PowerPoint Presentation - Intro to Optics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
PowerPoint Presentation - Intro to Optics
Description:
Single Lens Imaging System Human photoreceptor cells are named for their shapes Rods Cones Anatomy of a Compound Microscope Upright Microscope Contrast Microscopy ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:157
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PowerPoint Presentation - Intro to Optics
1
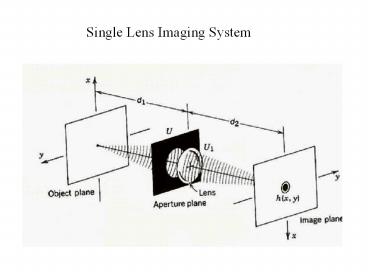
Single Lens Imaging System
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
Retina
Photoreceptors
Neurons
Cone
Rod
Opticnervefibers
Retina
Fovea
Opticnerve
Figure 29.8B
5
(No Transcript)
6
- Human photoreceptor cells are named for their
shapes - Rods
- Cones
ROD
Cell body
CONE
Synapticknobs
Membranous discscontaining visual pigments
Figure 29.8A
7
Vertebrate Eye
Rods Cones
Slide 15
Slide 15
Slide 15
8
Three Cone Opsins (red, green, blue)
9
R(ed), G(reen) B(lue) Monitors
10
Robert Hooke (1635 - 1703)
Built one of the first useful compound
microscopes Observed structure of cork Coined the
term Cell. Published Micrographia (1665)
11
1665 Hooke publishes Micrographia 1678
van Leeuwenhoek observes protozoa (little
animals) 1838-9 Schleiden Schwann proposed
Cell Theory 1860 Pasteur confirms Cell
Theory 1931 Ruska invents electron
microscope 1932 Zerniki develops phase
contrast microscopy 1955 Minsky invents the
laser scanning microscope (LSM) 1989 Webb,
Denk Strickler invent multiphoton LSM
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
Anatomy of a Compound Microscope
trinocular tube
eye piece
objective turret
stand
stage
substage condenser
base
lamp housing
17
Upright Microscope
18
Contrast Microscopy
Koehler Illumination Dark Field Phase
Contrast Differential Interference
Contrast Hoffman Modulation
19
Condensers
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
Koehler IlluminationCondenser lens is adjusted
so that an image of the field diaphragm is
focused onto the object (specimen) plane
23
Koehler Illumination
1. focus specimen2. stop down field diaphragm
until edges are visible3. focus condenser until
image of field diaphragm is sharp4. open field
diaphragm until edges are no longer visible
24
(No Transcript)
25
Conjugate Planes of Focus
26
Path of Imaging Rays
Conjugate Planes
27
Path of Illuminating Rays
Conjugate Planes
28
Light Paths
Illuminating and imaging rays do not share
conjugate planes
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
Projector vs Microscope
32
Microscope produces a virtual image of the back
focal plane of the objective
33
Histochemistry
Immunohistochemistry
Hematoxylin Eosin (H E stain)
34
Oil immersion
n 1.0
n 1.52
n 1.5
n 1.5
35
Effect of Oil
36
Contrast Microscopy
Koehler Illumination Dark Field Phase
Contrast Differential Interference
Contrast Hoffman Modulation
37
(No Transcript)
38
Darkfield Images
Brightfield
Darkfield
39
(No Transcript)
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
(No Transcript)
45
(No Transcript)