Orbitals PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Orbitals
1
Orbitals
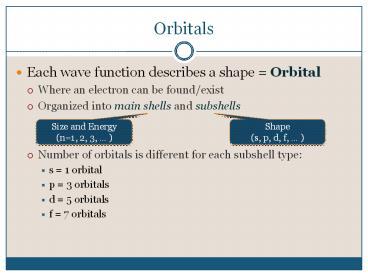
- Each wave function describes a shape Orbital
- Where an electron can be found/exist
- Organized into main shells and subshells
- Number of orbitals is different for each subshell
type - s 1 orbital
- p 3 orbitals
- d 5 orbitals
- f 7 orbitals
Size and Energy (n1, 2, 3, )
Shape (s, p, d, f, )
2
Allowed Orbitals
- The probability density can only take certain
shapes at each n energy level, or main shell
3
(No Transcript)
4
ENERGY
4f ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
___ 4d ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 4p
___ ___ ___ 4s ___
4
- 1, 2, and 3 correspond to the major energy levels
(main shells) - At the same main shell level, a p orbital will be
at a higher energy than an s orbital
5
What type of orbital is this?
- s
- pz
- dxy
- dxz
6
Which type of orbital cant exist?
- 1px
- 2px
- 2s
- 3dxy
7
NODES- Where electrons dont go
Spherical Nodes
8
Hydrogen
9
You too can play with hydrogen
http//homepages.ius.edu/kforinas/physlets/quantum
/hydrogen.html
10
Quantum Rules
- There are four different quantum numbers n, l,
ml, and ms - n, l, and ml are integers
- n cannot be zero
- l can be 0 to n-1
- ml can be anything from l to l
- ms can be ½ or -½
11
Quantum Numbers and Orbitals
nshell, energy level
lsubshell, shape
mlone for each orbital N, l
12
Nodes, Revisited
- of planar nodes l
- of spherical nodes n l 1
- Total nodes n 1
- Example 3d orbital
13
What orbital has these quantum numbers?n 3, l
2, ml -1
- 4p
- 3d
- 3p
- 1d
- 2f
14
What are the quantum numbers for the 5dxy orbital?
- n 5, l 2, ml 0
- n 5, l -2, ml 3
- n 4, l 2, ml 2
- n 5, l 3, ml 0
- n 5, l 2, ml -5
15
Which is not a valid set of quantum numbers?
- n 4, l 1, ml -1
- n 1, l 0, ml 0
- n 6, l 5, ml -5
- n 2, l 2, ml 1
- n 3, l 2, ml 2
16
(No Transcript)
17
Rules for filling orbitals
- Pauli Exclusion Principle
- No two electrons can have the same 4 quantum
numbers - An orbital has a maximum of 2 electrons of
opposite spin - Aufbau/Build-up Principle
- Lower energy levels fill before higher energy
levels - Hunds Rule
- Electrons only pair after all orbitals at an
energy level have 1 electron - Madelungs Rule
- Orbitals fill in the order of the value of n l
18
Orbital Filling Order
19
ENERGY
4f ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
___ 4d ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 4p
___ ___ ___ 4s ___
4
- 1, 2, and 3 correspond to the major energy levels
(main shells) - At the same main shell level, a p orbital will be
at a higher energy than an s orbital