General Introduction - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 47
Title:
General Introduction
Description:
Calyx. Renal Pelvis. Renal Hilus. Kidneys: Structure. Juxtamedullary and Cortical Nephrons ... Calyx. Renal pelvis. Ureter. Bladder. Urethra. Out of body ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:39
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: General Introduction
1
General Introduction
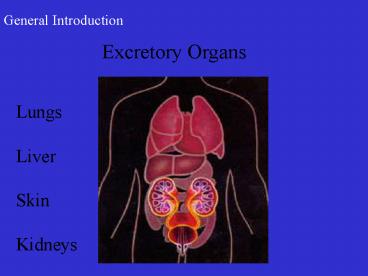
Excretory Organs
Lungs Liver Skin Kidneys
2
Jareds Surgery
- Moved his maxilla forward and mandible back,
- Added cheek bone implants to make up for the lack
of actual bone mass in the maxilla, - Cleaned up of a severely smashed septum, (bone
in the bridge of the nose)... - The maxilla cut twice and widened while the
mandible shortened (bone removal)... - The bone from the mandible was then added to the
maxilla in the two places it had been cut... - All of this was done to line up the teeth and
align the jaws to a normal position... his jaws
were then wired shut where they will remain for
the next 6 - 8 weeks.
3
Post Op
Pre-Op
4
Pre-Op
Post Op
5
Urinary System
6
Posterior View
7
Functions of the Urinary System
A. Filters Waste Products from Blood B. Regulates
Ion Levels in the Plasma C. Regulates Blood pH D.
Conserves Valuable Nutrients E. Regulates Blood
Volume F. Regulates RBC Production G. Stores
Urine H. Excretes Urine
8
Organs of the Urinary System
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra
9
Kidneys Function
- Filter wastes and produce urine by
- Filtration
- Reabsorption
- Secretion
10
Kidneys Location
Retroperitoneal
11
Kidneys Structure
Renal capsule Several layers of fat
12
Kidneys Structure
2 layers Cortex Medulla
13
Kidneys
14
Kidneys Structure
Calyx Renal Pelvis Renal Hilus
15
Kidneys Structure
16
Juxtamedullary and Cortical Nephrons
17
Nephron
- Glomerulus
- Bowmans capsule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
18
(No Transcript)
19
Nephron
20
Glomerulus and Bowmans Capsule
21
Glomerulus and Bowmans Capsule
22
Bowmans Capsule
Podocytes Pedicels Filtration Slits
23
Convoluted Tubules
24
Collecting Ducts and Loops of Henle
25
Tubular Section of Nephron
Figure 23.4b
26
Collecting Duct
27
Summary of Flow of Fluid
Glomerular capsule Proximal convoluted
tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted
tubule Collecting duct Renal papilla Calyx Renal
pelvis Ureter Bladder Urethra Out of body
28
Ureters Structure
- Mucosa epithelium
- Muscularis two layers
- Adventitia connective tissue
a lumen b mucosa c circular muscle layer d
longitudinal muscle layer e adventitia
29
Ureters
30
Ureters Structure
31
Ureters Function
- Carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary
bladder
32
Urinary Bladder Structure
- Mucosa (rugae)
- Muscularis (Detrusor muscle)
- Adventitia
33
Urinary Bladder Function
Micturition Reflex Animation
- Stores and expels urine
34
Urinary Bladder
35
Urethra Structure
Mucosa Muscularis Adventitia
36
Urethra Function
Transports urine from bladder to outside body
37
Female Urethra
38
Female Urethra
39
Male Urethra
40
Male Urethra
Prostatic Membranous Spongy/Penile
41
Blood Flow Through the Kidney (A RAGE PRV I)
- Abdominal Aorta
- Renal Artery
- Afferent Arterioles
- Glomerular Capillaries
- Efferent Arterioles
- Peritubular Capillaries
- Vasa Recta
- Renal Vein
- Inferior Vena Cava
42
Blood Flow Through the Kidney
43
Hormones that Regulate Electrolyte Balance
- Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH or vasopressin)
- Renal-Angiotensin Aldosterone
- Erythropoetin
- Atrial Natriuretic Hormone
44
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
- Released in response to increase in concentration
of electrolytes in blood or a fall in blood
volume or pressure - ADH decreases the amount of water lost at the
kidneys, which reduces the concentration of
electrolytes. - ADH also constricts peripheral blood vessels,
which helps to increase blood pressure.
45
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
- The enzyme renin is released by kidney in
response to a decrease in blood volume, blood
pressure or both. - Renin starts chain of reactions that lead to
formation of hormone in liver called angiotensin
II. - AG II stimulates adrenal cortex to make
aldosterone and posterior pituitary gland to make
ADH. - Both inhibit salt and water loss at kidneys
resulting in increased blood volume and blood
pressure.
46
Erthyropoietin
- Released by kidneys in response to low O2 levels
- Stimulates production of RBCs in bone marrow.
- Increase number of RBCs elevates blood volume.
47
Atrial Natriuretic Hormone
- Cells in right atrium make this hormone in
response to increased blood volume. - Stimulates loss of sodium ions and water at the
kidneys - Inhibits renin release
- Inhibits secretion of ADH and aldosterone
- Result is reduced blood volume and blood pressure.