U.S. History Final Format - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 331
Title:
U.S. History Final Format
Description:
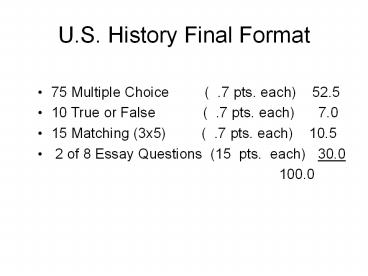
U.S. History Final Format 75 Multiple Choice ( .7 pts. each) 52.5 10 True or False ( .7 pts. each) 7.0 15 Matching (3x5) ( .7 pts. each ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:496
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: U.S. History Final Format
1
U.S. History Final Format
- 75 Multiple Choice ( .7 pts. each)
52.5 - 10 True or False ( .7 pts. each)
7.0 - 15 Matching (3x5) ( .7 pts. each)
10.5 - 2 of 8 Essay Questions (15 pts. each) 30.0
-
100.0
2
Junior 15pt. Essay Themes
- These essays are to be answered in Knockout
Format! Both Content and Style matter! - Usually Knockouts are 5 paragraphs. You may add
extra paragraphs if you have more than 3 seeds. - Rise and Fall of Racial Segregation
- Industrial Revolution (Business, Industry,
Transportation, Communication) - Railroads (Expansion v. Plains Indians)
- Age of Imperialism / Western Hemi. Relations
- Progressives (Labor, Immigration, Corruption,
Women, Urban Centers) - Reasons and Results of Entering World War I
- Causes of the Stock Market Crash
- Examples of New Deals Goals of Relief, Recovery
Reform
3
Unit 6 Civil War
4
Cotton
- Cotton gin invented by Eli Whitney in 1793
- Demand for cotton
- Leads to land butchery
- westward expansion
- more slavery
- ½ of worlds cotton grown in South
- South believes their economic importance to the
world would give them support in case of war with
North
5
Cottonocracy
- Antebellum (pre-Civil War South)
- Oligarchy government by a small number of elite
- About 1,700 families had large plantations with
more than 100 slaves - Had the most political power
- Social ranking system
- 1. elite, large slave-owners
- 2. small farmers owned a few slaves
- 3. poor, non-slave owning whites (3/4 of white
population) - Despised wealthy slave owners
- Still pro-slavery, very racist
6
Plantation Slavery
- Slave importation banned in 1808
- Not regulated or enforced
- Slave population self-sufficient through
childbirth - Slaves investment
- Protected from dangerous jobs
- Deep South SC, Louisiana
- Most strict, tough areas for slaves
- Slave revolts (Denmark Vesey, Nat Turner) caused
tighter security and worse laws for blacks
7
Abolitionist Movements
- Uncle Toms Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe
- Emotional and chilling portrayal of slavery
- HUGE impact on debate of slavery
- Frederick Douglass
- Escaped slave
- William Lloyd Garrison
- Extremist-abolitionist
- Seen as disruptive to unity, Northern economy
8
Souths Defense
- Bible supported slavery
- Slave owners convert their slaves to Christianity
- Whites and happy darkies get along
- Slaves and slave-owners like family
- Slaves lived better lives than Northern wage
slaves
9
1840s America
- William Henry Harrison dies after a month in
office VP John Tyler is new president - Tyler not very Whig-minded
- Vetoes Whig legislation kicked out of party
- Tyler deals with numerous foreign affairs
- Canadian attack on American ship
- Borders of Maine (U.S. vs. Britain)
- British giving escaped slaves asylum
- James K. Polk wins election of 1844
- Democratic party
- Platform of expansion and Manifest Destiny
10
Polks Presidency
- Very successful and efficient
- 4 part plan
- Lower the tariff
- Restore independent treasury
- Clear up the Oregon border issue
- Get California
- Accomplished all in 4 years
- Issue with Texas
- Still independent Texas becoming friendly with
European countries - Dilemma for America
- Slavery issue, economic factors, Monroe doctrine
- Polk invites Texas to join the U.S. in 1845
11
Mexican-American War (1846-1848)
- Polk wants California (Mexican territory)
- Offers to buy first, uses force when refused
- Baited Mexico into a war
- Santa Anna cleverly returns to lead Mexican Army
- U.S. dominates Mexico in 3 phases
- Occupy California
- Secure Texas
- Conquer Mexico City
12
(No Transcript)
13
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
- Mexican Cession forced to give up present day
CA, NV, AZ, NM, CO, UT - Gadsden Purchase made in 1854
- Needed land for railroad route
14
1840s-1850s America
- Gen. Zachary Taylor wins presidency under Whig
Party in 1848 - Challenged by Free Soil Party
- People moving west (new land, gold in CA)
- Issue of slavery slave or free states?
- Huge debate between North and South
- Clay, Webster, Calhoun
- Slowly working towards compromise
- Taylor (anti-slavery) threatens to veto if North
makes any concessions - Taylor dies, compromising VP Millard Fillmore
takes over
15
Compromise of 1850
- North gets
- California is a free state balance tipped to
free side - Texas gives up disputed New Mexico land
- Slave trade now illegal in D.C. (symbolic
significance only) - South gets
- Popular sovereignty in new Mexican Cession lands
- New states vote whether to be a free state or
slave state - Texas paid 10 million for loss of land given to
New Mexico - Fugitive Slave Law runaway slaves given no due
process, money paid for catching and returning
of slave, Northern officials forced to catch
slaves - North passes laws to avoid forced capture
- Leads to further dissention between North and
South
16
1850s America
- President Franklin Pearce wins election in 1852
- Democratic party, safe choice no enemies
- Kansas-Nebraska Act
- Transcontinental railroad compromise
- Kansas open to popular sovereignty
- Becomes battleground between North and South
- Extreme and violent abolitionist John Brown
- murderer or martyr?
