T cell activation and effector functions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 25
Title:
T cell activation and effector functions
Description:
Kill target cell (antigen-MHC I) Perforin, granzyme, FasL. Site of ... phagocyte. Inflammation. Tissue damage. Destruction of RBC. Hypersensitivity. Type III ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:241
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: T cell activation and effector functions
1
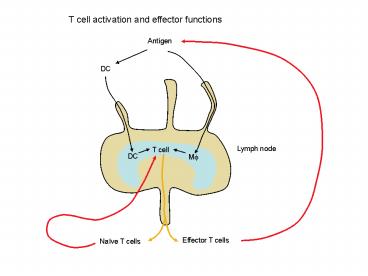
T cell activation and effector functions
Antigen
DC
Lymph node
T cell
DC
M?
Effector T cells
Naïve T cells
2
CD4 T cell
APC
Antigen-MHC II B7
Naïve CD4 T cell
Activated T cell
IL4
IL12, IFN-g
TH2
TH1
3
TH1 cells
Lymphoid tissue
Site of infection
TH1 cells
FasL
Target cell
TNF-???
IFN-?
IL2
Effector T cells
inflammation
Macrophage Antigen-presentation
4
TH2 cells
IL4, IL5, IL10, TGF-b
Lymphoid tissue
B cell activation
IgG, IgA, IgE
5
Activation of CD8 T cells
DC
Antigen-MHC I
TH1
B7
CD8 T cell
Lymphoid tissue
CTL
Site of infection
CTL
Perforin, granzyme, FasL
Kill target cell (antigen-MHC I)
6
B cell activation
Antigen
BM
GC
Lymph node
B cell
TH
antibody
Plasma cell
plasmablast
Naïve B cells
7
TH
CD40L-CD40
Hyper-IgM syndrome
TI antigens
Cytokines
B cell activation
AID Cytokines
AID
Somatic hypermutation
Class switch
IgG, IgA, IgE
Affinity maturation
Plasma cells, memory cells
8
NK cell activation and function
infection
IL12, IL15, IFN-a/b
Stimulatory ligand
Loss of MHC I
NK cell
IFN-g
Perforin, granzyme, FasL
macrophage
Antigen presentation
Kill target cell
9
Stimulatory and inhibitory receptors
Stimulatory ligand
IgG
MHC I
AR
CD16 (FcgRIII)
IR
ADCC
integration
10
Eosinophil activation and function
IgE, IgG, IgA
Fc receptor
Eosinophil activation
Toxic proteins
Inflammatory mediators
Kill helminth Tissue damage
11
Mast cells
C3a, C5a
IgE
CR
FceR
Mast cell
Inflammatory mediators cytokines
12
Immune response to extracellular bacteria
innate immune response
Bacteria, toxin
complement
Macrophage
Inflammation
Lysis
phagocytosis
Mast cell
Neutrophil Monocyte/Macrophage
Phagocytosis degranulation
13
Immune response to extracellular bacteria
adaptive immune response
Bacteria, toxin
APC
B cell
CD4 TH cell
antibodies
Opsonization for phagocytosis
neutralization
Complement activation
14
Immune response to intracellular bacteria
Innate immune response
bacteria
DC
macrophage
IL12, IL18, TNF-a
NK cell
IFN-g
Macrophage activation
Antigen presentation
TH1
15
Adaptive immune response to intracellular
bacteria
bacteria
DC
Antigen-MHC II
IL12, IFN-g
CD4 T cell
inflammation
TNF
Mf activation
IFN-g
IL2
TH1
CD40L
CD8 T cell activation
CD40L
FasL
IFN-g
Kill infected cell
Antigen presentation
16
Adaptive Immune response to intracellular bacteria
bacteria
CD40L
DC
Antigen-MHC I (cross-priming)
TH1
IL2
CD8 T cell
CTL
Perforin Granzyme FasL
Kill infected cell
17
Innate immune response to virus
Virus
dsRNA, unmethylated CpG
Target cell
NK cell
MHC I
IFN-a,b
PKR
OAS
RNA degradation
Inhibit protein synthesis
apoptosis
18
Innate immune response to virus
IFN-a,b, IL15
IL12
NK cell
Loss of MHC I
IgG (ADCC)
Stimulatory ligand
Perforin, granzyme, FasL
IFN-g
Antigen presentation
TH1
Kill target cell
19
Adaptive immune response
Virus
Antigen-MHC II IL12, IFN-g
Antigen-MHC I
DC
TH1
CD4 T cell
CD8 T cell
TH1
CTL
IFN-g
IL2
Kill infected cell
20
B cell response
virus
B cell
TH
antibodies
NK cell (ADCC)
neutralization
Complement activation
21
Immune response to parasite
Protozoa
Leishmania, similar to immune response to
intracellular bacteria
Antibodies play a more important role for
parasites with extended extracellular stage of
life cycle.
Helminth
inflammation
Mast cell
IgE
TH2
B cell
eosinophil
Toxic proteins
22
Immune response to tumor
T cell, NK cell
Tumor cell
Loss of MHC I stimulatory ligand (MIC)
tumor antigen-MHC I
TH1, CTL
NK cell
23
Hypersensitivity
Type II
Type I (allergy)
RBC antigen
allergen
IgM, IgG
TH2
IL4
Complement phagocyte
IgE
Mast cell
Inflammation Tissue damage
Destruction of RBC
eosinophil
24
Hypersensitivity
Type IV
Type III
Antigen
Antigen excess
Small immune complex
APC
TH1
Tissue deposition
CTL
Inflammation macrophage
Complement activation
Tissue damage
inflammation
25
Tolerance and autoimmunity
Central tolerance (editing, deletion, anergy)
AIRE
CTLA4
Negative feedback
FasL-Fas
AICD
Competition for survival factor
IL7, BAFF
Co-stimulation
inflammation
FoxP3, TGF-b, IL10
Regulatory T cell
Eye, myelin basic protein
Antigen sequestration