PHOTOSYNTHESIS - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Description:
PHOTOSYNTHESIS SOUTH DAKOTA ADVANCED SCIENCE STANDARDS 9-12.L.1.1A. Students are able to explain the physical and chemical processes of photosynthesis and cell ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:409
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PHOTOSYNTHESIS
1
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
2
Photosynthesis
- Involves the Use Of light Energy to convert Water
(H20) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) into Oxygen (O2)
and High Energy Carbohydrates (sugars, e.g.
Glucose) Starches
3
The Photosynthesis Equation
4
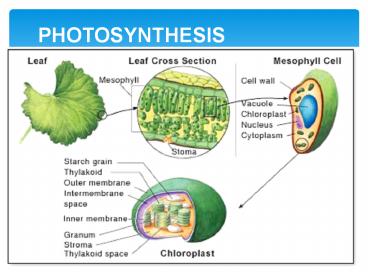
PHOTOSYNTHESIS HAPPENS IN CHLOROPLASTS
THYLAKOIDS
GRANUM (pl. grana)
- sac-like
- photosynthetic stack of thylakoids
- membranes
- inside chloroplast
5
SPACES
THYLAKOIDSPACE
STROMA
Gel-filled space inside chloroplast
surrounding thylakoid sac
Gel-filled space Inside the thylakoid sac
cytoplasm
Gel-filled space OUTSIDE chloroplast but inside
the cell membrane
6
PHOTOSYNTHESIS HAPPENS IN CHLOROPLASTS
- Proteins that are part of the thylakoid membrane
organize - ________________________________ into clusters
called - _____________________
Light absorbing PIGMENTS
PHOTOSYSTEMS
7
Pigments
- In addition to water, carbon dioxide, and light
energy, photosynthesis requires Pigments - Chlorophyll is the primary light-absorbing
pigment in autotrophs - Chlorophyll is found inside chloroplasts
8
Light and Pigments
- Light Contains A Mixture Of Wavelengths
- Different Wavelengths Have Different Colors
9
Light Pigments
- Different pigments absorb different wavelengths
of light - Energy from light excites electrons in the
plants pigments - Excited electrons carry the absorbed energy
10
(No Transcript)
11
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Light-Dependent
Reaction
Light-Independent Reactions
12
LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS
ATP SYNTHASE
INSIDE THYLAKOID SPACE
?
- PHOTOSYSTEM II
?
ELECTRON TRANSPORTSYSTEM
?
PHOTOSYSTEM I
OUTSIDE THYLAKOID IN STROMA
13
WHY DOES PHOTOSYSTEM II COME BEFORE PHOTOSYSTEM
I?
It was discovered and named 1st
- PHOTOSYSTEM II
?
?
PHOTOSYSTEM I
14
REMEMBER DIFFUSION?
- Molecules move
- automatically from
- where theres A LOT
- to where theres NOT
15
- Diffusion happens anytime there is a difference
in concentration in one place compared to another - ________________________
CONCENTRATION GRADIENT
16
LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS
SEE A MOVIEATP SYNTHASEIN ACTION
17
- LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION
- Requires ______________
- Pigments that absorb light are part of
____________________________ - Made up of ____________________________
- connected by ______________________________
- ___________________
- Uses light energy to create
- _______ and
- _________
- Breaks apart ______ molecules and
releases _____________
LIGHT
THYLAKOID membranes
PHOTOSYSTEMS II I
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
ATP SYNTHASE
ATP
NADPH
H20
oxygen
18
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Light-Dependent
Reaction
19
PHOTOSYNTHESIS OVERVIEW
Pearson Education Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
20
Video 5
Calvin Cycle (8E)
- Click the image to play the video segment.
21
Calvin Cycle
CO2 Enters the Cycle
Energy Input
5-Carbon Molecules Regenerated
6-Carbon Sugar Produced
See Calvin cycleanimation
Sugars and other compounds
22
- CALVIN CYCLE
- (also called _________________________)
- ____________ require ____________
- Happens in the _________ between thylakoids
- NADPH donates ________________________
- ATP donates _________________
- CO2 donates ____________________
- to make __________
LIGHT INDEPENDENT
DOES NOT
LIGHT
STROMA
Hydrogen electrons
ENERGY
Carbon oxygen
GLUCOSE
http//www.estrellamountain.edu/faculty/farabee/bi
obk/BioBookCHEM2.html
23
Factors that Affect Photosynthesis
AMOUNT OF WATER
- ____________________
- Water is one of the raw materials needed, so
- A shortage of water can ________________
- photosynthesis
slow or stop
Desert plants and conifers that live in dry
conditions have a waxy coating on their leaves
to prevent water loss.