- Kansas wins vote to become slave state
(scandal) - President James Buchanan wins election in 1856
- Democratic
- Ran against John Fremont (Republican)
- Northerner, but sympathetic towards South
17
Dred Scott Case
- Slave moved by master from South to North, then
back to South - Tried to sue for freedom ? lost case
- Decision Stated slaves not citizens ? cannot use
legal process - Also stated Congress cannot outlaw slavery
- Infuriates North
- South now had advantage politically (president,
Supreme Court, Constitution) - North has powerless majority Congress
18
Compromise of 1850
- North gets
- California is a free state balance tipped to
free side - Texas gives up disputed New Mexico land
- Slave trade now illegal in D.C. (symbolic
significance only) - South gets
- Popular sovereignty in new Mexican Cession lands
- New states vote whether to be a free state or
slave state - Texas paid 10 million for loss of land given to
New Mexico - Fugitive Slave Law runaway slaves given no due
process, money paid for catching and returning
of slave, Northern officials forced to catch
slaves - North passes laws to avoid forced capture
- Leads to further dissention between North and
South
19
Dred Scott Case
- Slave moved by master from South to North, then
back to South - Tried to sue for freedom ? lost case
- Decision Stated slaves not citizens ? cannot use
legal process - Also stated Congress cannot outlaw slavery
- Infuriates North
- South now had advantage politically (president,
Supreme Court, Constitution) - North has powerless majority Congress
20
1850s America
- Panic of 1857
- Caused by over-speculation, inflation caused by
California gold, and overproduction of grain - 1858 Illinois Senate Race Lincoln (Rep) vs.
Douglas (Dem) - The Great Debates
- Douglas wins election, loses his heavy support
from South after Freeport Doctrine - Stated people hold power to vote down slavery,
despite the Supreme Court - Lincoln loses, but becomes national figure
21
Election of 1860
- Democrats split
- North wants Stephen Douglas to run
- Popular sovereignty position
- South wants John C. Breckinridge
- Pro-slavery position
- Republicans select Abe Lincoln
- Campaign successfully unites many Northern
factions - Free-Soilers (will stop slaverys expansion)
- Manufactures (will raise the import tariff)
- Immigrants (will secure better rights)
- Westerners (will build a NW railroad)
- Farmers (will establish homesteading)
- System of federal land grants
22
Election of 1860
- Lincoln not an abolitionist, but was a
Free-Soiler ? hated by the south - SC threatens to secede if Lincoln wins election
- Southern votes split between Douglas and
Breckenridge - Lincoln wins comfortably in November, 1860
- Scheduled to take office in March 1861
23
The South Secedes
- SC secedes in Dec. 1860
- Soon followed by Deep South
- Alabama, Mississippi, Florida, Georgia,
Louisiana, Texas - Feb 1861 Southern states form Confederate
States of America - Elect Jefferson Davis as President of C.S.A.
- President Buchanan did almost nothing to stop the
secession - One final compromise offered Crittendon
Compromise (extend Missouri Compromise line
north free, south slave) - Lincoln takes over, crushes compromise
- Honest Abe took free-soil pledge, wouldnt
break it
24
(No Transcript)
25
Why the South Seceded
- Institution of slavery threatened by North
- Would kill Southern economy if outlawed
- Believed starting own nation allows own
development - Economy, industry, banking, shipping, etc
- Compared their secession to independence of
American colonies in 1776 - U.S. breaks from England, South breaks from North
- South didnt think North would try to stop their
secession - If war did break out, Europe would support South
due to its economic value
26
Civil War Begins
27
Lincolns Inauguration (Mar. 4, 1861)
- Primary goal
- REUNITE THE NATION
- Problems with South leaving
- Dividing country impossible due to geographic
reasons - They still owe national debt
- Runaway slave issues would surely lead to
conflict - Europe could prey on a weak and split America
(economically, diplomatically, militarily)
28
War Begins (1861)
- Lincolns inauguration (Mar)
- Southern delegates offer peace treaty to Lincoln
- Lincoln refuses
- Fort Sumter, SC (April)
- Island fort held by North, being surrounded by
South - Supplies running out, reinforcements too late
- South open fires on Ft. Sumter
- North surrenders after day
- War officially begins
29
Lincoln Preps for War
- Call to arms
- 75,000 soldiers
- Orders naval blockade of South
- 4 undecided states secede and CSA
- Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and NC
30
Border States
31
Border States
- Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland
- All slave states that had not seceded
- Importance
- Would increase Souths population
- Would increase Souths industrial potential
- Lincolns plan to gain border states
- Declared martial law in Maryland
- Railroad importance, buffer to D.C.
- Convinced border states his motives were to end
war, not slavery - Splits between border states
- Tennessee volunteers
- Anti-slavery West Virginia breaks away from
Virginia
32
Advantages
- North
- Larger population
- 3x Souths population
- Industry
- Railroads
- U.S. Navy
- Naval blockades importance
- More money
- South
- Only had to defend, not conquer
- North needed a decisive victory to win
- Geographical advantages
- Better military leadership
- Robert E. Lee
- Stonewall Jackson
33
Warm Up
- Of the advantages and disadvantages we know of,
which do you think will be the most important
throughout the course of the war? - Which will help the North the most?
