Fluid dynamics PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title: Fluid dynamics
1
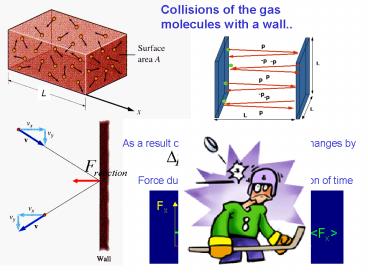
Collisions of the gas molecules with a wall..
As a result of a collision the momentum changes by
Force due to one molecule as a function of time
2
Collisions of the gas molecules with a wall
(cont.)
Newtons second law for an instantaneous force
change of momentum in a collision
For the average force on the wall it becomes
time between collisions
Now Dt is a long time interval the time between
two consecutive collisions with the wall.
Dt
3
Dt
Now Dt is the time between two consecutive
collisions with the wall.
4
Kinetic theory of the ideal gas.
one molecule
Collective effect of N molecules moving with
different velocities
5
Kinetic theory of the ideal gas.
Pressure on the wall with surface area A
Velocity of a molecule
The average velocity average of a sum is equal
to the sum of averages
All the directions of motion (x, y, z) are
equally probable!
6
Pressure on the wall with surface area A
The average kinetic energy of a molecule
The ideal gas law (experimental fact!)
Therefore
7
Physical meaning of the absolute temperature a
measure of the average kinetic energy of a
molecule.
The average speed of a molecule thermal speed
8
Number of molecules having speeds in an interval
of width Dv around v. It is proportional to Dv,
the total number of molecules, N, and to the
height of the distribution curve.
9
Kinetic theory of the ideal gas
Kinetic energy is the only form of molecular
energy that is important and it is preserved in
the collision events.
10
Collisions do not change the situation as long
they are elastic
Colliding particles exchange momenta and
velocities.
Collision with a wall the velocity components
along the wall stay the same.
11
The ideal gas law
What happens if we reduce T to zero. Is volume of
the gas, V, going to become zero?
Not necessarily, since it maybe the pressure, P,
which becomes zero at T 0.
Wait! We can set P ? 0. Then what?
By the ideal gas law we would have V 0, which
cannot be true.
We can correct for it by a term equal to the
total volume of the gas molecules, when totally
compressed (condensed) nb.
Now at T 0 and P ? 0 we have V nb.
12
When and why does the ideal gas law stop working?
- The molecules occupy a significant fraction of
the volume. - Collisions are more frequent.
- There is less volume available for molecular
motion. - 2. There are long range attractive Van der
Waals forces between the molecules, which become
more important as the density grows.
Real gas Van der Waals equation.
Introduces corrections to the ideal gas law to
take into account some of these effects.
Attractive force between couples of molecules.
Goes as (n/V)2 square of the concentration.
Less volume available for motion, because of n
moles of the gas.