Modeling Tradeoffs - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Modeling Tradeoffs
Description:
Title: Slide 1 Author: christ Last modified by: Christ, Kevin P Created Date: 4/27/2006 1:48:43 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:39
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Modeling Tradeoffs
1
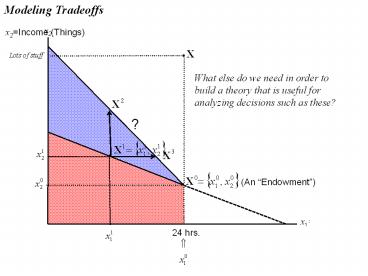
Modeling Tradeoffs
x2
x2Income (Things)
What else do we need in order to build a theory
that is useful for analyzing decisions such as
these?
(An Endowment)
x1 Time (Leisure)
24 hrs.
2
Budget Constraints
x2
Budget Line (efficient consumption)
Feasible consumption set
x1
3
Budget Constraints
Price Changes
Income Changes
4
Modeling Preferences
- Fundamental axioms
1. Completeness
Necessary for rank ordering and functional
representation.
2. Transitivity
3. Continuity
- Supplemental axioms
4. Monotonicity
Defines well-behaved preferences.
5. Convexity
5
Indifference Curves, Preferences, and Rational
Ordering
6
Indifference Curves, Preferences, and Rational
Ordering
7
Indifference Curves and Utility
16
U 16
8
4
U 8
U 4
U 2
16
4
8
8
Bentham and Utilitarianism
By utility is meant that property in any
object, whereby it tends to produce benefit,
advantage, pleasure, good, or happiness (all
this in the present case comes to the same
thing) or (what comes again to the same thing)
to prevent the happening of mischief, pain, evil,
or unhappiness to the party whose interest
is considered The interest of the community
then is what? -- the sum of the interests of
the several members who compose it. An action
then may be said to be conformable to the
principle of utility when the tendency it has
to augment the happiness of the community is
greater than any it has to diminish it. An
Introduction to the Principles of Morals and
Legislation, 1780 Elsewhere, the greatest
happiness principle.
Jeremy Bentham 1748 1832
9
(No Transcript)
10
Individual Demand
11
Substitution Income Effects Normal Good The
Slutsky Approach Pivot and Shift
Price Decrease for x1 (p1?)
A
B
A
SE
IE
12
Substitution Income Effects Normal Goods The
Slutsky Approach Pivot and Shift
x1 (p1, p2, m) 10 m/10p1 p10 3 p11 2
m0 120
13
Substitution Income Effects x1,Normal Good
x2, Inferior Good The Slutsky Approach Pivot
and Shift
A
SE
A
IE
B
SE
IE
14
Substitution Income Effects Inferior Good The
Slutsky Approach Pivot and Shift
Price Decrease for x1 (p1?)
B
A
A
SE
IE
15
Substitution Income Effects Giffen
Good Slutsky Approach Pivot and Shift
Price Decrease for x1 (p1?)
B
A
A
SE
IE
16
Substitution Income Effects Normal Good The
Hicksian Approach Rotate and Shift
Price Decrease for x1 (p1?)
A
B
A
SE
IE
17
Buying Selling
Initial Endowment
Net Demander of good
Initial Endowment
Net Supplier of good
Net Demander of good
Net Supplier of good
18
Buying and Selling Consumer Choice Theory with
Endowments Decomposition of effects of a price
change into substitution, ordinary income and
endowment income effects Price decrease of a
good currently being demanded.
19
Buying and Selling Consumer Choice Theory with
Endowments Decomposition of effects of a price
change into substitution, ordinary income and
endowment income effects Price increase of a
good currently being demanded.
20
Buying and Selling Consumer Choice Theory with
Endowments Decomposition of effects of a price
change into substitution, ordinary income and
endowment income effects Price decrease of a
good currently being supplied.
SE
OIE
EIE
21
Buying and Selling Consumer Choice Theory with
Endowments Decomposition of effects of a price
change into substitution, ordinary income and
endowment income effects Price increase of a
good currently being supplied.
22
Buying and Selling Consumer Choice Theory with
Endowments Decomposition of effects of a price
change into substitution, ordinary income and
endowment income effects Price increase of a
good currently being supplied.
An outcome illustrating perfectly inelastic
demand for x1
SE
OIE
EIE
23
Labor-leisure tradeoffs and labor supply
consumption, c
C0 (w/p)L0
A
c0
E
C0
leisure, l
l0
L0
Leisure
Labor