Mechanism of Fumarase - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title:
Mechanism of Fumarase
Description:
Figure 22-1 The sites of electron transfer that form NADH and FADH2 in ... 22-3 Freeze-fracture and freeze-etch electron micrographs of the inner and outer ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:146
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Mechanism of Fumarase
1
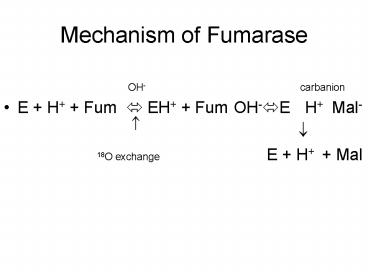
Mechanism of Fumarase
- OH- carbanion
- E H Fum ? EH Fum?OH-?E ? H ?Mal-
- ? ?
- 18O exchange E H Mal
2
Chapter 22 Electron Transport and Oxidative
Phosphorylation
3
Figure 22-1 The sites of electron transfer that
form NADH and FADH2 in glycolysis and the citric
acid cycle.
Page 798
4
Figure 22-2a Mitochondria. (a) An electron
micrograph of an animal mitochondrion.
Page 799
5
Figure 22-2b Mitochondria. (b) Cutaway diagram of
a mitochondrion.
Page 799
6
Figure 22-3 Freeze-fracture and freeze-etch
electron micrographs of the inner and outer
mitochondrial membranes.
Page 799
7
Figure 22-7 The malateaspartate shuttle.
Page 801
8
Figure 22-8 The glycerophosphate shuttle.
Page 802
9
Figure 22-9 The mitochondrial electron-transport
chain.
Page 803
10
Table 22-1 Reduction Potentials of
Electron-Transport Chain Components in Resting
Mitochondria.
Page 806
11
Table 22-1 (continued) Reduction Potentials of
Electron-Transport Chain Components in Resting
Mitochondria.
Page 806
12
Table 22-1 (continued) Reduction Potentials of
Electron-Transport Chain Components in Resting
Mitochondria.
Page 806
13
Table 22-1 (continued) Reduction Potentials of
Electron-Transport Chain Components in Resting
Mitochondria.
Page 806
14
Figure 22-11 Effect of inhibitors on electron
transport.
Page 805
15
Figure 22-12 Electron micrographs of mouse liver
mitochondria. (a) In the actively respiring
state. (b) In the resting state.
Page 806
16
Figure 22-13 Determination of the stoichiometry
of coupled oxidation and phosphorylation (the P/O
ratio) with different electron donors.
Page 807
17
Figure 22-14The mitochondrial electron-transport
chain.
Page 808
18
Figure 22-15 Structures of the common ironsulfur
clusters. (a) FeS cluster. (b) 2Fe2S
cluster. (c)4Fe4S cluster.
Page 808
19
Figure 22-17 Oxidation states of the coenzymes of
complex I. (a) FMN. (b) CoQ.
Page 810
20
Figure 22-20 Active site interactions in the
proposed mechanism of the QFR-catalyzed reduction
of fumarate to succinate.
Page 812
21
Figure 22-21a Visible absorption spectra of
cytochromes. (a) Absorption spectrum of reduced
cytochrome c showing its characteristic a, b, and
g (Soret) absorption bands.
Page 813
22
Figure 22-21Visible absorption spectra of
cytochromes.(b) The three separate a bands in
the visible absorption spectrum of beef heart
mitochondrial membranes (below) indicate the
presence of cytochromes a, b, and c.
Page 813
23
Figure 22-22a Porphyrin rings in cytochromes.
(a) Chemical structures.
Page 813
24
Figure 22-22b Porphyrin rings in cytochromes. (b)
Axial liganding of the heme groups contained in
cytochromes a, b, and c are shown.
Page 813
25
Figure 22-25c X-Ray structure of fully oxidized
bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase. (c) A protomer
viewed similarly to Part a showing the positions
of the complexs redox centers.
Page 816
26
Figure 22-28 Proposed reaction sequence for the
reduction of O2 by the cytochrome a3CuB
binuclear complex of cytochrome c oxidase.
Page 819
27
Figure 22-29 Coupling of electron transport
(green arrow) and ATP synthesis.
Page 821
28
Alfonse, Biochemistry makes my head hurt!!
\