Microbiology : Unit - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 37
Title:
Microbiology : Unit
Description:
Microbiology : Unit #2 : Bacteria. Bacteria are small living organisms found ... Bacteria are prokaryotes which are typically unicellular. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:62
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Microbiology : Unit
1
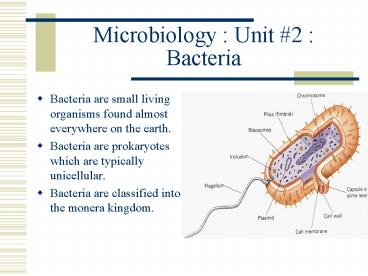
Microbiology Unit 2 Bacteria
- Bacteria are small living organisms found almost
everywhere on the earth. - Bacteria are prokaryotes which are typically
unicellular. - Bacteria are classified into the monera kingdom.
2
Classification of Bacteria
- Bacteria are classified into two major groups
archaebacteria and eubacteria. - Archaebacteria live without oxygen, and obtain
their energy from inorganic compounds.
3
Archaebacteria
- Archaebacteria can survive and thrive in harsh
environments. - Examples of archaebacteria include
methane-producting bacteria in cows stomachs,
salt-loving bacteria, and heat and acid loving
bacteria which thrive in hot springs.
4
Archaebacteria
- Archaebacteria found in the stomachs of cows
allow for the cow to break down and digest the
cellulose in plant cells. These bacteria help
cows turn cellulose into glucose. The bacteria
produce methane gas in this process.
5
Eubacteria
- Eubacteria display a wide array of habitats and
metabolism. Eubacteria are divided into groups
including - Heterotrophs
- Photosynthesic Autotrophs
- Chemosynthetic Autotrophs
6
Eubacteria
- Eubacteria differ from Archaebacteria in
differences of cell walls, plasma membrane, and
sequence of DNA bases.
7
Eubacteria
- Most common bacteria are classified as
eubacteria. - Eubacteria include the phostosynthetic bacteria
called cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria include many
different colors, based upon the pigments they
contain to trap sunlight to make their own food.
8
Bacteria Structure
- Bacteria have different shapes and structures,
but a structures found in bacteria include - Flagella (some)
- Capsule (some)
- Cell wall
- Plasma membrane
- DNA
- Pili (some)
9
Bacteria Structure/Function
- Flagella allows movement
- Pili extensions of plasma membrane, help
sticking - Plasma membrane lipid layer
- Capsule extra barrier (gelatinous), bacteria
with capsules are more likely to cause disease. - DNA genetic material for the cell
- Cell Wall rigid, protection for cell, different
composition with different bacteria.
10
Bacteria Shapes
- Most bacteria are found in colonies.
- Bacteria can be round, spiral, or rod shaped.
- Round coccus
- Spiral spirillum
- Rod bacillus
11
Bacteria Groups
- Bacteria are also classified into the shape of
groups or colonies they form. - Diplo paired cells
- Staphylo grapelike clusters
- Strepto long chains
12
Journal Activity 1
- Using the website below answer the following
questions - 1) Describe archaea microbes, and the
thermophiles, halophiles, methanogens, and
psychrophiles. - Name two different bacteria found in the Friend
or Foe section of the website. Include its
function and other information you can gather
about it. - http//www.microbe.org/index.html
13
Journal Activity 1
- Describe the work that Ali S. Khan does as an
epidemiologist. Include a brief description of
the outbreak of a virus in 1993 in the Southwest
U.S. ( Careers tab)
14
Bacteria Metabolism
- Most bacteria require oxygen to metabolize.
These bacteria are called obligate aerobes. - Bacteria which dont use oxygen, and are killed
by it are termed obligate anaerobes.
15
Endospores
- Some bacteria when faced with unfavorable
conditions form an endospore. An endospore has a
hard outer covering which is resistant to drying
out, or temperature, etc. - When conditions are favorable the endospore
germinates and reproduces.
16
Botulism
- One group of bacteria called clostridia, can form
endospores. Clostridium botulinum, produces a
toxin. If canned food is not properly sterilized
these endospores can become active inside a can
and the disease botulism can occur.
17
Bacteria Reproduction
- Bacteria reproduce by the process of binary
fission. - Binary fission involves the copying of the DNA
and the splitting into two new cells.
18
Bacteria Reproduction
- Under optimum conditions bacteria can reproduce
every 20 minutes. - Bacteria reproduction is controlled by various
factors including temperature and food
availability.
