The Plasma Membrane and Transport across it - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
The Plasma Membrane and Transport across it
Description:
The Plasma Membrane and Transport across it Cell Membrane Controls what enters and leaves the cell Like water, nutrients and waste The membrane is Selectively ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:302
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Plasma Membrane and Transport across it
1
The Plasma Membrane and Transport across it
2
Cell Membrane
- Controls what enters and leaves the cell
- Like water, nutrients and waste
- The membrane is Selectively Permeable
- Membrane selects which molecules can permeate
(pass through) into the cell. - Like a window screen allows what you want in
and keeps others out.
3
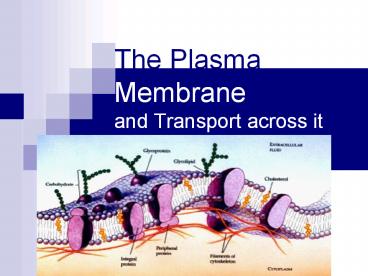
Structure of Plasma Membrane
- Lipid Bilayer (2 layers of phospholipids)
- Lipids with phosphate heads attached
- Head of phospholipid is polar
- Hydrophilic (points outward, likes watery
environment) - Fatty acids (tails) are nonpolar
- Hydrophobic (points inward, avoids water)
4
Other Membrane Molecules
- Membrane Proteins - (transport)
- Allow substances/waste to move in and out of the
cell. - Creates a tunnel that can be closed or open.
- Carbohydrates/ Other Proteins-
- Stick out of cell surface (id card for other
cells to see)
5
Cell Membrane Structures
6
How stuff gets into the cell
- 2 ways cell gets nutrients it needs and gets rid
of waste - Passive Transport
- Requires no energy
- Active Transport
- Requires an input of energy
7
PassiveTransport
- Occurs due to concentration gradient
- Molecules naturally move from areas of higher
concentration to lower concentration (no energy
required) - Diffusion natural movement of molecules
- Facilitated Diffusion through protein channels
- Osmosis diffusion of water molecules
8
Diffusion
- In nature, molecules ALWAYS move from areas of
higher concentration to areas of lower
concentration, as is shown in this picture. - They move to reach equilibrium
- This also happens across the cell membrane!
These odor molecules are diffusing from the
bottle (area of high concentration) to the
surrounding air (lower concentration)
9
Facilitated Diffusion
- Diffusion of molecules through protein channels
in the cell membrane - Used for substances that the cell needs but
cannot pass through the membrane - Large molecules
- Charged (ions)
10
Osmosis
- The diffusion of water molecules is called
osmosis - Just like diffusion
- Water molecules move from areas of higher conc.
to areas of lower water conc. - They will move until there are equal
concentrations of water (and solute) molecules
everywhere - Called equilibrium
- Molecules still diffuse, but at equal rates
11
Osmosis
- The movement of water molecules across a membrane
- Water moves from areas of high water conc. to
areas of lower water conc. - This is how cells maintain a stable internal
environment - Homeostasis reacting to environment
Blue water molecules, easily pass through
membrane Red large (or charged) molecules,
cant pass through membrane
12
Passive Transport Video
13
Isotonic Solutions - Iso equal
- Cells that are in equilibrium with the
surrounding solution do not experience osmosis.
- These cells have the same concentration of solute
(and water) as the surrounding solution
14
Hypotonic Solutions hypo lower
- solute (solute concentration) is lower outside
the cell
- More water outside, so water moves into the cell,
to try to reach equilibrium - The cell swells with the extra water.
- Animal cells may swell so much, they may burst
(especially in pure water) - Plant cells cell swells and membrane pushes
against the cell wall - Like celery in water crisp/ rigid from pressure
on cell walls
15
Hypertonic Solutions - hyper higher
- solute is higher outside of the cell.
- Less water outside the cell, more inside. Water
moves out of the cell. - Animal cells shrivel because of water loss.
- Plant cell membranes move away from cell wall as
water moves out. - Why plants wilt.
16
Other Forms of Transport
- Active Transport (needs energy)
- Large particle transport
- Endocytosis cell surrounds molecule(s), which
are then engulfed by cell - doesnt pass through membrane
- Exocytosis - expulsion/secretion of materials.
Opposite of endocytosis
17
Active Transport (cont)
- Movement of molecules against (up) the
concentration gradient - From areas of lower concentration to areas of
higher concentration - For instance, if a cell needs a high
concentration of something (that would normally
diffuse OUT of cell)
18
Summary!