Biochemistry: A Short Course - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
Biochemistry: A Short Course
Description:
Milk-Sugar Disaccharide Metabolism What causes lactose intolerance? Lactose intolerance symptoms? UDP-galactose-4-epimerase converts galactose to glucose ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:173
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Biochemistry: A Short Course
1
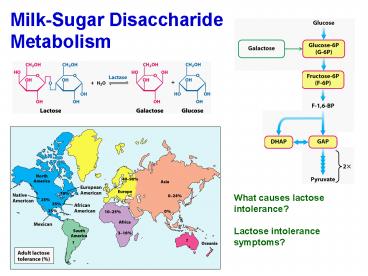
Milk-Sugar Disaccharide Metabolism
What causes lactose intolerance? Lactose
intolerance symptoms?
2
Galactose Metabolism
UDP-galactose-4-epimerase converts galactose to
glucose Phosphoglucomutase isomerizes
glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate
3
Galactose Metabolism
Transferase mutation causes toxic galactose
accumulation in the body
4
Galactose Toxicity with Galactose 1-Phosphate
Uridyl Transferase Inactivity
- Elevated blood-galactose levels
- Liver enlargement with possible
- cirrhosis
- Cataract formation
What foods might make people susceptible to
cataracts?
5
Fructose Entry Points for Glycolysis
Major dietary sugars sucrose (table sugar) and
fructose (high-fructose corn syrup)
6
Fructose Metabolism
Glycerol 3-phosphate a precursor to
triacylglycerol Fructose catabolism bypasses
phosphofructokinase regulation
7
Metabolic Regulation
Irreversible reactions are potential regulatory
sites (e.g. hexokinase, phosphofructokinase and
pyruvate kinase)
What duel role does ATP play in PFK-1
catalysis? How is ATP acting as an allosteric
regulator of phospho-fructokinase?
8
Energy Status Regulates Glycolytic Flow
Elevated ATP sufficient energy elevate AMP
low energy ADP ADP ? ATP AMP ltadenylate
kinasegt
Muscle Tissue
9
Energy Status Regulates Glycolytic Flow
Phosphofructokinase-1 catalyzes the committed
step of glycolysis therefore the most important
controlling element
Muscle Tissue
10
Fructose-2,6-Bisphosphate an Allosteric Regulator
of Phosphofructokinase-1
Front activation by fructose-6P
F-2,6-BP amplifies or diminishes PFK-1 activity?
11
Fructose-2,6-Bisphosphate Reduces ATP Inhibition
of Phosphofructokinase-1
ATP is a substrate and inhibitor of PFK-1
12
Tissue-Specific Glucose Uptake and Extracellular
Traffic
Muscle Tissue Liver Tissue Hexokinase Glucok
inase Low KM High KM Glucose-6-phosphatase Gl
ucose-6-phosphatase Not present Active
Where will glucose preferentially reside? Why is
muscle but not liver glucose cell contained once
phosphorylated?
13
Tissue-Specific Phosphorylation Regulates
Pyruvate Kinase Activity
L-type (liver) PK can be phosporylated while the
M-type (muscle and brain tissue) is not
covalently modified
14
Glucose Transporters
15
Hypoxia Inducible Glycolysis
Exercise and solid tumors initiate increases in
glycolysis efficiency Hypoxia-inducible
transcription factor (HIF-1)
HIF-1 Regulated Genes
16
High Glucose Sensing by Pancreatic Beta Cells
Triggers Energy Storage Response
High energy ratio closes ATP-sensitive potassium
channels Change in cellular ionic environment
opens Ca2 channels Ca2 triggers insulin release
Pancreatic ß cell
17
Phosphofructokinase-1 from the Hyperthermophile
Pyrococcus furiosus
How does this PFK-1 differ from human
PFK-1? What effect do AMP and ATP have on enzyme
activity?