- Which will hurt the South the most?
34
Souths Foreign Aid?
- South believed Europe would help them
- Economic importance cotton
- Reasons help never came
- Some Europeans wanted a split U.S.
- Other Europeans were anti-slavery
- Effect of Uncle Toms Cabin
- Englands reliance on Southern cotton decreasing
- Had started own crops in colonized Egypt and
India - North sends food over to famine-affected Europe
throughout war ? support grows
35
Foreign Affairs
- England gives very little support to South
- Trent affair
- Northern ship stops British ship with 2 Southern
diplomats on it ? arrested ? released - CSS Alabama
- Staffed with British forces, attacked U.S. ships
worldwide, but not in U.S. waters - Brits never follow though with promise to build
raider ships for South ? could hurt England one
day - U.S.-Canada border issues
- Puppet government set up in Mexico by Napoleon
III (France) - violates Monroe doctrine
36
A. Lincoln vs. J. Davis
- Stable established government
- Can easily exert power
- Better foreign relations
- Navy at disposal
- Telegraph and railroad system
- Never popular
- (Elected by delegates, not common people)
- An unstable confederacy
- Loosely united
- Weak by design
- Hard to govern
- Hard to exert power
37
Lincoln vs. the Constitution
- Unconstitutional actions
- Martial law declared in Maryland
- Increases the size of the Army
- Created draft too
- Paid 2 million to a few private citizens for
undisclosed military purposes - Suspended habeas corpus
- Anti-unionists arrested and held without trial
- Supervised Border State elections
- Turn and talk with a partner
- Which actions are the worst? Rank them.
- Do you think these actions are acceptable? Why or
why not? - Do the ends justify the means?
38
Economies During War
- NORTH
- Raises import tax
- Railroads and open seas
- Sold war bonds
- Funded 62 of war for North
- Recreated National Banking System
- Secured and regulated money in economy
- War boomed industry
- Womens role increased
- Factory workers, Red Cross
- SOUTH
- Union naval blockade killed Souths money flow
- Could not export cotton
- Could not import for (no import tax)
- Massive inflation
- New CSA currency fails
- Southerners held 30 of nations wealth before
secession ? 12 after - Lack of money kills Souths war effort
39
War Starts
- Ft. Sumter (April 1860)
- Both sides confident war will be short
- Ninety-Day War
- North wants to take Richmond, VA (CSA capital)
- July 1860 Battle of Bull Run (VA)
- Both sides unprepared, unorganized
- Southern Gen. Thomas Jackson holds line, fights
off North - Stonewall Jackson
- North panics retreats, South wins the first
major battle of the Civil War - Significance?
- Realization war was going to take much longer
- Both sides needed better preparation
- 5,000 casualties in one day
40
- Both sides stall to prepare for long war
- Lincoln puts Gen. George McClellan in charge
- Organized, master planner
- Planned to take Richmond
- Would end war
- The Peninsula Campaign (Summer 1862)
- Stonewall Jackson bluffs attack on D.C.
- Northern troops split
- Southern Gen. Jeb Stuarts cavalry circles
outflanks McClellan - Southern Gen. Robert E. Lee attacks in Seven
Days Battles - Pushes McClellan back to sea
- South wins another huge battle
- 35,000 total dead
41
Norths New Strategy
- Norths quick solution to war fails twice
- Lincolns new plan TOTAL WAR
- Blockade, divide, conquer
- Strengthen naval blockade
- Free the slaves
- Divide the South along Mississippi River
- Capture Richmond, VA (CSA Capital)
- Engage battle anywhere possible
- Abandons using only large, planned battles
- South would be pounded into submission in every
facet of war
42
Northern Gen. Winfield Scotts Anaconda Plan
43
Naval Blockade
- Penetrable at first, strengthened over time
- Stopped and searched any ships coming in or out
- C.S.S. Merrimack ironclad ship threatened
blockade - North builds U.S.S. Monitor
- Monitor defeats Merrimack in Chesapeake Bay
March, 1862 - New plan replace wooden ships with iron, steam
ships - Whos more likely to manufacture more and at a
faster rate?
44
Antietam
- Aug 1862 Second Battle of Bull Run
- North beaten badly by South, led by Lee
- South undoubtedly winning the war
- Lee marches forward invades Antietam, MD
- Wants to lure Border States to join CSA
- Draw war off of Virginias farmland
- Make a symbolic victory on Northern soil
- Loses battle plans found by North
- Gen. McClellan (back in charge) prepares for
battle
45
Antietam
- Battle of Antietam Creek (Sep. 1862)
- Most critical battle of war so far
- Could be knockout punch for South
- Northern victory would keep war alive, convinces
Europe to stay out of war - North wins
- Overpowers South with numbers
- Over 20,000 killed
46
Emancipation Proclamation
- First, much awaited victory for North
- Gives Lincoln a stage to announce next part of
plan free the slaves - Not just a war to reunite the nation, but now to
end slavery as well - Gives North a moral rationale for fighting
- Proclamation did not free slaves in Border States
- States too fragile ? could leave secede in anger
- No real legal repercussions to Proclamation
why? - Lincoln holds no political power in South
- Lincoln didnt have authority to free slaves even
in the Union - North would have to win the war for it to go into
effect - South complains Lincoln is stirring slave
rebellion
47
Black Soldiers Join Effort
- Free Black men in the North banned from enlisting
at first - As war progressed, more soldiers were needed
- Black men now allowed to enlist
- 10 of army made up of Black men
- Southern army often just executed captured Black
soldiers rather than treat them as POWs - Massacre at Ft. Pillow, Tennessee
- Advancing Northern armies freed slaves, some of
which joined the war
48
Futile Northern Generals
- Gen. McClellan demoted again after Antietam
- Had Lees plans!!!
