Alternation of Generations: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
Alternation of Generations:
Description:
microspore divides to produce tube cell and generative cell ... adaxial. abaxial. Figure 1.9. Secondary development: Vascular cambium (ray and fusiform) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:75
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Alternation of Generations:
1
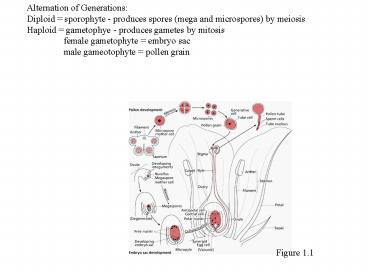
Alternation of Generations Diploid sporophyte
- produces spores (mega and microspores) by
meiosis Haploid gametophye - produces gametes
by mitosis female gametophyte embryo sac male
gameotophyte pollen grain
Figure 1.1
2
- Double fertilization generates zygote and
endosperm - microspore divides to produce tube cell and
generative cell - Generative cell divides to form 2 sperm cells
- Megaspore divides to form 8 nuclei (7 cells)
- 1 sperm fuses with egg cell to form zygote
- 2nd sperm fuses with 2 nuclei of central cell to
form triploid endosperm
Figure 1.1
3
Embryo develops apical/basal and radial
polarity Cotyledons, hypocotyl, radicle, Root
and shoot meristems Epidermis, ground meristem,
procambium
Figure 1.2
4
Germination epigeal (e.g. Arabidopsis) -
elongation of hypocotyl raises cotyledons above
ground Hypogeal (e.g. pea) - elongation of
epicotyl, cotyledons stay on ground
Figure 1.3
5
Primary Vegetative and reproductive development
Figure 1.4
6
Root apical meristem (RAM)
Figure 1.5
Protoxylem/phloem - differentiates during
elongation Metaxylem/phloem - differentiates
after elongation Endodermis - contains casparian
strip Pericycle - meristematic - forms lateral
roots (adventitious shoots
7
- Shoot Apical Meristem (SAM)
- Central zone (CZ) - large, slow division
- Peripheral zone (PZ) - small, fast division
- Tunica (anticlinal), corpus (all directions)
Figure 1.6
8
Dicot Leaf formationtime between leaf
initiation plastochron Position of leaves
phyllotaxy
adaxial
abaxial
Figure 1.7
9
- Secondary development
- Vascular cambium (ray and fusiform)
- Cork cambium
Figure 1.9
10
Reproductive development Transition from
vegetative to flowering
heteroblasty
Figure 1.10
11
Floral development Meristem (SAM or lateral)
produces modified leafy organs (sepals, petals,
stamens and carpels)
Figure 1.11