Population Dynamics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Population Dynamics
Description:
Population Dynamics Joohee Kim IB Biology Sec. II Population Group of organisms of the same species Live in the same area at the same time Collection of inter ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:185
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Population Dynamics
1
Population Dynamics
- Joohee Kim
- IB Biology
- Sec. II
2
Population
- Group of organisms of the same species
- Live in the same area at the same time
- Collection of inter-breeding organisms
3
Population Dynamics
- Short- and long-term changes in the size and age
composition of populations - Biological and environmental processes
influencing changes
4
History
- Dominant branch of mathematical biology
- History of more than 210 years
- First principle
- exponential law of Malthus, modeled by
Malthusian growth model
5
Malthusian Growth Model
- Simple exponential growth model
- Based on constant rate of compound interest
- Formula P(t) P0ert
- where P0 Initial Population
- r growth rate, t time
6
Changes to Size of Population
- There are four ways in which the size of a
population can change - 1. Natality birth
- 2. Mortality death
- 3. Immigration move into area
- 4. Emigration move out of area
7
Population Change
- Populations are often affected by all four of
these things and the overall change can be
calculated using an equation - Population Change
- (natality immigration) (mortality
emigration)
8
Population Growth Curves
- If the size of a population is measured
regularly, a curve can be plotted. - When a species spreads into a new area, the
population growth curve is often sigmoid
(S-shaped).
9
3 Phases of Curve
- The three phases of the curve are explained by
changes in natality and mortality. - 1. Exponential Phase
- 2. Transitional Phase
- 3. Plateau Phase
10
Exponential Phase
- Population increases exponentially
- Natality Rate gt Mortality Rate
- Resources needed by the population are abundant
- Diseases and predators are rare
11
Transitional Phase
- Natality rate starts to fall
- Mortality rate starts to rise
- Still, Natality Rate gt Mortality Rate
- Rise less rapidly
12
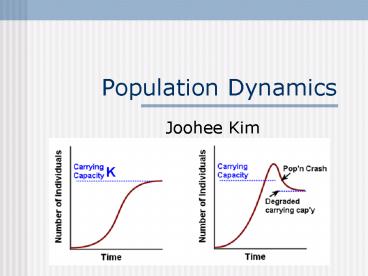
Plateau Phase
- Natality Mortality
- Constant population size
- Reached carrying capacity (max population size
that can be supported by environment)
13
Limiting Factors of Population
- Shortage of resources (food)
- More predators
- More disease or parasites
- Limit population increase because they become
more intense/crowded as the population rises - Reduce natality rate
- Increase mortality rate