- Barely won the battle
- Largely because of numbers
- Failed to pursue and crush Lee
- Gen. Burnside takes over
- Defeated at Fredericksburg, VA (Dec, 1862)
- Gen. Hooker takes over
- Defeated at Chancellorsville, VA (May, 1863)
- Lees most impressive victory
- Humiliating loss for the North
- Stonewall Jackson mistakenly killed by own men
- Gen. Meade takes over
49
Gettysburg
- Lee again goes for knockout punch
- Invades North again
- Battle of Gettysburg, PA (July 1863)
- South wins first two days of battle forcing North
to retreat up into hills - Third Day Picketts Charge
- Lee sends 15,000 men across open field to crush
the North with frontal assault - Fails miserably Northern lines hold
- North wins HUGE battle
50
Gettysburg
- Biggest win for North thus far
- Massive loss for South
- 25,000 casualties
- Turning point in war
- South could not keep up with Norths influx of
soldiers, supplies - Chances at victory dwindling fast
- Gettysburg Address (Nov 1863)
- Lincoln returned to battlefield to give speech to
troops - Meant to boost morale, rationalize war
51
Gettysburg Address
- Four score and seven years ago our fathers
brought forth on this continent, a new nation,
conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the
proposition that all men are created equal. - Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing
whether that nation, or any nation so conceived
and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met on
a great battlefield of that war. We have come to
dedicate a portion of that field, as a final
resting place for those who here gave their lives
that that nation might live. It is altogether
fitting and proper that we should do this. - But, in a larger sense, we can not dedicate --
we can not consecrate -- we can not hallow --
this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who
struggled here, have consecrated it, far above
our poor power to add or detract. The world will
little note, nor long remember what we say here,
but it can never forget what they did here. It is
for us the living, rather, to be dedicated here
to the unfinished work which they who fought here
have thus far so nobly advanced. It is rather for
us to be here dedicated to the great task
remaining before us -- that from these honored
dead we take increased devotion to that cause for
which they gave the last full measure of devotion
-- that we here highly resolve that these dead
shall not have died in vain -- that this nation,
under God, shall have a new birth of freedom --
and that government of the people, by the people,
for the people, shall not perish from the earth.
52
Blockade, Divide, Conquer
- Ulysses S. Grant
- Unconditional Surrender
- Rose to fame by capturing Jackson and Vicksburg,
MS - One day after Gettysburg
- Divides South at Mississippi River
- Gen. Sherman divides South from Tennessee to
Atlanta (Spring 1864) - March to Sea
- Total war tactics
- Destroyed everything in his path
- Burns Atlanta to ground
53
Election of 1864
- Lincoln had some Northern opposition
- Radical Republicans felt Lincoln was
mismanaging war - Democrats split on Lincoln support
- War Dems vs. Peace Dems
- Lincoln forms Union Party
- Combines Republicans and War Democrats
- George McClellan runs vs. Lincoln
- Lincoln easily wins election
54
The Final Stages Lee vs. Grant
- Grant promoted to Commanding General Army
- South blockaded divided
- GRANTs strategy now
- Beat the South by outlasting the South
- North has strength in numbers
- Series of battles in VA grinds away at South
- The Wilderness (May 1864)
- Spotsylvania Courthouse (May)
- Cold Harbor (June 1864)
- Petersburg (June 1864 - Mar 1865)
- All result in Northern
- victories
55
The South Surrenders
- Petersburg was Souths last stand
- After it falls, South doomed
- Grant marches to Richmond
- Scorched earth method of South causes fires in
Richmond - Evacuation allows for easy capture of capital
- April 1865 Lee surrenders at Appomattox
Courthouse in VA
56
Aftermath
- 600,000 dead
- A whole generation gone
- 15 billion spent
- Long-term animosity
- Physically destroyed the South
- Pro Slavery ended forever
- Lincoln assassinated 5 days after the war ends
- At a play at Fords Theater in D.C.
- Shot by John Wilkes Booth in part of plot to
still help South win the war - Lincoln an instant martyr in North
- Died reuniting the nation, ending slavery
- Assassination celebrated in South, ironically
dooms them - Radical Reps who replace Lincoln not as forgiving
as Lincoln
57
The Reconstruction
- Freedmen freed slaves in tough situation
- Most stayed (either by choice or force) on
plantation - U.S. Army freed all slaves eventually
- Some fled North
- Some rioted against former masters
- New social structure for blacks is shaky
- Churches grow and become pillar of black
community - Freedmans Bureau created to help blacks adjust
to free life provided food, clothing, education - Improved literacy, failed in most other areas
- Disliked by Southerners, Pres. Johnson
58
President Andrew Johnson
- Tennessee Democrat chosen by Lincoln to balance
ticket in 1864 election - Was only Southern Congressman to not secede
- Disliked by both North and South
- Stubborn, confrontational, short-tempered white
supremacist
59
The Reconstruction Plan
- Lincolns plan The 10 Plan
- Southern states could rejoin the U.S. after 10
of the voters take oath of loyalty and respect
for emancipation - Plan seen as very forgiving
- Radical Republicans wanted to punish South
- Propose Wade-Davis Bill up to 50, add laws to
protect freed blacks - Lincoln vetoes why?
