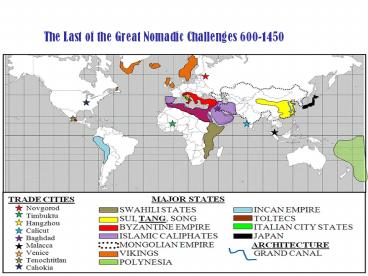
The Last of the Great Nomadic Challenges 600-1450
1 / 28
Title:
The Last of the Great Nomadic Challenges 600-1450
Description:
... to Russia during the 8th and 9th centuries looting and destroying communities and churches and monasteries. ... the indirect beginnings of the rise of Western ... –
Number of Views:119
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Last of the Great Nomadic Challenges 600-1450
1
The Last of the Great Nomadic Challenges 600-1450
- Expanding Communities
2
Demographic and Environmental Changes
- Nomadic Migrations
- Vikings
- Turks
- Aztecs
- Mongols
- Arabs
- Predict the impact of these movements.
3
Demographic and Environmental Changes
- Migration of Agricultural Peoples
- Bantu migrations
- Europeans to Eastern and Central Europe
- Consequences of Disease
- For ex. Black Plague 1348
- Growth and Role of Cities
- Urbanization (Ghuang Zhou, Canton,
Changan,Cairo, Cordova, Samarkand, Baghdad,
Damascus, Venice, Constantinople, Tenochtitlan,
Timbuktu, etc.) - How much of this demonstrates continuity?
4
Compare the Aztecs to
- Group 1-Arabs
- Group 2-Turks
- Group 3- Vikings
- Group 4- Bantus
- Group 5- Mongola
- Aztecs were nomadic and settled around Lake
Texcoco, established a militaristic empire based
on tribute, became expert engineers constructing
chinampas (floating gardens) demanding tribute
from their peripheral states and creating a
flourishishing marketplace in Tenochtitlan. Their
religious polytheistic components could be felt
in everything from their monumental architecture,
calendars and human sacrifice to appease the
Gods. Theiir military is how they established and
maintained their empire while creating gender
paralellism where spearate spheres of work were
establiehd fore men and women.
5
Arabs
- Early post-classical movements along the Arabian
Peninsula. Bedouin merchants facilitated spread
of Islam invaded and eventually settled in Middle
East, Northern Africa and Southern Europe.
Although the notion of Caliphate would be sacked
by Mongols in 1258, Islam held areas together
culturally, and mixed with native customs and
religions. Despite political conflict over
succession (Sunni-Shiite) Dar Al Islam would
unite much of AfroEurasia
6
Vikings
- These sea-faring marauders swept into many parts
of Europe from Normandy to Mediterranean areas,
to Russia during the 8th and 9th centuries
looting and destroying communities and churches
and monasteries. Some settled and intermarrying
with groups like Normans and Rus (Russia). Served
in Black sea trade with Byzantium but are mostly
known for providing the threat to Western
European armies developed under the auspices of
Feudalism
7
Turks
- Originally Indo-Europeans who migrated into the
Middle east dating various time in this era. The
Seljuk Turks invaded the Byzanitne Empire
sparking another Great migration to the Middle
Eats-crusader. Indirectly responsible for
Europes interest and involvement in
long-distance trade. Also served as mercenaries
and militia in both Tang and Abbasid armies. By
the end of this era, the Ottoman Turks were on
the rise capturing Constantinople (thanks to the
Mongols) by 1453. Turks (Afghan) even invaded
India forming the Delhi Sultanate and introduced
Islam into India with such force that the
consequences reverberated throughout the rest of
Indian history.
8
Mongols
- Identified by many historians as the end on the
nomadic era. Clearly the good was their ability
to establish a Khanate system where safe trade,
religious tolerance and a relatively peaceful
existence (Pax Mongolica) facilitated an East
meets west connecting Middle East, South Asia,
East Asia and Europe. For even a brief time
Central Asian Empire the Timurud Dynasty will
become a major Islamic center of trade and
scholarship in the great city of Samarkand ruled
by Tamerlane. They would also contribute to the
spread of the black death, the end of the Song
Dynasty and the Abbasid Caliphate and the
indirect beginnings of the rise of Western
European age of exploration.
9
Aztecs
- Migrated to the Central Valley of Mexico around
Lake Texcoco according to legend ( area where
Eagle perched on a cactus with a snake in its
talons). Developed an agricultural method of
tying reeds to floating gardens known as
chinampas. Established a thriving militaristic
state using tribute from surrounding areas to
develop thriving city Tenochtitlan.
Decentralized in nature, the development of
causeways and bridges and roads would facilitate
trade within the city dubbed the Venice of the
Americas by the Spanish conquistadores who
encountered it for the first time. Many war
captives were either enslaved or sacrificed.
10
Inter-regional networks and Contacts
- Mediterranean trade circuit
- Silk Routes
- Indian Ocean
- Trans-Saharan Trade
- Trans-American circuits
- Religious connections missionaries,
inter-religious contact - Impact of Mongols
11
Mediterranean Circuits
12
Silk Routes
13
Indian Ocean
14
Trans-Saharan Trade
15
Trans-American trade
16
Religious Connections
17
COMP Thesis
The Mongols and Aztecs both established large
empire based on military prowess and might, both
collected tribute from peripheral states in
return for protection and autonomy, however, the
Mongol Empire was established into a massive
interregional trading network while the Aztecs
regional connections were much smaller extending
into only the Central Valley of Mexico
18
Impact of Mongols Blessing or a Curse
19
China Internal and External Expansion
- Tang Dynasty
- Technological innovations compass, paper,
gunpowder etc. - Influence on Japan
- Footbinding, Neo-Confucianism
- Song Dynasty
- All the makings of an industrial revolution
- Early Ming
- Zheng He voyages, eunochs and nomadic threats
20
Islamic World Dar al-Islam
- Expanding cultural, economic and political
influence - Al-Andalus/ Islamic Spain
- North and West Africa
- Indian Ocean East Africa, India, SE Asia
- Technological accomplishments astrolabe,
algebra, philosophy, cartography
21
Al-Andalus
22
Islamic World Sample Comparisons
- Compare Islam to Christianity
- Compare Islamic contacts with Europe and with
Africa - Crusades- points of view compared
- Compare gender changes
- Compare support/ patronage of arts and sciences
23
Europe
- Break in eastern and Western Christendom
political significance? - Religious schisms compared
- Eastern Orthodox and Roman Catholicism
- Mahayana and Theravada Buddhism
- Sunni/ Shiite in Islam
24
Europe
- Restructuring of institutions
- Role of religion Papacy, Crusades, architecture
and education - Development of feudalism
- Comparison of feudalism in Europe and Japan
- Increasing importance of monarchy over church
25
Amer-Indian World
- Migrations over the Bering Strait at least 10,000
years ago. - Northern America Cahokia
- Southwest Hohokam
- Meso-America Olmecs, Maya, Toltec (Aztec)
- South America Nazca, Moche, (Inca)
26
Sub-Saharan Africa
- West African kingdoms Ghana, Mali, Songhay
- East African city states Axum, Kilwa, Mombasa
- Southern Africa Great Zimbabwe
- Contacts with Islamic World, Indian Ocean world,
and within Africa - Role of Trade, Education and Religion
27
Questions we will focus on
- Was there a world economic network in this time
period? - How did gender roles change?
- How can material culture and urban history help
us to understand early societies?
28
Conclusions
- Examples of continuity?
- Examples of change?
- Think about new and old players.
- Similar patterns and trends demographic, social
and cultural, technological. - New avenues of intersection.