5. Tracheophytes - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
5. Tracheophytes
Description:
5. Tracheophytes b. Groups i. Lycopodiophytes ii. Monilophytes iii. Gymnosperms iv. Angiosperms - characteristics Flower: leaf-like whorls fulfill different functions. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:373
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 5. Tracheophytes
1
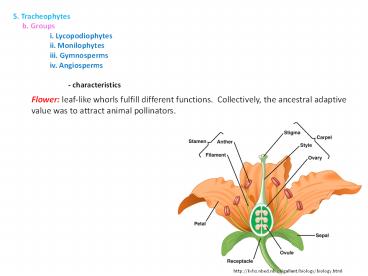
5. Tracheophytes b. Groups i.
Lycopodiophytes ii. Monilophytes iii.
Gymnosperms iv. Angiosperms -
characteristics
Flower leaf-like whorls fulfill different
functions. Collectively, the ancestral adaptive
value was to attract animal pollinators.
http//kvhs.nbed.nb.ca/gallant/biology/biology.htm
l
2
Pollinators forage non-randomly, and they can
learn. So, by bribing pollinators with nectar,
and advertising the location with large colorful
petals, pollinators learn to visit flowers for
food and they trapline, going from flower to
flower. Pollen transport is much more efficient
than wind dispersal less pollen is needed (but
there are additional costs of flower ad nectar
production.
3
Flowers can evolve to limit pollination to a
particular type (or even species) of pollinator.
Flies are attracted to flowers that smell like
carrion.
This increases the chance that the NEXT flower
the pollinator visits will be a member of the
same plant species.
Hummingbirds are attracted to red tubular
flowers, where the nectar is too deep for most
insects to reach
4
Flowers can evolve to limit pollination to a
particular type (or even species) of pollinator.
Butterfly flowers offer a place to stand and
probe many flowers from one place
Many bat flowers are large, to receive the head
of the bat. White is common for these flowers
that open at night.
5
Flowers can evolve to limit pollination to a
particular type (or even species) of pollinator.
Orchids are one of the most derived groups of
plants, and they show the most specialized flowers
6
In some flowering plants, the flowers have become
very reduced they no longer attract pollinators
the plants have returned to a wind-pollinated
lifestyle.
Oak flowers
Ragweed flowers
7
5. Tracheophytes b. Groups i.
Lycopodiophytes ii. Monilophytes iii.
Gymnosperms iv. Angiosperms -
characteristics
Fruit modification to ovary tissue (typically)
to attract animals to consume fruit and disperse
seeds.
http//technabob.com/blog/2008/03/07/edible-apple-
logo-reminds-me-of-the-fruit-salad-days/
http//sharon-taxonomy2010-p2.wikispaces.com/Angio
sperms
8
Plants with dry, wind dispersed seeds are more
common in fields, or in canopy trees. Fleshy
fruits dispersed by animals are more common in
forest understory and forest edges, where animals
are more common.
9
5. Tracheophytes b. Groups i.
Lycopodiophytes ii. Monilophytes iii.
Gymnosperms iv. Angiosperms -
characteristics - life cycle
http//bioweb.uwlax.edu/bio203/s2009/herman_jaci/R
eproduction.htm
10
Double Fertilization
http//www.tutorvista.com/biology/fertilisation-in
-plants
11
5. Tracheophytes b. Groups i.
Lycopodiophytes ii. Monilophytes iii.
Gymnosperms iv. Angiosperms -
characteristics - life cycle
- evolutionary history
12
5. Tracheophytes b. Groups i.
Lycopodiophytes ii. Monilophytes iii.
Gymnosperms iv. Angiosperms -
characteristics - life cycle
- diversity (90 of plant species)
http//www.flickr.com/photos/colbugspotter/3373136
155/
http//www.hiltonpond.org/ThisWeek040622.html
http//www.humanflowerproject.com/index.php/weblog
/2006/01/P8/
http//thebathduck.wordpress.com/category/garden/
13
5. Tracheophytes b. Groups i.
Lycopodiophytes ii. Monilophytes iii.
Gymnosperms iv. Angiosperms -
characteristics - life cycle
- diversity (90 of plant
species)
14
Amborella the most primitive flowering plant,
of New Caledonia
Nymphaea water lilies
Magnoliids - 9000 sp of Magnolias, Laurels,
Black Pepper, Nutmeg
15
Monocots 60,000 species of grasses, grains,
palms, bamboos, lilies, irises, orchids, tulips,
etc.
16
Eudicots over 200,000 species! From vegetables
to roses, trees (that arent gymnosperms, palms
or Magnolias), asters, etc.
17
5. Tracheophytes 6. Summary Algae
aquatic non-tracheophytes cuticle Lycopodio
phytes vascular tissue and dominance of the
sporophyte (tall) Monilophytes true
leaves Gymnosperms Seeds and
pollen Angiosperms Flowers and fruit