60
The Reconstruction Plan
- Lincoln assassinated
- Johnson adds some changes
- Former Confeds cannot vote
- Secession ordinances repealed
- U.S. repudiated Confed debts
- States must ratify the 13th amendment
- Outlaws slavery
- Souths social structure workforce demolished
and disassembled
61
The Black Codes
- White Southerners pass Black Codes
- Laws designed to keep freed blacks under control
of their white employers - Contracts forcing blacks to work for whites
- Very discriminatory
- Blacks given little rights, punishable offenses
- Northerners outraged
62
Battle for Congress
- North dominated Congress during war
- Passed many major bills during war
- Dec 1865 Johnson allows all Southern states to
rejoin the U.S. - Southern politicians return to Congress
- Could gain more representation now than before
- Three-Fifths Compromise eradicated now
63
Johnson vs. Congress
- Johnson vetoed all Republican bills
- Civil Rights Bill grants blacks citizenship,
weakens Black Codes - Congress creates 14th Amendment
- Blacks get citizenship
- Didnt guarantee suffrage
- States lose Congressional representation if
blacks were denied voting - Confederate leaders banned from federal offices
- Johnson battles Congress with round the circle
speeches backfires - Ratified by states in 1868
64
Congressional Reconstruction
- Republicans now in control of Reconstruction
- Split (Radicals vs. Moderates
- Radical Reps
- Led by Sen. Charles Sumner and Thaddeus Stevens
- Wanted a slow Reconstruction to institute major
social and economic changes to South - Moderate Reps
- Wanted a more hands-off approach to
Reconstruction - Both groups wanted black suffrage
65
The Reconstruction Act
- Passed March 1867
- Divides South into 5 military districts
- Army occupied each to maintain order
- Southern states not fully readmitted to U.S.
until - 14th Amendment is ratified
- Black suffrage guaranteed
- Radical Reps pass 15th Amendment in 1870 to
ensure suffrage cannot be removed
66
Unit 7 Postwar
67
The Reconstruction
- Freedmen freed slaves in tough situation
- Most stayed (either by choice or force) on
plantation - U.S. Army freed all slaves eventually
- Some fled North
- Some rioted against former masters
- New social structure for blacks is shaky
- Churches grow and become pillar of black
community - Freedmans Bureau created to help blacks adjust
to free life provided food, clothing, education - Improved literacy, failed in most other areas
- Disliked by Southerners, Pres. Johnson
68
President Andrew Johnson
- Tennessee Democrat chosen by Lincoln to balance
ticket in 1864 election - Was only Southern Congressman to not secede
- Disliked by both North and South
- Stubborn, confrontational, short-tempered white
supremacist
69
The Reconstruction Plan
- Lincolns plan The 10 Plan
- Southern states could rejoin the U.S. after 10
of the voters take oath of loyalty and respect
for emancipation - Plan seen as very forgiving
- Radical Republicans wanted to punish South
- Propose Wade-Davis Bill up to 50, add laws to
protect freed blacks - Lincoln vetoes why?
70
The Reconstruction Plan
- Lincoln assassinated
- Johnson adds some changes
- Former Confeds cannot vote
- Secession ordinances repealed
- U.S. repudiated Confed debts
- States must ratify the 13th amendment
- Outlaws slavery
- Souths social structure workforce demolished
and disassembled
71
The Black Codes
- White Southerners pass Black Codes
- Laws designed to keep freed blacks under control
of their white employers - Contracts forcing blacks to work for whites
- Very discriminatory
- Blacks given little rights, punishable offenses
- Northerners outraged
72
Battle for Congress
- North dominated Congress during war
- Passed many major bills during war
- Dec 1865 Johnson allows all Southern states to
rejoin the U.S. - Southern politicians return to Congress
- Could gain more representation now than before
- Three-Fifths Compromise eradicated now
73
Johnson vs. Congress
- Johnson vetoed all Republican bills
- Civil Rights Bill grants blacks citizenship,
weakens Black Codes - Congress creates 14th Amendment
- Blacks get citizenship
- Didnt guarantee suffrage
- States lose Congressional representation if
blacks were denied voting - Confederate leaders banned from federal offices
- Johnson battles Congress with round the circle
speeches backfires - Ratified by states in 1868
74
Congressional Reconstruction
- Republicans now in control of Reconstruction
- Split Radicals vs. Moderates
- Radical Reps
- Led by Sen. Charles Sumner and Thaddeus Stevens
- From Sumner-Brooks Affair (1856)
- Wanted a slow Reconstruction to institute major
social and economic changes to South - Moderate Reps
- Wanted a more hands-off approach to
Reconstruction - Both groups wanted black suffrage
75
The Reconstruction Act
- Passed March 1867
- Divides South into 5 military districts
- Army occupied each to maintain order
- Southern states not fully readmitted to U.S.
until - 14th Amendment is ratified
- Black suffrage guaranteed
- Radical Reps pass 15th Amendment in 1870 to
ensure suffrage cannot be removed
76
Progression of Black Rights
- 13th amendment abolishes slavery
- 14th amendment makes ex-slaves citizens
- 15th amendment protects black suffrage
77
14th Amendment
- The right to vote at any election is denied to
any of the male inhabitants of such State, being
twenty-one years of age, and citizens of the
United States, or in any way abridged (if
violated) the basis of representation therein
shall be reduced in the proportion which the
number of such male citizens shall bear to the
whole number of male citizens twenty-one years of
age in such State.
78
15th Amendment
- The rights of citizens of the U.S. to vote
shall not be denied or abridged by the U.S. or by
any state on account of race, color, or previous
condition of servitude - What is controversial about the language used in
the 14th and 15th amendments?
