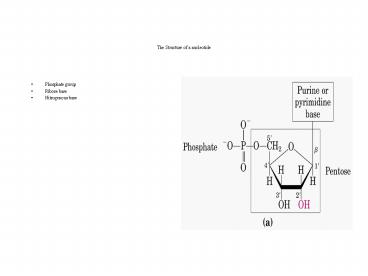
The Structure of a nucleotide
- Phosphate group
- Ribose base
- Nitrogenous base
2
(No Transcript)
3
The Four Nucleotides
- Adenine (A)
- Thymine (T)
- Guanine (G)
- Cytosine (C)
4
- Phosphodiester bonds link the nucleotides
together - The linkage is between the phosphate group and
the ribose (pentose) sugar - The 5 hydroxyl group of one nucleotide is linked
to the 3 hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
5
(No Transcript)
6
- The nucleotides have an orientation of 5 -gt 3
- The 5 -gt 3 orientation is very important
because it is the direction that enzymes (i.e.
DNA polymerase) read DNA
7
(No Transcript)
8
- DNA is double stranded
- The two strands are anti-parallel
- The ribose bases form hydrogen bonds between the
two DNA strands - A T
- G C
9
(No Transcript)
10
Complementary strands of DNA5 GTATCC 33
CATAGG 5Note5 referred to as upstream3
referred to as downstream
11
gagggctggc cagtgaggct cggcccgggg aaagtgaaag
tttgcctggg tcctctcggc gccagagccg
ctctccgcat cccaggacag cggtgcggcc ctcggccggg
gcgcccactc cgcagcagcc agcgagcgag cgagcgagcg
agggcggccg acgcgcccgg ccgggaccca gctgcccgta
tgaccgcgcc gggcgccgcc gggcgctgcc ctcccacgac
atggctgggc tccctgctgt tgttggtctg tctcctggcg
agcaggagta tcaccgagga ggtgtcggag
tactgtagcc acatgattgg gagtggacac ctgcagtctc
tgcagcggct gattgacagt cagatggaga cctcgtgcca
aattacattt gagtttgtag accaggaaca gttgaaagat
ccagtgtgct accttaagaa ggcatttctc ctggtacaag
acataatgga ggacaccatg cgcttcagag ataacacccc
caatgccatc gccattgtgc agctgcagga actctctttg
aggctgaaga gctgcttcac caaggattat gaagagcatg
acaaggcctg cgtccgaact ttctatgaga cacctctcca
gttgctggag aaggtcaaga atgtctttaa tgaaacaaag
aatctccttg acaaggactg gaatattttc agcaagaact
gcaacaacag ctttgctgaa tgctccagcc aagatgtggt
gaccaagcct gattgcaact gcctgtaccc caaagccatc
cctagcagtg acccggcctc tgtctcccct catcagcccc
tcgccccctc catggcccct gtggctggct tgacctggga
ggactctgag ggaactgagg gcagctccct cttgcctggt
gagcagcccc tgcacacagt ggatccaggc agtgccaagc
agcggccacc caggagcacc tgccagagct ttgagccgcc
agagacccca gttgtcaagg acagcaccat cggtggctca
12
- DNA is organized into genes
- Genes are organized into chromosomes genomes
which includes genes and non-coding DNA - Chromosomes are organized into a genome
- Note a genome is not contiguous
13
The Central Dogma
- DNA -gt RNA -gt protein
- DNA -gt RNA transcription
- Facilitated by RNA polymerase
- Note a one to one correspondence between DNA and
RNA - RNA -gt Protein translation
- Facilitated by ribosome
- Three RNA molecules 1 amino acid
14
Important facts about RNA
- RNA is a stranded molecule
- Also has phosphodiester linkage
- 5 -gt 3 directionality
- Replaces Adenine with Uracil
- Synthesized by RNA polymerase
- Can form into secondary structure
15
(No Transcript)
16
- RNA polymerase binds to promoter sequence in DNA
- The probability that a particular DNA sequence
will occur is P (1/4)n where n is the length
of the DNA sequence - In prokaryotes the length of a promoter is
approximately 13 nts - Thus a promoter sequence will occur by chance
about every 70 million nts in prokaryotes
17
- The structure of a chromosome affects the
availability of a promoter in eukaryotes this is
not true in prokaryotes - Condensed chromatin is transcriptionally inactive
- Thus the conformation of a chromosome is
important in eukaryotic transcription
18
- There is not a simple one to one correspondence
between nts and amino acids (i.e. 1 nt does not
equal 1 aa) - 3 nts 1 aa
- Problem there are 64 different combinations of
3nts (43) but only 20 aa - Solution 18 of the 20 aa coded by more than
triplet - The genetic code is degenerate
- Codon is a functional unit of RNA that codes
for an amino acid
19
(No Transcript)
20
- Initiation codon AUG also codes for Met
- Termination codon UAA, UAG, and UGA
- Also called stop codons or nonsense codons
21
Reading frames can alter the sequence of a
protein
22
- An open reading frame is a reading frame that is
at least 50 aa in length and does not contain a
termination codon.
23
Introns and exons
- Introns are intervening mRNA sequences that are
removed before mRNA is translated - Exons are the mRNA sequences that are retained
- The process of removing the introns is known as
splicing - Alternative splicing is a mechanism of generating
different mRNAs from a single mRNA transcript
24
(No Transcript)