19
Conjugation
- Some bacteria can reproduce sexually in a process
called conjugation. - In conjugation one bacteria is able to transfer
its DNA into another bacteria by means of a pilus
(pili)
20
Journal Activity 2
- Use the website below to describe the following
bacteria. Include the shape and other
information - Escherichia coli 0157H7
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Salmonella enteritidis
- Clostridium tetini
- http//www.cat.cc.md.us/gkaiser/goshp.html
21
Bacteria- Cell Wall Structure
- Bacteria are divided into two groups based upon
the composition of their cell walls. - Gram positive two layers ( lipid, peptidoglycan
sugar/amino acids network) - Gram negative three layers, lipid,
peptidoglycan, and lipopolysaccharide.
Gram
Gram -
22
Antibiotics
- Bacteria have a cell wall which gives protection.
The cell walls of bacteria are made of long
sugar chains linked with short amino acid chains. - Most bacteria live in a hypotonic environment.
(This means theres usually more water outside
the cell than inside the cell)
23
Antibiotics
- Most antibiotics aim to break down part of the
cell wall to cause water to move in and rupture
the bacteria cell. - Penicillin is one bacteria to work this way.
24
Journal Activity 3
- Using the internet or textbooks answer the
following - 1) Describe the discovery of the first
antibiotic penicillin. - 2) Describe one other antibiotic and explain how
it works to kill bacteria cells.
25
Bacteria/Uses
- Bacteria can be helpful or harmful to humans.
Bacteria play many different roles in their
environment. - A few ways humans use bacteria is in the
production of yogurt, swiss cheese and pickles.
26
Bacteria
- One major role of bacteria in the envrironment is
to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere into a
useable form for plants. - Several species of bacteria living in the soil
have the ability to take diatomic nitrogen (N2)
and convert it into ammonia (NH3). Other
bacteria convert this ammonia into nitrite (NO2)
and nitrate (NO3)
27
Nitrogen Fixation
- Some nitrogen fixing bacteria form symbiotic
relationships with legumes. ( beans, peas,
soybeans, peanuts, etc.) - These bacteria live on the roots of the plants
and add nitrate and nitrite (useable forms of
nitrogen for plants) into the soil. - These crops are sometimes grown in off years to
enrich the soil with useable nitrogen
Rhizobium bacteria live on legume roots.
28
Bacteria - Decomposers
- Bacteria break down organic matter in dead
organisms. - These heterotrophic bacteria help recycle
nutrients from dead plants and animals back into
the soil.
Bacteria help break down leaves into useable
compounds in the soil.
29
Bacteria
- Bacteria are very metabolically diverse.
- Different bacteria produce different waste
products during fermentation. (Making ATP without
oxygen) - These waste products are used to make different
food products (yogurt/pickles/swiss cheese/
sauerkraut/ vinegar, etc)
30
Bacteria
- Bacteria also are used to make antibiotics. Some
helpful bacteria will produce chemicals which
will kill pathogenic bacteria. - Streptomycin and erythromycin are a few examples
of antibiotics made from bacteria.
31
Journal Activity 4
- Use the internet and other sources to answer the
following - 1) Pick one food which bacteria is used to
produce and explain what bacteria does for the
process. - 2) Wastewater (sewage) plants use bacteria
extensively. Research and describe how bacteria
is used wastewater plants.
32
Harmful Bacteria
- Most bacteria are not harmful, but a few cause
disease in animals and plants. - Its estimated that about half of all human
diseases are caused by bacteria.
33
Bacteria Caused Diseases
- Bacteria can cause the following diseases
- Tuberculosis
- Pneumonia
- Strep throat
- Staph infections
- Scarlet fever
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- Chlamydia
- Boils
- Tetanus
- Lyme disease
- Ear infections
34
Bacteria and Disease
- Bubonic Plague/Black Death.
- In the 1330s the bubonic plague originated in
China. This disease caused by bacteria spread
quickly to England and other parts of present day
Europe. - This bacteria was mainly found on rodents but
fleas are thought to have carried it to humans.
35
Bubonic Plague
- The bubonic plague killed an estimated 1/3rd of
all Europeans. - The bacteria caused boils which started as red
bumbs on the skin, and then turned into black
dots. Black Death. - The bacteria Yersinia pestis is thought to have
caused this disease.
36
Pneumonia
- Pneumonia is a disease which can be caused by a
virus or bacteria. - Pneumonia involves a build-up of the pathogen in
the lungs or respiratory system. - The most common pneumonia is caused by the
bacteria Streptococcus pneumonia. This bacteria
grows in the lungs, causing the disease.
37
Other Bacterial Diseases
- Many sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are
caused by bacteria. - Gonorrhea
- Syphilus
- Chlamydia