Fermentation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
Fermentation
Description:
After the inoculation of a sterile nutrient solution with microorganisms and cultivation under physiological conditions, ... plant and tissue culture, ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:274
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Fermentation
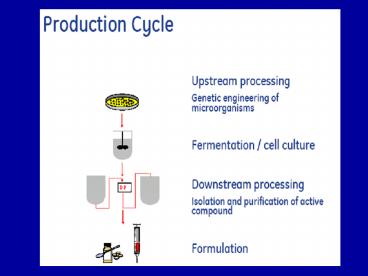
1
(No Transcript)
2
Fermentation
- Fermentation is the term used by
microbiologists to describe any process for the
production of a product by means of the mass
culture of a microorganism.
3
Fermentation Basics
- The product can either be
- The cell itself referred to as biomass
production. - A microorganisms own metabolite referred to as
a product from a natural strain. - A microorganisms foreign product referred to as
a product from recombinant DNA technology or
genetically engineered strain, i.e. recombinant
strain.
4
Batch Fermentation
- A batch fermentation can be considered to be a
closed system. - At time t0 the sterilized nutrient solution in
the fermentor is inoculated with microorganisms
and incubation is allowed to proceed. - In the course of the entire fermentation, nothing
is added, except oxygen (in case of aerobic
microorganisms), and acid or base to control the
pH
5
Batch Fermentation
- The composition of the culture medium, the
biomass concentration, and the metabolite
concentration generally change constantly as a
result of the metabolism of the cells. - After the inoculation of a sterile nutrient
solution with microorganisms and cultivation
under physiological conditions, four typical
phases of growth are observed
6
(No Transcript)
7
Growth Phases
- Lag phase
- Physicochemical equilibration between
microorganism and the environment. - Log phase
- Growth of the cell mass can now be described
quantitatively as a doubling of cell number per
unit time for bacteria.
8
- Stationary phase
- As soon as the substrate is metabolized or toxic
substances have been formed, growth slows down or
is completely stopped. - Death phase
- In this phase the energy reserves of the cells
are exhausted.
9
Downstream processing Downstream Processing
comprises all operations required for extraction
and purification of a product produced by a
biotechnological process such as microbial
fermentation, plant and tissue culture,
transgenic plants and animals.
10
Stages in downstream processing
Bioreactor
Chromatography
Cell separation
Cell disruption
Clarified culture medium
Cell debries removal
Capture
Downstream processing
Interm- ediate Purific.
Product recovery and concentration
Chromatography
Final
Polishing formulation
11
Downstream processing
Generalized flow chart for purification of a
protein from a culture broth
12
Downstream processing / Bioseparations /
Purifications
It may not always be neccessary to follow a long
and difficult path to obtain a pure protein
Proper planning and a smart choice and
integration of separation techniques can be used
to fulfil the need for an efficient, clean and
cost-effective process.
13
Every technique offers a balance between
resolution, capacity, speed and recovery.
14
- Economic aspects of downstream
- processing
- Recombinant technology has established well
- upstream processing
- Downstream processing/bioseparation is a major
- challenge for bioindustry
- Upto 80 of the product costs are incurred on
- downstream processing
15
Protein bioseparation costs
__________________________________________________
__________ Product
Approximate relative Biosep. cost as of
price
total cost of
production _______________________________________
_____________________ Food additives
1
10 30 Nutraceuticals 2 10
30
50 Industrial enzymes 5 - 10
30 50 Diagnostic
proteins 50 -100
50 70 Therapeutic proteins 50
500 60
80 _______________________________________________
______________
16
- Why downstream/purification?
- Reduction in bulk
- Concentration enrichment
- Removal of specific impurities (e.g., toxins from
therapeutic products) - Prevention of catalysis other than the type
desired (for enzymes) - Recommended product specifications (e.g.,
pharmaceuticals - requirement)
- Enhancement of protein stability
- Reduction of protein degradation (e.g. by
proteolysis)
17
- Modify the upstream processes to aid in
downstream - purification by
- Selection of organisms that do not produce
undesirable - pigments or metabolites
- Modify the fermentation conditions so that
undesirables - are not produced
- Precise timing of harvest
- pH temperature control after harvesting
- 5) Addition of flocculating agents
- 6) Addition of antifoams that do not cause
purification problems
18
Protein Products
Food/Food additives/Nutraceuticals
Industrial Enzymes Egg albumin
Hemicellulose Casein Glucose isomerase Soy
proteins Alpha amylase Whey protein
concentrate Penicillin G acylase Protein
hydrolysates Alkaline proteases Alpha
lactalbumin Celluloses Beta lactoglobulin Lysoz
yme Diagnostic enzymes
Peroxidase Pharmaceuticals Glucose
oxidase Monoclonal antibodies Serum
albumin Miscellaneous Serum immunoglobulins D
etergent enzymes Tissue plasminogen
activator Digestive enzymes Urokinase Enzymes
used in cosmetics Streptokinase Insulin Interfero
n ------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------
--
19
RIPP
- Removal
- Isolation
- Purification
- Polishing
20
Downstream processing - Operation sequence
- Removal of particulates (insolubles) common
operations are filtration, centrifugation, also
sometimes settling/decanting, also - new absorbents developed
- Primary isolation solvent extraction,
precipitation, ultrafiltration - desired product concentration increases
significantly - Purification Fractional precipitation, several
types chromatography- bulk impurity removal as
well as further product concentration - Final product isolation (Formulation) final
centrifugation, freeze drying, stability
considerations, regulatory approvals, toxin and
pyrogen free etc.
21
Unit operations in downstream processing
Cell separation High resolution
techniques flocculation chromatography centrif
ugation electrophoresis filtration dialysis C
ell disruption Finishing/packaging homogenizers
crystallization hydrolytic enzymes filtration
gel chromatography drying Clarification ce
ntrifugation filtration Concentration precipita
tion chromatography ultrafiltration partitionin
g distillation



















![Precision Fermentation Ingredients Market: Trends, Opportunities, and Forecasts [Latest] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/9995646.th0.jpg?_=20240206014)



![[DOWNLOAD]PDF Fermentation for Life: 100 Easy Japanese Inspired Recipes Using Probiotic-Ri PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10065463.th0.jpg?_=202406271111)






![[PDF READ ONLINE] Beginner’s Guide to Pickling & Fermentation: A Complete Cookbook for Pi PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10080078.th0.jpg?_=202407170610)