79
Women Suffrage
- 14th amendment refers to citizens as males
- 15th amendment claims voting cant be denied by
race, color, or previous servitude - Women outraged, feel left out, see opportunity
- Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Susan B. Anthony lead
womens movement - Fought to keep these amendments from entering
Constitution without guaranteeing womens
suffrage - Failed amendments passed
80
Reconstruction in Action
- Blacks begin to organize, create Union League
- Web of associations working together to help
black communities, consolidate political power,
etc. - Many white southerners temporarily unable to vote
leads to blacks gaining power politically - Hiram Revels becomes first black Senator (1870)
81
- White Southerners infuriated
- Blacks freed, serving over whites in Congress and
state legislatures - Scalawags whites who were sympathetic towards
North - Carpetbaggers Northerners who moved to South
after the war - Some came to help, some came to profit, some
swindled - Underground movement among White Southerners
gaining strength
82
Southern White Retaliation
- The Ku Klux Klan
- The Invisible Empire of the South
- Formed in Tennessee (1866)
- Thrived on fear, unknown membership
- Threatened, lynched, murdered blacks
- Effective in slowing down black progress
- White Southerners use political tricks to
disenfranchise blacks - Started literacy tests as requirement to vote
- Targets illiterate blacks problem?
- Add grandfather clauses to protect illiterate
whites - Allows voting rights to any citizen whos
grandfather could vote
83
Congress vs. Johnson
- Johnson impeding Congressional Reconstruction
- Radical Reps plot to impeach Johnson
- Pass Tenure of Office Act (1867)
- President needs Senate approval to fire anyone
who had been previously appointed to him - Rational Senate approves appointees when hired,
thus should approve when fired - Johnson wants to replace Sec. of War Edwin
Stanton - Appointed by Lincoln
- Conspiring against Johnson with Radical
Republicans - Lose-lose for Johnson, Win-Win for Congress
- Allow Stanton to stay Radical Reps happy
- Fire Stanton breaking the law, could be
impeached
84
Impeachment?
- Johnson fires Stanton in 1868
- Congress votes to impeach Johnson on high crimes
and misdemeanors - Generally due to all of Johnsons misdoings
during Reconstruction, specifically due to firing
Stanton - Impeachment trials
- Johnson remains silent
- His lawyers argue he was acting under
Constitution, not Tenure of Office Act - Senate needs 2/3 to support impeachment, fall
short by one vote - Johnson remains in office
- Radical Republicans claim the non-guilty verdict
as a dangerous precedent
85
Purchase of Alaska
- Russia willing to sell Alaska
- William H. Steward Johnsons Sec. of State
- Expansionist, pushed for purchase of Alaska
- Unpopular campaign
- Sewards Folly, Sewards Icebox
- Eventually gains enough support in Senate
- Purchased for 7.2 million
- Seward scorned for purchase
- Adds to Johnsons unpopularity
- Vindicated long after death gold and oil
discovered
86
Legacy of Reconstruction
- Reconstruction just as bad as the war for South
- Loss of infrastructure, economy, political power,
massive physical destruction - Causes decades of animosity
- South felt beaten down, humiliated
- Civil War referred to as War of Northern
Aggression - Emancipation gives somewhat false hope to blacks
- Progress made with 13th, 14th, 15th Amendments
- But in some cases, had it better in antebellum
times - Violence, tricky politics keep blacks down
- Significant progress not made again until the
1950s and 60s
87
The Gilded Age (1870-1900)Gilded Covered
thinly with gold paint
- Times appeared great
- Railroads
- Industry booms
- Westward Expansion
- Relative Peace
- Wealth
- but numerous problems
- Corruption
- Crooked business practices
- Tight and chaotic political races
- Ethnic conflict
- Wealth Gaps
88
Political Division of the Gilded Age
- Republicans
- Supported in North and West
- Grand Army of the Republic (G.A.R.)
- Military veteran group devout to Republican party
- Allude to Puritan ancestry
- Most political power after Civil War
- Democrats
- Supported mostly by the South
- Supported by Lutherans and Catholics
- Very little political power after Civil War
- Various political parties emerge during era in
response to problems of the Gilded Age
corruption, economy, labor rights, etc.
89
Election of 1868Ulysses S. Grantvs.Horatio
Seymour
- Grant and the Republicans (Radical)
- Radicals needed a strong president to enforce
their policies - Grant had no political experience Reps. relying
on what? - War-hero, slogan wave the bloody shirt
- Hoping military heroics would be enough to win
election - Seymour and the Democrats
- Seymour a former Governor from NY
- Party extremely disorganized
- Agreed on only one thing
- Dislike of military Reconstruction
- Grant narrowly wins election what does this
imply? - Political campaigns now tightening up, more
efficiently run
90
Grants Reconstruction
- Implemented Radical Rep policies of
Reconstruction - Protection of equal rights for blacks
- Civil Rights Act (1875)
- Creates Dept. of Justice
- Helps prosecute KKK leaders, members
- Used military to
- Enforce fair voting practices
- Quell KKK violence
- Grants support would slowly decline during
terms - Why?
