Urinary System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Urinary System
Description:
Urinary System – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:31
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Urinary System
1
Chapter 26
- Urinary System
2
Urinary System Functions
- Filtering of blood
- Regulation of
- blood volume
- concentration of blood solutes
- pH of extracellular fluid
- blood cell synthesis
- Synthesis of Vitamin D
3
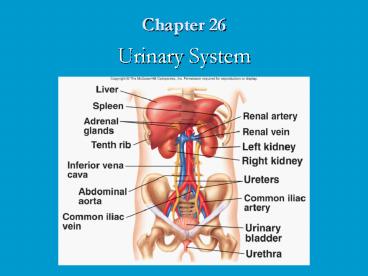
Urinary System Anatomy
4
(No Transcript)
5
Location and External Anatomyof Kidneys
- External Anatomy
- Renal capsule
- Surrounds each kidney
- Perirenal fat
- Engulfs renal capsule and acts as cushioning
- Renal fascia
- Anchors kidneys to abdominal wall
- Hilum
- Renal artery and nerves enter and renal vein and
ureter exit kidneys
- Location
- Lie behind peritoneum on posterior abdominal wall
on either side of vertebral column - Lumbar vertebrae and rib cage partially protect
- Right kidney slightly lower than left
6
Internal Anatomy of Kidneys
- Cortex Outer area
- Renal columns
- Medulla Inner area
- Renal pyramids
- Calyces
- Major Converge to form pelvis
- Minor Papillae extend
- Nephron Functional unit of kidney
- Juxtamedullary
- Cortical
7
(No Transcript)
8
The Nephron
9
(No Transcript)
10
Histology of the Nephron
11
Internal Anatomy of Kidneys
- Renal corpuscle
- Bowmans capsule
- Parietal layer
- Visceral layer
- Glomerulus
- Network of capillaries
- Arterioles
- Afferent
- Blood to glomerulus
- Efferent
- Drains
- Tubules
- Proximal (convoluted) tubule
- Loops of Henle
- Descending limb
- Ascending limb
- Distal (convoluted) tubules
- Collecting ducts
12
Renal Corpuscle
13
Kidney Blood Flow
14
Ureters and Urinary Bladder
- Ureters
- Tubes through which urine flows from kidneys to
urinary bladder - Urinary bladder
- Stores urine
- Urethra
- Transports urine from bladder to outside of body
- Difference in length between males and females
- Sphincters
- Internal urinary
- External urinary
15
Ureters and Urinary Bladder
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
Urine Formation
19
Filtration
- Filtration
- Renal filtrate
- Plasma minus blood cells and blood proteins
- Most (99) reabsorbed
- Filtration membrane
- Fenestrated endothelium, basement membrane and
pores formed by podocytes
- Filtration pressure
- Responsible for filtrate formation
- Glomerular capillary pressure (GCP) minus capsule
pressure (CP) minus colloid osmotic pressure
(COP) - Changes caused by glomerular capillary pressure
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
Filtration Pressure
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
Tubular Reabsorption
- Reabsorption
- Passive transport
- Active transport
- Cotransport
- Specialization of tubule segments
- Substances transported
- Active transport moves Na across nephron wall
- Other ions and molecules moved by cotransport
- Passive transport moves water, urea,
lipid-soluble, nonpolar compounds
26
Tubular Secretion
- Substances enter proximal or distal tubules and
collecting ducts - H, K and some substances not produced in body
are secreted by countertransport mechanisms
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
Urine Production
- In ascending limb of loop of Henle
- Na, Cl-, K transported out of filtrate
- Water remains
- In distal tubules and collecting ducts
- Water movement out regulated by ADH
- If absent, water not reabsorbed and dilute urine
produced - If ADH present, water moves out, concentrated
urine produced
- In Proximal tubules
- Na and other substances removed
- Water follows passively
- Filtrate volume reduced
- In descending limb of loop of Henle
- Water exits passively, Filtrate volume reduced 15
30
Reabsorption in Proximal Nephron
31
(No Transcript)
32
Reabsorption in Loop of Henle
33
(No Transcript)
34
(No Transcript)
35
Reabsorption in Loop of Henle
36
Medullary Concentration and Urea Cycling
37
Urine Concentration Mechanism
- When large volume of water consumed
- Eliminate excess without losing large amounts of
electrolytes - Response is kidneys produce large volume of
dilute urine
- When drinking water not available
- Kidneys produce small volume of concentrated
urine - Removes waste and prevents rapid dehydration
38
Urine Concentrating Mechanism I
39
Urine Concentrating Mechanism II
40
Hormonal Mechanisms
- ADH
- Secreted by posterior pituitary
- Increases water permeability in distal tubules
and collecting ducts - Aldosterone
- Produced in adrenal cortex
- Affects Na and Cl- transport in nephron and
collecting ducts
- Renin
- Produced by kidneys, causes production of
angiotensin II - Atrial natriuretic hormone
- Produced by heart when blood pressure increases
- Inhibits ADH production
- Reduces ability of kidney to concentrate urine
41
Effect of ADH on Nephron
42
Aldosterone Effect on Distal Tubule
43
(No Transcript)
44
(No Transcript)
45
(No Transcript)
46
(No Transcript)
47
(No Transcript)
48
(No Transcript)
49
Internal Anatomy of Kidneys
- Cortex Outer area
- Renal columns
- Medulla Inner area
- Renal pyramids
- Calyces
- Major Converge to form pelvis
- Minor Papillae extend
- Nephron Functional unit of kidney
- Juxtamedullary
- Cortical
50
(No Transcript)
51
(No Transcript)
52
(No Transcript)
53
(No Transcript)
54
(No Transcript)
55
(No Transcript)
56
(No Transcript)
57
(No Transcript)
58
Clearance and Tubular Load
- Plasma clearance
- Volume of plasma cleared of a specific substance
each minute - Used to estimate GFR
- Used to calculate renal plasma flow
- Used to determine which drugs or other substances
excreted by kidney
- Tubular load
- Total amount of substance that passes through
filtration membrane into nephrons each minute - Normally glucose is almost completed reabsorbed
59
Tubular Maximum
- Tubular maximum
- Maximum rate at which a substance can be actively
absorbed - Each substance has its own tubular maximum
60
(No Transcript)
61
(No Transcript)
62
(No Transcript)
63
Urine Flow and Micturition Reflex
- Urine flow
- Hydrostatic pressure forces urine through nephron
- Peristalsis moves urine through ureters
- Micturition reflex
- Stretch of urinary bladder stimulates reflex
causing bladder to contract, inhibiting urinary
sphincters - Higher brain centers can stimulate or inhibit
reflex
64
Tubular flow and Micturition Reflex
65
Effects of Aging on Kidneys
- Gradual decrease in size of kidney
- Decrease in kidney size leads to decrease in
renal blood flow - Decrease in number of functional nephrons
- Decrease in renin secretion and vitamin D
synthesis - Decline in ability of nephron to secrete and
absorb
66
Kidney Dialysis