Regulation of Gene Expression - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
Regulation of Gene Expression
Description:
TATA Binding protein. Jmol model. Gene Regulation. 6 ... TATA box associated. RNA polymerase II associated. polymerase phosphorylation. Gene Regulation ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:75
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Regulation of Gene Expression
1
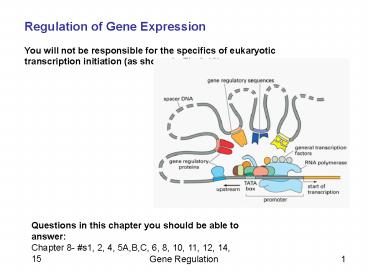
Regulation of Gene Expression You will not be
responsible for the specifics of eukaryotic
transcription initiation (as shown in Fig 8-10)
Questions in this chapter you should be able to
answer Chapter 8- s1, 2, 4, 5A,B,C, 6, 8, 10,
11, 12, 14, 15
2
Why and when does gene regulation
occur? Differentiation Development Response
Housekeeping vs Inducible genes
3
Where in the flow of information from DNA to
protein does regulation occur?
RNAi
4
What is an operon?
What are the two major types of gene regulatory
proteins? Repressors Activators
5
How do regulatory proteins recognize appropriate
sequences?
Homeodomain
TATA Binding protein Jmol model
Leucine zipper
Zinc finger
6
How is a gene activation state passed on during
cell replication? cellular memory Positive
feedback loop Is one model Heterochromatin /
euchromatin state can also be passed during cell
replication e.g., see question 5-12
Question 8-2, 276
7
How does a repressor protein function? The
tryptophan operon model trp operon encodes
genes for tryptophan synthesis Promoter
element Operator element Repressor protein
8
How does an gene activating protein function?
e.g., Catabolic Activator Protein (CAP)
9
How can gene repression and activation yield
subtle regulatory control? e.g., the lac
operon Encodes genes for Lactose breakdown
CAP binds cAMP high GLU low cAMP low GLU
high cAMP
Virtual Cell Animation Lac operon
10
How is transcriptional control different in
eukaryotes? 4 concepts
- 3 RNA polymerases
- RNA polymerase I
- RNA polymerase II
- RNA polymerase III
- 2) General transcription factors
- TATA box associated
- RNA polymerase II associated
- polymerase phosphorylation
11
3) Enhancer and silencer Elements Combinationa
l control
Question 8-6
12
4) Regulation by chromatin structure
Figure 5-30
13
What is mechanism of gene regulation by RNA
interference RNAi ? How does RNAi cause gene
repression? dsRNA is cleaved -- dicer
enzyme siRNA or microRNA Pieces bind to
complementary target mRNA mRNA cleaved by
RISC enzyme
14
What are sources of dsRNA? What are roles of the
iRNA system?
Image is adapted from http//fig.cox.miami.edu/cm
allery/150/gene/how_siRNA_works.htm2 A good
RNAi resource is at http//www.ambion.com/techlib/
resources/RNAi/
15
8-21 The gene for a hormone necessary for insect
development contains binding sites for three gene
regulatory proteins called A, B, and C. Because
the binding sites for A and B overlap, A and B
cannot bind simultaneously. You make mutations in
the binding sites for each of the proteins and
measure hormone production in cells that contain
equal amounts of the A, B, and C proteins. The
results of your studies are summarized in Figure
Q8-22. In each of the following sentences,
choose one of the phrases within square brackets
to make the statement consistent with the above
results. A. Protein A is a stronger/weaker
activator of transcription than protein B. B.
Protein A binds to its DNA binding site more
tightly/less tightly than protein B binds to its
DNA binding site. C. Protein C is able to prevent
activation by protein A only/protein B only/both
protein A and protein B.