Complement functions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Complement functions
Description:
Complement functions Host benefit: opsonization to enhance phagocytosis phagocyte attraction and activation lysis of bacteria and infected cells regulation of ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:123
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Complement functions
1
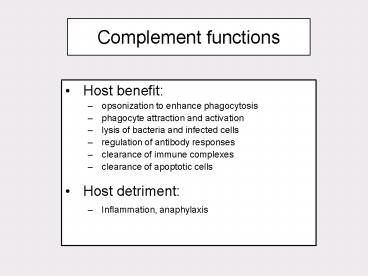
Complement functions
- Host benefit
- opsonization to enhance phagocytosis
- phagocyte attraction and activation
- lysis of bacteria and infected cells
- regulation of antibody responses
- clearance of immune complexes
- clearance of apoptotic cells
- Host detriment
- Inflammation, anaphylaxis
2
Proteins of the complementsystem (nomenclature)
- C1(qrs), C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9
- factors B, D, H and I, properdin (P)
- mannose binding lectin (MBL), MBL associated
serine proteases (MASP-1 MASP-2) - C1 inhibitor (C1-INH, serpin), C4-binding protein
(C4-BP), decay accelerating factor (DAF),
Complement receptor 1 (CR1), protein-S
(vitronectin)
3
Pathways of complement activation
LECTIN PATHWAY
CLASSICAL PATHWAY
ALTERNATIVE PATHWAY
4
Components of the Classical Pathway
C4
C2
C3
C1 complex
5
Classical Pathway Generation of C3-convertase
C4
6
Classical Pathway Generation of C3-convertase
C2
C4a
_____ C4b2a is C3 convertase
Mg
C4b
7
Classical Pathway Generation of C5-convertase
C2b
C4a
________ C4b2a3b is C5 convertase it leads into
the Membrane Attack Pathway
Mg
C3
C4b
8
Lytic pathway
Generation of C5 convertase leads to the
activation of the Lytic pathway
9
Components of the lytic pathway
C6
C5
C 9
10
Lytic pathwayC5-activation
C5
11
Lytic pathwayassembly of the lytic complex
C6
12
Lytic pathwayinsertion of lytic complex into
cell membrane
C 9
C 9
C 9
C 9
C 9
C 9
C 9
C 9
C 9
13
Biological Activities of Classical Pathway
Components
Component Biological Activity
C2b Prokinin cleaved by plasmin to yield kinin, which results in edema
C3a Anaphylotoxin can activate basophils and mast cells to degranulate resulting in increased vascular permeability and contraction of smooth muscle cells, which may lead to anaphylaxis
C3b Opsonin Activation of phagocytic cells
C4a Anaphylaotoxin
C4b Opsonin
14
Components of thealternative pathway
D
C3
B
P
15
Spontaneous C3 activation
Generation of C3 convertase
D
H2O
B
C3
C3
C3iBb complex has a very short half life
16
C3-activationthe amplification loop
If spontaneously-generated C3b is not degraded
D
B
C3
17
C3-activationthe amplification loop
D
B
C3
C3a
C3a
18
C3-activationthe amplification loop
C3a
C3a
C3a
19
C3-activationthe amplification loop
C3a
C3a
C3a
20
C5-convertase of the two pathways
C5-convertase of the Classical and lectin Pathways
C5-convertase of the Alternative Pathway
Bb
C3b
C3b
21
Biological effects of C5a
22
Biological properties of C-activation products
23
Biological properties of C-activation products
24
Opsonization and phagocytosis