Protocol Layering PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Protocol Layering
1
Protocol Layering
2
Motivation for Protocol Layering - The
Programming Language Analogy
- Computer programming
- Program -gt Compiler -gt Assembly Code -gt
Assembler -gt Machine Code -gt Hardware - Internet programming
- Application -gt Transport Protocol -gt
Connectionless Datagram Delivery Protocol -gt
Physical Network
3
The Internet Protocol Suite
- Internetworking does not use a single protocol to
transmit data - Imagine how hard it would be to write one that
- Ran on all underlying network technologies
- Transmitted and routed all traffic on the
internet - Handled hardware failure, network congestion,
delays, data loss, data corruption, data
duplication, sequencing errors - Internetworking uses a set of cooperating
protocols (each with its own job)
4
Benefits of Protocol Layering
- Complexity hidden from application-level
programmer - Physical network details hidden in low-level
protocols - Each layer of software can be written, tested,
and modified independently
5
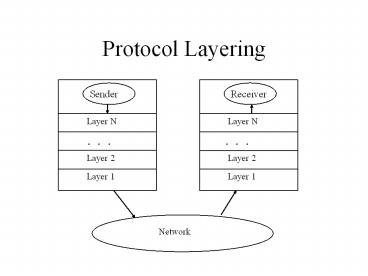
Protocol Layering
- Each layer provides services to the layer above
and utilizes services from the layer below
6
Protocol Layering
- The path of a datagram
7
Functionality of the Layers
- ISO 7-Layer Reference Model
8
ISO 7-Layer Reference Model
- Physical Layer (ISO Layer 1)
- Service transmission of a raw bit stream over a
communication channel ensuring a reliable
delivery of 0s and 1s - Functions conversion of bits into electrical or
optical signals - Examples X.21, RS-232-C
9
ISO 7-Layer Reference Model
- Data Link Layer (ISO Layer 2)
- Service reliable transfer of frames over a link
- Functions synchronization, error control, flow
control - Examples HDLC, CCITT, LAP-D
- Network Layer (ISO Layer 3)
- Service provide switching and routing functions
to transfer data between hosts - Functions routing, addressing, switching,
congestion control - Examples IP, X.25, CLNP
10
ISO 7-Layer Reference Model
- Transport Layer (ISO Layer 4)
- Service control delivery of messages between
hosts - Functions connection management, error control,
flow control, multiplexing - Examples TCP, UDP, ISO TP0 - TP4
- Session Layer (ISO Layer 5)
- Service support communication between
cooperating application programs - Functions session management, synchronization,
recovery - Examples ISO session protocol, RPC
11
ISO 7-Layer Reference Model
- Presentation Layer (ISO Layer 6)
- Service handle compatibility issues
- Functions virtual device support, syntax
conversion, cryptography - Examples ASN.1, ISO presentation protocol
- Application Layer (ISO Layer 7)
- Service provide network access to application
programs - Functions (application specific)
- Examples Telnet, FTP, E-mail, WWW
12
ISO 7-Layer Reference Model
- Designed by committee - International
Organization for Standardization (ISO) - Reference model, not an implementation
- Implemented by a set of protocols known as X.25
13
TCP/IP Internet Layering Model
- Functionality of the layers
Objects Passed Between Layers
Conceptual Layer
14
TCP/IP Internet Layering Model
- Network Interface Layer (TCP/IP Layer 1)
- Service accepts IP datagrams and transmits them
over a specific network - Functions conversion of datagrams to physical
frames - Examples device drivers
- Internet Layer (TCP/IP Layer 2)
- Service connectionless datagram delivery
- Functions inter-host communication, routing
- Examples IP
15
TCP/IP Internet Layering Model
- Transport Layer (TCP/IP Layer 3)
- Service provide reliable end-to-end
communication - Functions flow control, sequencing,
acknowledgments - Examples TCP
- Application Layer (TCP/IP Layer 4)
- Service (application specific)
- Functions (application specific)
- Examples Telnet, FTP, E-mail, WWW
16
Internet Model vs. ISO Model
- Similarities
- Differences
17
The Protocol Layering Principle
- Layered protocols are designed so that layer N
at the destination receives exactly the same
object sent by layer N at the source.
Application
Identical message
Identical packet
Identical datagram
Identical frame
Network
18
Boundaries in the TCP/IP Model
Boundary
Software outside the operating system
Software inside the operating system
Only IP addresses used
Physical addresses used
19
Protocol Layering
- Advantages
- Disadvantages