CNS Neuroglial Cells - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
CNS Neuroglial Cells
Description:
CNS Neuroglial Cells Greatly outnumber neurons in the CNS (think worker ants vs. Queen ant) Microglial cells Scattered throughout CNS Support neurons and phagocytize ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:81
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: CNS Neuroglial Cells
1
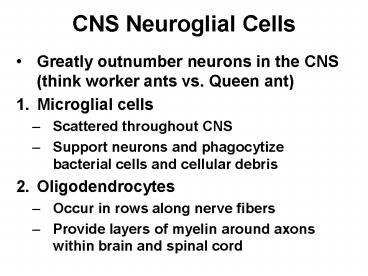
CNS Neuroglial Cells
- Greatly outnumber neurons in the CNS (think
worker ants vs. Queen ant) - Microglial cells
- Scattered throughout CNS
- Support neurons and phagocytize bacterial cells
and cellular debris - Oligodendrocytes
- Occur in rows along nerve fibers
- Provide layers of myelin around axons within
brain and spinal cord
2
CNS Neuroglial Cells, continued.
- Astrocytes
- Found between neurons and blood vessels
- Provide structural support, help regulate
nutrients and ions in tissues - Form scar tissue to fill spaces after CNS
injuries - Ependymal cells
- Form epithelial-like membrane in parts of the
brain (choroid plexuses) - Form inner linings that enclose ventricles in the
brain and central canal in the spinal cord
3
CNS Neuroglial Cells
4
PNS Neuroglial cells
- Schwann cells form myelin sheath around axons
5
Neurons
- Vary in size and structure, but have common
features - Cell Body
- Dendrites
- Axon
- Mature neurons do not divide, but neural stem
cells can divide and form neurons or neuroglial
cells.
6
1. Cell Body
- Contains normal cellular structures (golgi
apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, cell
membrane, etc.) - Neurofibrils fine threads that extend into the
axon - Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substances)
- Membranous sacs in the cytoplasm
- Similar to rough ER
- Ribosomes on Nissl bodies synthesize ______
7
2. Dendrites
- Usually short and highly branched (dendr ?)
- The main receptive surfaces for receiving
communication from axons of other neurons
8
3. Axons
- Arise from a slight elevation of the cell body,
called the axonal hillock. - Conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body
- Contains many mitochondria, microtubules, and
neurofibrils - Originates as a single structure, but may have
branches, especially at the end to interact with
receptive surfaces of other cells
9
PNS Axons
- Enclosed in myelin sheaths composed of many
Schwann cells - Myelin is a lipoprotein.
- Neurilemma sheath surrounds the myelin sheath
- Nodes of Ranvier narrow gaps in the myelin
sheath between the Schwann cells
10
Classification of Neurons
- Classification based on Structural differences
- Bipolar neurons
- Unipolar neurons
- Multipolar neurons
- Classification based on Functional differences
- Sensory neurons (afferent neurons)
- Interneurons (association or internuncial
neurons) - Motor neurons (efferent neurons)
11
Structural Differences
- Sketch the neurons below. Notes on the next 3
slides
12
Structural Differences, cont..
- Bipolar
- 2 processes
- Axon
- Dendrite
- Found in specialized parts of the eyes, nose, and
ears
13
Structural Differences, cont..
- Unipolar
- 1 process divides into 2 branches, which function
as a single axon - 1 branch (peripheral process) associated with
dendrites - Other branch (central process) enters brain or
spinal cord
14
Structural Differences, cont..
- Multipolar
- Many processes arising from cell body
- 1 axon
- Many dendrites
- Most neurons whose cell bodies lie in the brain
or spinal cord are multipolar. - Direction of impulse is ALWAYS from dendrites to
axon.
15
Functional Differences
- Sensory (afferent) neurons
- From peripheral body parts to the brain or spinal
cord - Have specialized receptor ends at the tips of
their dendrites OR - Dendrites closely associated with receptor cells
in the skin or sensory organs. - Most are unipolar, but some are bipolar.
16
Functional Differences, cont..
- Interneurons (association or internuncial
neurons) - Lie entirely in the brain or spinal cord
- Multipolar and link other neurons
- Transmit impulses from one part of the brain or
spinal cord to another - Motor (efferent) neurons
- Multipolar
- Carry nerve impulses from brain or spinal cord to
effectors - Stimulate muscles or glands