- Mission already accomplished many felt
Reconstruction was largely complete by 1870 - Corruption
91
Corruption
- Time period AKA The Era of Good Stealings
- Widespread corruption after Civil War
- JubileeJim Fisk Jay Gould
- Caught with scheme to cornerstone gold market
- Boss Tweed
- Ran Tammany Hall, a political organzation in
NYC - Bribes, rigged elections, cronyism
- Prosecuted by Samuel J. Tilden
92
Corruption
- Credit Mobilier scandal
- Railroad company caught fixing hiring process to
get paid double - Bribed Congressmen and VP Schuyler Colfax with
stocks - Whiskey Ring
- Revenue from liquor tax being stolen
- Large ring of government workers Grants
secretary - Grant Let no man escape doesnt prosecute
secretary - William Belknap
- Grants Sec. of War caught swindling 24,000 from
Indians
93
Grants Presidency
- Grant a very honest man not involved in any
scandals - But still condemned as corrupt
- Major corruption in administration
- Failed to recognize it
- Failed to deal with it properly
- Reformers form own party to combat crooked
Republicans Liberal Republican Party - Included both ex-Reps and ex-Dems
- Main goal clean up government corruption
94
Election of 1872Ulysses S. Grantvs. Horace
Greeley
- Republican Grant tries for second term
- Horace Greeley nominee for Liberal Republicans
- Editor of NY Tribune, little political experience
- Stubborn abolitionist, and harsh critic of
Democrats - Still gets support from Southern Dems why?
- Soft on Southern Reconstruction
- Dems desperately eager to gain office
- Extreme mudslinging
- Greeley called an atheist, communist, vegetarian,
Confederate sympathizer - Grant drunk, stupid, swindler
95
Results of Election of 1872
- Grant
- Popular vote 55
- Electoral vote 286 (of 352)
- Greeley
- Popular vote 46
- Electoral vote 3 (of 352)
(Last 63 Electoral votes spread out among various
Democratic and Liberal Republican politicians)
What happened?
Greeley dies during election after popular
vote, but before electoral vote. Grant easily
wins election.
96
Effects of Election of 1872
- Popular vote was close enough to scare Reps
- Republican Congress begins to reform
- The Amnesty Act (1872)
- Removed voting and office-holding restrictions on
many ex-Confederates - Efforts to reduce tariff rates
- Would help Southern economy
- Clean up the corruption in Grants administration
- Fired any workers involved in any past scandals
97
Panic of 1873
- Industrialization of U.S. caused over-growth
- Railroads manufacturing boom
- Economic downturns every twenty years in 1800s
(1819, 1837, 1857, 1873, 1893) - Panic of 1873 What caused it?
- Over-speculation
- Overspending, overinvesting with borrowed money
- Railroads and factories specifically
- Banks giving too-easy credit
- Young American industry hit hard
- Black communities hurt especially why?
- Economic downturn ? less jobs ? last to be hired
- Debate ensues on how to fix economy
98
Soft Money vs. Hard Money
- AKA Cheap Money
- Policies call for forced inflation
- Paper currency fluctuating value
- Would ease debt payments of masses
- Supported by middle and lower classes
- Policies keep amount of money stable by keeping
it correlated with amount of gold - Coin currency defined value
- Inflation unfair lent money would be less
valuable once paid back - Supported by wealthy, banks
99
- SOLUTION
- Grant supports hard money policy, passes
Resumption Act - Aimed to lower paper money in circulation
phase it out - Backfires starts contraction amount of
money in circulation decreases ? worsens
recession ? value of dollar bill increases - Greenback Labor Party emerges in 1878 main
goal - CHEAP MONEY POLICIES
100
Grants Presidency (1878-1876)
- How did public rate his presidency?
- How do you rate it?
- General historical view
- Good and honest leader but presidency is marred
and burdened by widespread corruption, economic
downturn
101
Election of 1876
- Grants two terms complete
- Republican split redevelops
- Stalwarts (Radicals) led by Roscoe Conkling
- Half-Breeds (Moderates) led by James G. Blaine
- Agree to nominate Rutherford B. Hayes
- The Great Unknown
- Neutral Republican
- From Ohio (important swing state)
- Democrats nominate Samuel Tilden
- Famous for prosecuting Boss Tweed
102
Election of 1876Rutherford B. Hayesvs. Samuel
Tilden
- Tilden gets 51 of popular vote, but falls one
electoral vote short of winning election - But 20 votes disputed due to questionable process
of return and handling - Near chaos ensues
- Both Reps and Dems send officials to investigate
- Both sides claim victory
- Recount called for but who in Congress would
count? - Democratic majority in House, Republican majority
in Senate - Congress creates Electoral Count Act which sets
up commission of 15 men to solve crisis
problem? - Uneven number 8 Republicans, 7 Democrats
- Republicans claim victory, Democrats filibuster
to stop process
103
Compromise of 1877
- North gets
- Hayes elected as Republican president
- South gets
- Removal of military occupation
- Reconstruction now officially over
- Effects of Compromise of 1877
- Southern blacks unprotected now
- White Southerners regain more political power
- Civil Rights Act of 1875 significantly cut back
- Pass Jim Crow Laws
104
Jim Crow Laws
- Many laws created to keep blacks in subservient
role in South - Many blacks were sharecroppers
- Farmed land they didnt own, paid landlords with
crops - System abused, designed to keep blacks poor
- Jim Crow Laws
- Many states had begun to legalize segregation
constitutional? - Forced segregation in all public facilities
- Schools, theaters, restrooms, transportation
- Violation could result in fines, imprisonment,
violence - Mob lynchings peak during this era
- 1896 Plessy v. Ferguson Supreme Court ruled
it legal separate but equal
105
Separate Yes but Equal?
