DATA AND COMPUTER COMMUNICATION - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
DATA AND COMPUTER COMMUNICATION
Description:
single processor, multiple processor, local network, metropolitan network, long ... fixed size packet (cell) less processing overhead. high speed: 10 ~ 100 Mbps ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:13
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: DATA AND COMPUTER COMMUNICATION
1
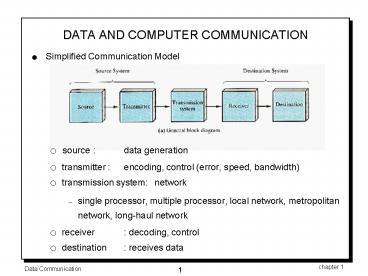
DATA AND COMPUTER COMMUNICATION
- Simplified Communication Model
- source data generation
- transmitter encoding, control (error, speed,
bandwidth) - transmission system network
- single processor, multiple processor, local
network, metropolitan network, long-haul network - receiver decoding, control
- destination receives data
2
- receiver decoding, control
- destination receives data
source transmitter transmission
system receiver destination
3
Data Communications
- data transmission
- signal transformation between transmitter and
receiver - transmission media
- physical path between transmitter and receiver
- data encoding
- conversion from data to signal
- interface
- asynchronous, synchronous transmission
- pin assignment
- data link control
- flow, error control
- multiplexing
- channel, network utilization
4
Data Communications Networking
- Wide-Area Networks
- circuit switching network
- dedicated communications path between two
stations using internal switches (physical link).
ex) telephone network - packet switching
- data is stored in a packet
- mainly used for computer communications
- data rate 64kbps
- frame relay
- low error rates (less control for error) with
modern high-speed telecommunication system - high data rates 2Mbps
- ATM (asynchronous transfer mode)
- cell relay
5
Example 1
6
Example 2
7
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode)
- evolution from frame relay and circuit switching
- fixed size packet (cell)
- less processing overhead
- high speed 10 100 Mbps
- virtual channel with dynamic data rate
- ISDN (integrated services digital network)
- worldwide public telecommunications network
- narrowband ISDN (1st generation)
- circuit switching with 64 kbps channel
- frame relay
- broadband ISDN (2nd generation)
- based on packet switching network
- ATM development in ISDN (on-going research)
8
Local Area Networks
- range a building or a cluster of buildings
- normally owned by same organization
- higher data transfer rate
- recently ATM LANS in fibre channel
9
Protocols and Protocol Architecture
- protocol a set of rules governing exchange of
data between two entities - key elements in protocol
- syntax data format
- semantics control information for coordination
and error handling - timing speed matching and sequencing
- Simplified Architecture for File Transfer
- path activation, destination ready to receive,
file management ready to receive, same file format
10
Three Layer Model
- application layer
- transport layer sequencing, error control
- network access layer
Protocol Architectures and Networks
11
Operation of protocol architecture
- Transport protocol header may include
- destination SAP (DSAP)
- sequence number (sending more than one data)
- error-detection code
- Network access protocol header may include
- destination computer address (destination host)
- facilities request priority bit
12
TCP/IP Protocol Architecture
- most widely used operable architecture
- based on packet-switched network ARPANET
- 5 layers
- Application layer support user application
- Transport layer transmission control protocol
(TCP) provides reliability of exchanging data - Internet layer internet protocol (IP) provides
routing function across multiple networks - Network access layer circuit switching, packet
switching (e.g., X.25), local area network
(Ethernet) - Physical layer physical interface between
devices and a transmission medium or network
13
OSI (open systems interconnection) Model
- 7 layers developed by International
Organization for Standardization (ISO) - Application provides access to OSI environment
for users and also provides distributed
information - Presentation provides application processes from
data representation (syntax) - Session provides the control structure for
communication between applications - Transport provides reliable, transparent
transfer of data between end points (error
recovery, flow control) - Network provides data transmission and switching
techniques to connect systems - Data link provides for the reliable transfer of
information across physical link - Physical transmission of unstructured bit stream
over physical medium
14
Comparison between TCP/IP and OSI
- Many OSI based protocols are developed
- However, TCP/IP dominates over OSI
- Protocol Architecture