http//www.hononegah.org/departments/Anderson/cact
us.JPG
24
Factors that Affect Photosynthesis
TEMPERATURE
- Photosynthesis enzymes function best between 0 C
- 35 C - At temperatures above or below this range,
photosynthesis will slow or stop - Conifers in winter may carry out
- photosynthesis only occasionally
http//www.sustland.umn.edu/maint/images/evergreen
10.jpg
25
REMEMBER CELL BIO
- Enzymes work BEST at a certain ___ and
__________. - Conditions that are TOO ACIDIC
- or TOO HOT cause proteins
- to unwind or _________
pH
temperature
DENATURE
http//www.desktopfotos.de/Downloads/melt_cd.jpg
http//www.nealbrownstudio.com/adm/photo/163_nb_fr
ied_egg.jpg
26
Denaturing changes the shape of the enzyme making
it not work
HOMEOSTASIS (keeping pH and temperature constant)
is important for maintaining enzyme function.
Image fromhttp//www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/far
abee/BIOBK/BioBookCHEM2.html
27
Factors that Affect Photosynthesis
LIGHT INTENSITY
- ____________________
- More light increases rate of photosynthesis
- up to a certain level until plant reaches its
- maximum rate of photosynthesis
See effect of light experiment
http//www.teachnet.ie/foneill/exper.htm
http//206.173.89.42/REALTYWITHALOHA_COM/piphoto/f
unny20sun20with20sunglasses.gif
28
THE BIG PICTURE
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS provides
- the _____________ we breathe
- and the __________
- heterotrophs (like us)
- consume to survive
OXYGEN
sugars
Carbondioxide
Sugars
WATER
Oxygen
_____________ ____________
_______________ ____________
29
Concept Map
Section 8-3
Photosynthesis
includes
takes place in
uses
use
take place in
to produce
to produce
of
30
Concept Map
Section 8-3
Photosynthesis
includes
takes place in
uses
use
take place in
to produce
to produce
of
31
SOUTH DAKOTA SCIENCE STANDARDS
- Chapter 8 - Photosynthesis
- The students will be able to
- explain the biochemical processes that a plant
uses in photosynthesis - explain the role ADP-ATP cycle has within the
chloroplast of the cell (9-12.L.1.1) - explain the light reaction (9-12.L.1.1)
- explain the steps of photophosphorylation and the
Calvin Cycle (9-12.L.1.1)
32
SOUTH DAKOTA CORE SCIENCE STANDARDS
LIFE SCIENCEIndicator 1 Understand the
fundamental structures, functions,
classifications, and mechanisms found in living
things
- 9-12.L.1.1. Students are able to relate cellular
functions and processes to specialized structures
within cells. - Photosynthesis and respiration
- ATP-ADP energy cycle Role of
enzymes Mitochondria Chloroplasts
33
Core High School Life SciencePerformance
Descriptors
High school students performing at the ADVANCED level explain the steps of photophosphorylation and the Calvin Cycle analyze chemical reaction and chemical processes involved in the Calvin Cycle and Krebs Cycle predict the function of a given structure predict how homeostasis is maintained within living systems
High school students performing at the PROFICIENT level describe and give examples of chemical reactions required to sustain life (hydrolysis, dehydration synthesis, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, ADP/ATP, role of enzymes) describe the relationship between structure and function explain how homeostasis is maintained within living systems predict how life systems respond to changes in the environment
High school students performing at the BASIC level name chemical reactions required to sustain life (hydrolysis, dehydration synthesis, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, ADP/ATP, role of enzymes) recognize that different structures perform different functions define homeostasis
34
SOUTH DAKOTA ADVANCED SCIENCE STANDARDS
LIFE SCIENCEIndicator 1 Understand the
fundamental structures, functions,
classifications, and mechanisms found in living
things.
- 9-12.L.1.1A. Students are able to explain the
physical and chemical processes of photosynthesis
and cell respiration and their importance to
plant and animal life. (SYNTHESIS) - Examples photosystems,
photophosphorylation, Calvin Cycle and Krebs
Cycle
35
SOUTH DAKOTA ADVANCED STANDARDS
LIFE SCIENCE
- Indicator 1 Understand the fundamental
structures, functions, classifications, and
mechanisms found in living things. - 9-12.L.1.2A. (Synthesis) Describe how living
systems use biofeedback mechanisms to maintain
homeostasis. - 9-12.L.1.4A. (Application) Identify factors that
change the rates of enzyme catalyzed reactions.