106
Class Conflict
- 1877 4 largest railroad companies agree to cut
wages by 10 - Workers strike, railroads shut down
- Cripples industry, transportation
- Hayes uses federal troops to suppress violent
strike - Several weeks pass workers lose
- Shows weakness of labor movement
107
Ethnic Conflict
- Chinese immigration
- Many young, poor Chinese men emigrate to
California - Find jobs building railroads
- Job competition with Irish
- Chinese willing to work for lower wages
- San Francisco Denis Kearney forms Irish gang
- Terrorizes Chinese community
- Chinese Exclusion Act (1882)
- Immigration from China cut off
- First immigration restriction in America
- Why were the Chinese targeted?
108
Election of 1880
- Reps nominate James A. Garfield
- Dark horse from Ohio
- Running mate Chester Arthur (a Stalwart)
- Dems nominate Gen. Winfield Scott Hancock
- Civil War veteran, no political experience
- Popular vote close, but electoral vote gives
Garfield the win
109
Garfields Presidency
- Heated feud between Stalwarts and Half-Breeds
- Hindered any progress for Garfield
- July 1881 Garfield assassinated
- Shot by Charles J. Guiteau (Stalwart)
- Dies in September
- VP Chester Arthur (Stalwart) takes over
110
President Chester Arthur
- A Stalwart, but more reform-minded than other
Stalwarts - (1883) Pendleton Act passed
- Political reform calling for merit based hiring
for government jobs - Civil Service Commission created to enforce act
- Effects Only applied to 10 of federal jobs but
- Stopped worst offenses of cronyism
- Stepping stone to future reform
111
Election of 1884
- Reps nominate James G. Blaine
- Half-Breed leader
- Blaine not very reform minded
- Reps wanting reform abandoned and supported Dems
- Mugwumps
- Dems nominate Grover Cleveland
- From New Jersey, but supported by South
- Seen as a man of principle, honest
- Extreme mudslinging
- Cleveland wins very close election
112
President Grover Cleveland
- First democrat elected since 1857 (James
Buchanan) - Democratic majority in Congress
- Believed in laissez-faire capitalism
- Pleased big businesses, upsets working class
- Names two former-Confeds to cabinet
- Aims to mend North and South
- Wants to follow merit system
- But pressure mounts from Dems
- Replaces 40,000 Reps with Dems
- Military pensions
- Powerful G.A.R. pushing bills to raise already
high pension - Many passed seen as exploitation
- Cleveland (not a veteran) in tough spot
- Doesnt want to disrespect and outrage veterans
- Vetoes many pension bills
113
President Grover Cleveland
- Budget surplus
- Extra money in government budget from high tariff
- Two options to use it
- Invest it
- Lower taxes
- Chooses to lower the tariff
- Reps, Dems, businesses Who supports this? Who
doesnt? - Dems support lowered tariff
- Reps and business owners support higher tariff
- Debate ensues, leads into election of 1888
114
Election of 1888
- Dems nominate Cleveland
- Reps nominate Benjamin Harrison
- From Indiana
- Grandson of Old Tippecanoe
- Benjamin wins very close race
115
Return of a Republican Congress
- Republicans win back power in Congress
- Elect Thomas Czar Reed as Speaker of the House
- Ran House like a dictator
- Tall, tough debater, vicious rhetoric
- Dems resist, refuse to answer roll call
- No roll call no quorum no meeting
116
(No Transcript)
117
Return of a Republican Congress
- Republicans win back power in Congress
- Elect Thomas Czar Reed as Speaker of the House
- Ran House like a dictator
- Tall, tough debater, vicious rhetoric
- Dems resist, refuse to answer roll call
- No roll call no quorum no meeting
- Reed changes role call stipulations
- and proceeds with meetings
- With no opposition in the House
- More hard money policies enacted
- Military pensions increase
- 1890 McKinley Tariff
- Increases tariff to 48
118
Political Discontent
- 1892 Populist Party emerges
- AKA Peoples Party
- Demanded
- Mostly inflation and cheap money policies
- Graduated income tax
- Higher salary higher income tax
- More government regulation on big business
- Direct election of U.S. senators
- Initiative and Referendum
- The people can propose laws, vote to pass them
- Shorter working day
- Immigration restrictions
- Who does this party represent?
- Farmers, working class, common people
119
Election of 1892
- Dems nominate Cleveland again
- Reps nominate Harrison again
- Populist Party nominate James B. Weaver
- Southern support why?
- Farmers, targeted Northern business
- South withdraws support from Populist ticket go
back to Dems why? - Populist party tried to help blacks vote upsets
white Southerners - Cleveland wins election
- Populist Party does relatively well in election
- Threatened white southerners tighten black voting
rights - Literacy tests and grandfather clause
120
Clevelands 2nd Presidency
- Depression of 1893 hits ironic?
- Cleveland now has budget deficit, not a surplus
- Gold supply dangerously low
- Cleveland makes deal with J.P. Morgan and other
bankers - Loan U.S. 65 million in gold to fix problem
- Cleveland loses popularity
- Image of common mans president takes hit with
JP Morgan deal - Promises to lower taxes fail with weak
Wilson-Gorman Tariff - Looked like Cleveland was helping rich, not the
poor
121
Th






![READ[PDF] Final Fantasy XIV: Shadowbringers -- The Art of Reflection - PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10103909.th0.jpg?_=20240821056)

![[DOWNLOAD]⚡️PDF✔️ The Unvarnished Truth: Exploring the Material History of Paintings (English an PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10051209.th0.jpg?_=20240608117)

![[DOWNLOAD]⚡️PDF✔️ The Unvarnished Truth: Exploring the Material History of Paintings (English an PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10050637.th0.jpg?_=20240608128)



















