Circulatory ( or cArdiovascular) System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Circulatory ( or cArdiovascular) System
Description:
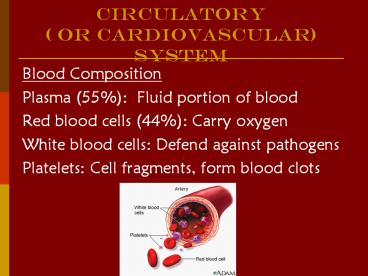
Circulatory ( or cArdiovascular) System Blood Composition Plasma (55%): Fluid portion of blood Red blood cells (44%): Carry oxygen White blood cells: Defend against ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:194
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Circulatory ( or cArdiovascular) System
1
Circulatory ( or cArdiovascular) System
- Blood Composition
- Plasma (55) Fluid portion of blood
- Red blood cells (44) Carry oxygen
- White blood cells Defend against pathogens
- Platelets Cell fragments, form blood clots
2
Red Blood Cells
- Hemoglobin Iron-containing molecule
- Loosely binds O2 in lungs (high concentration)
- Releases O2 in body tissue (low concentration)
- Shape of RBCs allows them to travel through
narrow capillaries more easily
3
Red Blood Cell Lifespan
- Produced in the marrow
- Only type of body cell without a nucleus
- Old RBC destroyed in liver, spleen
- Average lifespan 120 days
4
Blood Types
- RBC Marker Proteins
- A- A protein
- B- B protein
- AB- both A and B proteins
- O neither A nor B proteins
- Another marker protein is Rh factor.
- Rh has Rh factor Rh - no Rh factor
- Immune system produces antibodies against foreign
antigens (any protein etc. not produced in the
body) - AB is the universal receipient
- O is the universal donor
5
Blood Vessels
- Arteries ? Arterioles (thinner arteries) ?
- Capillaries ? Venules (thinner veins) ? Veins
- Arteries
- Carry blood away from the heart
- Most arteries contain oxygenated blood
- Blood is under greater pressure (most arteries
protected deeper within body) - Thick walled vessels
- Muscular walls expand/ contract to help move blood
6
Capillaries Site of Gas/Nutrient Exchange
- Microscopic blood vessels
- Lining is 1 cell thick
- Allows oxygen and nutrients to diffuse into body
cells - Waste from cells diffuses into blood
7
Veins
- Carry blood back to the heart
- Most veins carry deoxygenated blood
- Since many veins travel against gravity,
- equipped with one-way valves to prevent back-ups
Artery Thicker layer of smooth muscle
Vein One way valves
8
(No Transcript)
9
Heart
- Mainly cardiac muscle
- Cells have numerous mitochondria
- Mammalian hearts have 4 chambers
- 2 Upper Chambers Atria
- Receiving chambers
- 2 Lower Chambers Ventricles
- Pump blood out of heart
- Left and right sides separated by solid wall
(septum) to create two pumps
10
Video on Flow of Blood in the Heart click once
to start video
http//www.youtube.com/watch?vgn6QmETEm8s
11
VideoBlood Flow through the Body
https//www.youtube.com/watch?vPgI80Ue-AMo
12
Pathway of Blood
- Oxygen poor blood returning from body enters
right atrium - Right atrium ? right ventricle ?
- pulmonary artery ? lungs ?
- pulmonary vein ? left atrium ?
- left ventricle ?aorta ? arteries
- ? capillaries ? veins ?
- vena cavae
13
Amphibians and reptiles have a 3 chambered heart
rather than four chambered heart, which allows
mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Mammals and birds have a four chambered heart
which keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
separated and allows for more efficient transport
of oxygen. Discuss with your table partner why
amphibians (such as frogs) and reptiles (such as
crocodiles) do not require as efficient a heart
as mammals and birds.
14
Mammals and birds are warm-blooded
(endotherms.) A large expenditure of energy
(ATP) is used to keep the body warm. This ATP is
provided by cellular respiration, which requires
both food and oxygen. Endotherms require a
larger amount of both food and oxygen. Amphibians
and frogs are cold-blooded (ectotherms). Their
body temperature changes with the outside
temperature, and they do not require energy for
heating.
15
Heartbeat regulation
Region of heart called the sinoatrial node acts
as pacemaker, regulating the heart rate through
electrical impulses that spread through the
heart. Medulla oblongata regulates the
pacemaker, speeding or slowing the heart rate as
necessary.
16
Systolic and Diastolic Pressure
- Systolic pressure is the pressure exerted when
the heart beats. - Diastolic pressure is the lowest pressure, when
your heart relaxes between beats.