Patterson PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Patterson
1
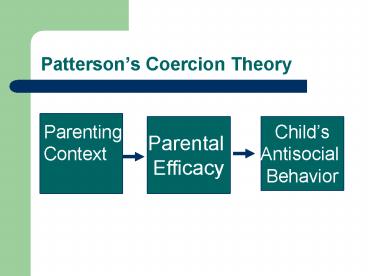
Pattersons Coercion Theory
- Parenting
- Context
Parental Efficacy
Childs Antisocial Behavior
2
Assumptions about Motivation towards crime
- Strain theory motivation from some sort of
strain (e.g. blocked opportunity) - Learning theory motivation from delinquent peers
- Control theory there is enough natural
motivation towards crime - No need to build in extra motivation
3
Types of Control
- Direct Control
- Direct punishments, rewards from parents, friends
- Indirect Control
- Refrain from deviance because you dont want to
risk friends, job, etc. - Internal Control
- Good self-concept, self-control, conscience
4
Travis HirschiCauses of Delinquency
- Identified 4 Elements of the Bond
- Attachment (emotional element)
- Commitment (stake in conformity)
- Involvement (in conventional activities)
- Belief (in the validity of the law)
- Focus here is on indirect controls
5
Evidence in Favor of Bonds
- Attachment
- Attachment to parents (wish to emulate, identify
with) - Commitment
- Grades, educational aspirations
- Belief
- Neutralizations
6
Criticisms of Hirschis Theory
- Delinquents do form relationships
- Attachment to delinquent peers or parents
increases, rather than decreases delinquency - Which comes first, bonds or delinquency?
- Bonds more salient for females, and early in
adolescence
7
Gottfredson and Hirschi (1990)
- A General Theory of Crime
- Same control theory assumptions
- If we are all inclined to be deviant, why
conform? - Because most of us develop self-control
- Internal control
- Developed by age 8, as the result of direct
control from parents
8
Nature of Crime, Nature of Low Self-Control
Criminal Acts Provide immediate gratification
of desires Are risky/thrilling Are
easy/simple Require little skill/planning Provide
few/meager long term benefits Result in
pain/discomfort to a victim
People with low self-control are
therefore Impulsive Risk-taking Physical (as
opposed to mental) Low verbal ability
Short-sighted Insensitive
9
The implications of low self-control
- Explains stability of criminal behavior
- But, how does it explain aging out?
- Explains all crime and analogous behaviors
- Analogous same nature as criminal acts
10
Empirical Support
- Moderate relationship between low self-control
and both crime and analogous behaviors - Holds for both males and females
- BUT
- Not the sole cause of crime
- May not explain white collar crimes
11
Policy Implications
- Hirschis Social Bond Theory
- Target attachment, commitment, belief
- Gottfredson and Hirschis General Theory
- Must focus on early childhood prevention
- Train parents?
12
REVIEW CONTROL VS. LEARNING
- Assumptions about motivation (and human nature)
- Differences over attachment to deviant others
- Differences in how neutralizations are
construed.