Network layer PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Network layer
1
Network layer
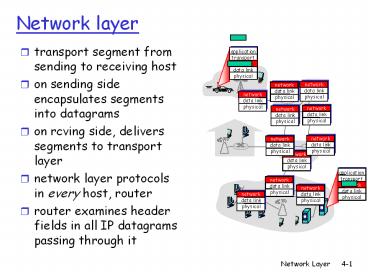
- transport segment from sending to receiving host
- on sending side encapsulates segments into
datagrams - on rcving side, delivers segments to transport
layer - network layer protocols in every host, router
- router examines header fields in all IP datagrams
passing through it
2
Two Key Network-Layer Functions
- forwarding move packets from routers input to
appropriate router output - routing determine route taken by packets from
source to dest. - routing algorithms
- analogy
- routing process of planning trip from source to
dest - forwarding process of getting through single
interchange
3
Interplay between routing and forwarding
4
Key Network-Layer Function
- What is the address for computers / routers?
- analogy
- Mailing a letter Process of planning
intermediate post offices from source to
destination
- requirement
- Need to know the addresses of the post offices
PIN10019
5
The Internet Network layer
- Host, router network layer functions
Transport layer TCP, UDP
Network layer
Link layer
physical layer
6
IP datagram format
IP protocol version number
32 bits
total datagram length (bytes)
header length (bytes)
head. len
type of service
ver
length
for fragmentation/ reassembly
fragment offset
type of data
flgs
16-bit identifier
max number remaining hops (decremented at each
router)
time to live
upper layer
header checksum
32 bit source IP address
32 bit destination IP address
upper layer protocol to deliver payload to
E.g. timestamp, record route taken, specify list
of routers to visit.
Options (if any)
data (variable length, typically a TCP or UDP
segment)
7
IP Addressing introduction
223.1.1.1
- IP address 32-bit identifier for host, router
interface - interface connection between host/router and
physical link - routers typically have multiple interfaces
- host typically has one interface
- IP addresses associated with each interface
223.1.2.9
223.1.1.4
223.1.1.3
223.1.1.1 11011111 00000001 00000001 00000001
223
1
1
1
8
Class Handouts(provided in class)
9
Subnets
223.1.1.1
- IP address
- subnet part (high order bits)
- host part (low order bits)
- Whats a subnet ?
- device interfaces with same subnet part of IP
address - can physically reach each other without
intervening router
223.1.2.1
223.1.1.2
223.1.2.9
223.1.1.4
223.1.2.2
223.1.1.3
223.1.3.27
subnet
223.1.3.2
223.1.3.1
network consisting of 3 subnets
10
Subnets
- Recipe
- To determine the subnets, detach each interface
from its host or router, creating islands of
isolated networks. Each isolated network is
called a subnet.
Subnet mask /24
11
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- Goal allow host to dynamically obtain its IP
address from network server when it joins network - Can renew its lease on address in use
- Allows reuse of addresses (only hold address
while connected an on) - Support for mobile users who want to join network
(more shortly) - DHCP overview
- host broadcasts DHCP discover msg optional
- DHCP server responds with DHCP offer msg
optional - host requests IP address DHCP request msg
- DHCP server sends address DHCP ack msg
12
DHCP client-server scenario
223.1.2.1
DHCP
223.1.1.1
server
223.1.1.2
223.1.2.9
223.1.1.4
223.1.2.2
arriving DHCP client needs address in
this network
223.1.1.3
223.1.3.27
223.1.3.2
223.1.3.1
13
DHCP client-server scenario
arriving client
DHCP server 223.1.2.5
DHCP offer
src 223.1.2.5, 67 dest 255.255.255.255,
68 yiaddrr 223.1.2.4 transaction ID
654 Lifetime 3600 secs
DHCP request
src 0.0.0.0, 68 dest 255.255.255.255,
67 yiaddrr 223.1.2.4 transaction ID
655 Lifetime 3600 secs
time
DHCP ACK
src 223.1.2.5, 67 dest 255.255.255.255,
68 yiaddrr 223.1.2.4 transaction ID
655 Lifetime 3600 secs
14
Numerical example
- A software company has 100 employees.
- What would be the ideal class from which the
company would choose its network IP to prevent
wastage of IP addresses? - How many bits would be assigned for network part
and - how many bits would be assigned for host part?
- The company suddenly goes through increase in
number of employees from 100 to 2040. - What would be the ideal class from which the
company would choose its network IP to prevent
wastage of IP addresses? - How many bits would be assigned for network part
and - how many bits would be assigned for host part?
- Solve!
15
IP addressing CIDR
- CIDR Classless InterDomain Routing
- subnet portion of address of arbitrary length
- address format a.b.c.d/x, where x is bits in
subnet portion of address - Back to the previous numerical example? How many
address wastage?