College Prep' Chemistry Ch' 3 p' 1 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
College Prep' Chemistry Ch' 3 p' 1
Description:
Democritus- A Greek Philosopher who first described the notion of the ... Nuclide- General term for an isotope of an element. College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 9 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:24
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: College Prep' Chemistry Ch' 3 p' 1
1
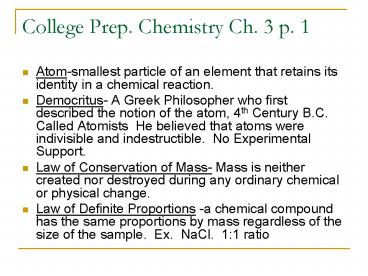
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 1
- Atom-smallest particle of an element that retains
its identity in a chemical reaction. - Democritus- A Greek Philosopher who first
described the notion of the atom, 4th Century
B.C. Called Atomists He believed that atoms
were indivisible and indestructible. No
Experimental Support. - Law of Conservation of Mass- Mass is neither
created nor destroyed during any ordinary
chemical or physical change. - Law of Definite Proportions -a chemical compound
has the same proportions by mass regardless of
the size of the sample. Ex. NaCl. 11 ratio
2
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 2
- Law of Multiple Proportions- If two or more
different compounds are composed of the same two
elements, then the ratio of the masses of the
second element combined with the first element is
in the ratio of small, whole numbers. Ex. CO and
CO2. - John Dalton- British scientist who did
experiments to explain his theories in the
1840s. - Daltons Atomic Theory
- 1. All elements are composed of indivisible
particles called atoms. - 2. Atoms of the same element are identical.
- 3. Atoms of different elements are different.
3
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 3
- Atoms of different elements can physically mix
together or can chemically combine with one
another in simple, whole number ratios to form
compounds. - Chemical reactions occur when atoms are
separated, joined or rearranged. However atoms
of one element are never changed into atoms of
another element as a result of a chemical
reaction. - Section Review p. 71 1-3
4
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 4
- Subatomic Particles- includes electrons, protons,
neutrons. - Protons are positively charged particles that are
found in the nucleus. Neutrons are neutral
particles found in the nucleus. Electrons are
negatively charged particles found on the outside
of the nucleus. - The nucleus is the small, dense, positively
charged region in the center of the atom. - Electrons were discovered in 1897 by J.J.
Thomson. - He performed experiments that involved passing
electric current through gases at low pressure.
5
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 5
- There were sealed tubes with metal disks called
electrodes at each end. P. 73 - Anode- positively charged electrode.
- Cathode-negatively charged electrode.
- Cathode Ray- Electron beam that travels from the
cathode to the anode. Electron beam is attracted
to the positive plate of the magnet. - Electrons, e- have 1 unit of negative charge.
- Mass 1/1840 amu.
- Millikans Oil Drop Experiment in 1916 reported
the charge to mass ratio of the electron.
6
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 6
- Rutherfords Experiment-Gold Foil Experiment,
he directed a narrow beam of alpha particles at a
very thin sheet of gold foil. P. 74. Alpha
particles are He nuclei. - A small amount of alpha particles were deflected,
most went through the gold foil. He proposed
that all of the mass and all of the positive
charge are in the small, dense part of the atom
called the nucleus. - Nucleus- center of the atom, contains n and p,
small dense part of the atom. - Electrons occupy most of the volume of the atom,
scattered outside the nucleus. Electrons have
very little mass.
7
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 7
- Nuclear Forces- short range proton-neutron,
proton-proton, neutron-neutron forces hold the
nuclear particles together. - Sizes of atoms are measured in picometers.
1x1012 pm 1 m. - Section Review p. 76 1-5
- Lab Constructing a Model (handout)
- Atomic Number- number of protons in the nucleus
of the atom. (Z) - A. It identifies the element., Elements are
arranged by increasing atomic number on the
periodic table. - Isotopes- Atoms that have the same number of
8
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 8
- Protons, but different numbers of neutrons.
- Isotopes have different mass numbers.
- 11H Hydrogen-1 (0 neutrons), 21H Deuterium-2 (1
neutrons), 31H Tritium-3 (2 neutrons). - Another Example Carbon-12 126C, Carbon-13
136C This is called a nuclear symbol. - Mass Number- is the total number of protons and
neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope. Isotopes
are identified by their mass numbers. Carbon-13. - Mass Number Atomic Number Number of Neutrons
- Nuclide- General term for an isotope of an
element.
9
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 9
- Sample Problem A p. 79
- Practice p. 80 1-3
- Atomic Mass- Masses are difficult to work with of
individual atoms. We use a comparative scale.
All atoms are compared relative to carbon. - Carbon-12 12 a.m.u. Hydrogen-1 is 1.007
a.m.u. 1.66 x 10-27 kg. - A.m.u. atomic mass unit
- Isotopes have similar chemical behavior, even if
they have different masses of the same element.
10
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 10
- Average atomic mass is the weighted average of
the atomic masses of the naturally occurring
isotopes of an element. - Ex. For Boron (10amu x .1991) (11amu x
.8009) 10.810 a.m.u. - .1991 19.91 .8009 80.09
- Mole- SI unit for the amount of substance. It is
the amount of a substance that contains as many
particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of
carbon-12.
11
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 11
- The number of particles in a mole is known as
Avogadros Number. 6.022 x 1023. This is
representative particles which includes
molecules, atoms, ions, and formula units. - 1 mole 6.022 x 1023 rep. particles
- Molar Mass the mass of one mole of a pure
substance is called the molar mass of that
substance. Ex. Li is 6.94 g/mole, Hg is 200.59
g/mole - Sample Problem B p. 84
- ? g 3.5 moles Cu x 63.5 g Cu/mole Cu 222 g Cu
12
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 12
- Practice p. 85 top 1-4, Bottom 1-3
- Sample Problem C p. 85
- ?moles Al 11.9 g Al x 1 mole Al/27 g Al .441
moles Al - Sample Problem D p. 86
- ? Moles Ag 3.01 x 1023 atoms Ag x 1 mole/ 6.02
x 1023 atoms Ag .5 moles Ag - Practice p. 86 1-3
13
College Prep. Chemistry Ch. 3 p. 13
- Sample Problem E p. 86-87
- ? g Cu 1.2 x 108 atoms Cu x 1 mole Cu/ 6.02 x
1023 atoms Cu x 63.5 g Cu/mole Cu 1.27 x 10-14
g Cu - Practice p. 87 1-3, Section Review p. 87 1-7
- Review p. 89-90 1, 3-9, 11, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19,
21-23, 28