Chapter 12: Gluconeogenesis, Pentose Phosphate Pathway, - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title:
Chapter 12: Gluconeogenesis, Pentose Phosphate Pathway,
Description:
Chapter 12: Gluconeogenesis, Pentose Phosphate Pathway, & Glycogen Metabolism Glucose catabolism for the production of energy requires a source of Glc. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:873
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 12: Gluconeogenesis, Pentose Phosphate Pathway,
1
Chapter 12 Gluconeogenesis, Pentose Phosphate
Pathway, Glycogen Metabolism
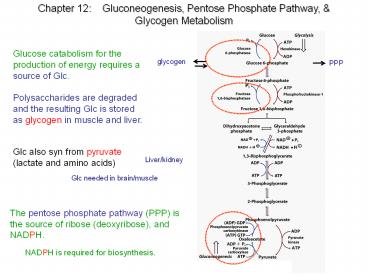
Glucose catabolism for the production of energy
requires a source of Glc. Polysaccharides are
degraded and the resulting Glc is stored as
glycogen in muscle and liver.
glycogen
PPP
Glc also syn from pyruvate (lactate and amino
acids)
Liver/kidney
Glc needed in brain/muscle
The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is the
source of ribose (deoxyribose), and NADPH.
NADPH is required for biosynthesis.
2
Pathway
1
Glycolysis Net Reaction Glucose 2 ADP 2 NAD
2 Pi ? 2 Pyruvate 2 ATP 2 NADH 2 H 2
H2O
3
Gluconeogenesis Net Reaction 2 Pyruvate 4
ATP 2 GTP 2 NADH 2 H 6 H2O ?
Glucose 4 ADP 2 GDP 2 NAD 6 Pi
Gluconeogenesis - glycolysis going backwards -
3 places differ- control points in glycolysis -
4 new enzymes (eukaryotes) - importance of near
equilibrium reactions - ATP energy, NADH
reducing equivalents consumed
10
3
Gluconeogenesis
6 ATP needed total 4 needed to overcome barrier
of production of 2 mol of PEP
4
Gluconeogenesis The Irreversible Steps
Pyruvate ? PEP reversing the pyruvate kinase
step of glycolysis.
4 subunits Biotin Allosteric acetyl CoA
Indicates CAC Backed-up
No allosteric reg
Hormonal induction
Transcriptional regulation glucagon
(fasting) - Insulin (fed state)
5
Gluconeogenesis
No ATP needed since Fru-1,6-bisP not high energy
intermediate
6
Fru-1,6-biP ? Fru-6-P reversing the PFK-1 step
of glycolysis.
Large DG and irreversible Allosteric
modulation - AMP - 2,6-Fru bisP (opposing effect
in glycolysis)
7
Glc-6 ? Glc reversing the Glc hexokinase step of
glycolysis.
Irreversible Allosteric modulation -
AMP Enzyme found only in liver, kidneys, small
intestine. Bound to ER lumenleads to release of
Glc into bldstream
Get to brain And muscle
Most cases Glc-6-P is end product---used in other
pathways (glycogen syn)
8
Gluconeogenesis Precursors
Major precurser in mammals Lactate and Amino
Acids,
Since the body does not transfer pyruvate
Amino Acids
Lactate
Pyruvate in tissues must go to liver
First converted to alanine
Cori cycle
Major source of C for Glc syn during fasting
Active muscle-- lactate
Amino arise from muscle protein breakdown
Lactate to pyruvate in liver
Provide temporary and readily available supply of
Glc to muscle (exercise)
9
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis -glucose biosynthesis found in
all organisms Some tissues require glucose
-brain, muscles After 16-24 hrs, glucose and
glycogen reserves depleted Some tissues
synthesis glucose from non-carbohydrate
precursor -liver, kidney -lactate,
alanine Easiest to start with pyruvate
-converted from lactate or a.a.
10
Gluconeogenesis Regulation
Low Glc glucagon increases protein kinase A
(activates Fru-2,6-bisP phosphatase) lowering
Fru-2,6-bisP. Activate Glc syn and Loss of
glycolysis stim
neg reg pyruvate kinase
Substrate Cycle
Dec the net flux of a pathway But allows a point
for reg flux
Modulate one enzyme effect 2 opposing pathways
Inhibit PFK-1 .. stim Glc syn
11
Regulation of Phosphofructokinase-1
Large oligomeric enzyme bacteria/mammals -
tetramer yeast - octamer
ATP - product of pathway - allosteric
inhibitor
AMP - allosteric activator - relieves
inhibition by ATP
Citrate - feedback inhibitor -
regulates supply of pyruvate - links
Glycolysis and CAC Fru-2,6-bisphosphate -
strong activator - produced by PFK-2 when
excess fru-6-phosphate - indirect means
of substrate stimulation or feed forward
activation
12
Regulation of Pyruvate Kinase
F 1,6 BP
Inactivation by covalent modification -blood
Glc drops, glucagon released -liver protein
kinase A (PKA) turned on -PKA phosphorylates
pyruvate kinase
Allosteric (feed-forward) activation
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate -allosterically
activates -produced in step three -links
control steps together
Allosteric inhibition by ATP -product of
pathway and CAC
Low blood Glc
High blood Glc
13
Regulation of Phosphofructokinase-1
Produced in pancreas in response to low Glc
Dual activities of PFK-2 reg steady-state conc of
Fru-2,6-bisP
Increased glycolysis Fruc-6P inc.inc
F-2,6-bisP Stim PFK-1
Dec F-2,6-bisP PFK-1 less active..dec glycolysis
Activate Protein Kinase A
PFK-1 and pyruvate kinase
Dec glycolysis Inc glc syn
Stimulate glycogen breakdown
Figure 11-17
14
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Shunt
glycogen
PPP
The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is the
source of ribose (deoxyribose), and NADPH.
NADPH is required for biosynthesis.
15
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Shunt
Synthesize 3 pentose phosphates
Ribulose 5-P
Xylulose 5-P
Ribose 5-P (DNA/RNA)
And NADPH
(for the reduction of RNA to DNA)
Or NADPH and glycolytic intermediates
Rapidly dividing cells need lots of NADPH and DNA
High PPP activity
16
The Oxidation Stage of PPP
Allosteric - NADPH
Major reg step
Loss of Carbon
17
The Non-Oxidation Stage of PPP
All equilibruim rxns
When cells need lot of NADPH and nucleotides -
ribulose 5-phosphate ? ribose 5-phosphate - end
of pathway
18
The Non-Oxidation Stage of PPP
Convert 5C sugars into glycolytic intermediates
Can be used in glycolysis of Gluconeogenesis
19
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Thru PPP
3 Glc-6-P 6 NADP 3 H2O ? 2 Fru-6-P
G3P 6 NADPH 3 CO2
Allow sub regeneration via PPP and glyconeogenesis
Recycle 6C sugar
6 ribulose 5-P
5 Glc 5-P
6 Glc-6-P 12 NADP ? 5 Glc-6-P 12
NADPH 6 CO2 Pi
Can be metabolized in Glycolysis or Glcneogenesis
20
Glycogen Metabolism
Glycogen is the storage form of Glc found in
muscles and liver. (Plants stored as
Starch)
Glycogen complex single glycogenin molecule
(Tyr -OH) and gt50,000 glucose residues
Stores of Glc in time of plenty and supplies it
in times of need
Muscle fuel for contraction
Liver produce Glcreleased to Bldstream to other
tissues
All regulated by hormones Glucagon, Epinephrin
and Insulin
21
Glycogen Metabolism
Synthesis
Different enzymes for syn and degradation
Driven by PPi hydrolysis
Major regulatory step
22
Key regulation by phosphorylation
(hormonally regulated)
Pre-existing Glycogenin primer
UDP-Glc synthases in protists, animals, and
fungi. ADP-Glc synthase in plants. Primer of 4 to
8 Glc on a Tyr (-OH) of glycogenin. 1st Glc from
UDP-Glc via Glc transferase. Remaining Glcs
tranferred by glycogenin. Amylo-(1,4
1,6)-transglycolase catalyzes the branch point.
(Alpha 1-6 link)
23
Degradation
Two subunits, two catalytic sites, allosteric
sites. AMP- activator ATP Glc-6-P
inhibitor. Phosphorylation active
(phosphorylase a). Dephosphorylated less active
(phosphorylase b).
Phosphorolysis rxn. Generates phosph-sugar not
free glc
Primary regulation
24
Branching inc speed of syn and degradation
phosphorolytic
Reg by ATP and G-6-P
Sequential removal of Glc From non-reducing
end Stops 4 Glc from branch pt
Primarily by phosphorylation
hydrolytic
Energy yield from glycogen Higher than from glc
25
Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism
Hormonal Regulation
Fed state
fasting
phosphatase
Via cAMP
Via PIP3
Decrease glycolysis
Insulin secreted by pancreas when Glc high
inc rate of transport into cell and glycogen syn
GLUT4
Glucagon secreted when Glc low
Epi released by adrenal gland in response to
neural signal (flight or flight)
Sudden energy response
26
Intracellular Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism
by Interconvertible Enzymes
Low glc activate kinase and breakdown
AMP
phosphodiesterase
cAMP
Simultaneous effect
Low Glc
27
Regulation of Phosphofructokinase-1
Produced in pancreas in response to low Glc
Dual activities of PFK-2 reg steady-state conc of
Fru-2,6-bisP
Increased glycolysis Fruc-6P inc.inc
F-2,6-bisP Stim PFK-1
Dec F-2,6-bisP PFK-1 less active..dec glycolysis
Activate Protein Kinase A
PFK-1 and pyruvate kinase
Dec glycolysis Inc glc syn
Stimulate glycogen breakdown
Figure 11-17
28
High Glc














![Figure 22-48 Schematic diagram depicting the coordinated control of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle by ATP, ADP, AMP, Pi, Ca2+, and the [NADH]/[NAD+] ratio (the vertical arrows indicate increases in this ratio). PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/3889887.th0.jpg?_=201301130811)















