The Urinary System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
The Urinary System
Description:
Title: The Urinary System Author: meryl.bentley Last modified by: Stephanie Bolton Created Date: 11/29/2006 7:10:00 PM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:133
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Urinary System
1
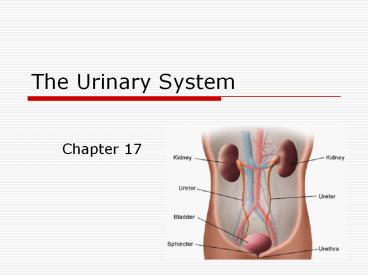
The Urinary System
- Chapter 17
2
Terminology
- Nephrology study of the S/F of the kidney
- Urology
- Males specialty of male urinary system
reproductive system - Females speciality of urinary system
- Dialysis (hemodialysis) removal of solutes from
urine artificially if kidneys are impaired - Incontinence lack of voluntary control of
bladder emptying
3
Dialysis
4
4 Functions of Urinary System
- Regulate blood volume composition (kidneys)
- Transportation of filtrate (ureters)
- Storage of urine (urinary bladder)
- Discharge of waste/excretion (urethra)
5
Kidneys - 2
- Sit above waist
- Back of abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal)
- Right kidney sits lower than left
- 4-5 inches long, 2-3 inches wide, 1 inch thick
bar of soap - Surrounded by adipose tissue
- Hilus where vessels enter/exit
6
Layers of the kidney
- Renal cortex (bark)
- Renal medulla (middle)
- Renal pyramids here
- Renal pelvis (inner)
- Funnel-shaped basin for draining urine
7
Basic Functioning Unit of Kidney
- The Nephron p. 474-475
- 2 parts
- Renal corpuscle (cortex) filtration
- Glomerulus
- Glomerular (Bowmans) capsule
- Renal tubules (cortex medulla) reabsorption
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting duct
8
The Nephron
9
Did you know
- Only 1 of what your kidneys filter is excreted
as urine - The other 99 is water and is reabsorbed to
prevent dehydration - Which hormones control this action??
10
Ureters - 2
- Transport urine from kidneys to urinary bladder
- Empty posteriorly and inferiorly into urinary
bladder
11
Urinary Bladder - 1
- For storage
- Capacity ¾ quart (600mL)
- Usually signals start at 150mL full
- Trigone area made by ureters and urethra
triangular area with no folds - Lots of folds to allow for stretching
- Do you remember what tissue makes up the urinary
bladder?
12
Urinary Bladder
13
Urination reflex
- To empty the bladder urination, voiding,
micturition - Spinal cord reflex
- Controlled by 2 sphincters (similar to defecation
reflex) - Internal sphincter released involuntarily when
bladder reaches a certain capacity controlled by
detruser muscle - External sphincter voluntarily controlled to
release urine when appropriate
14
Urethra - 1
- Tube that discharges urine from body
- Terminal end urinary meatus
- In males, it also dicharges semen
15
Urinalysis
- Analysis of volume, physical, chemical
microscopic urine properties - Normal characteristics
- 95 water
- Volume 1-2L (varies with fluid intake)
- Color yellow/amber ? clear
- Turbidity clear/transparent
- Odor after time, mild ammonia
- pH 4.6 8.0 (varies with fluid intake)
- Specific gravity/density 1.001 1.0035
(slightly more dense than water 1) - Normal solutes urea, uric acid, amino acids
16
Urinalysis continued
- Abnormal solutes
- Albumin (protein) (proteinuria)
- Glucose
- Ketones (ketonuria)
- Blood (hematuria)
- Stones
17
Disorders
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) bacterial
infection in any part of the urinary system - Cystitis infection of urinary bladder
- Nephritis infection of kidney (nephron)
- Polyuria increased urine production
- Nocturia increased urine output at night
- Dysuria painful urination often associated with
UTIs and STDs - Uremia/uremic poisoning toxic levels of urea in
the blood due to kidney failure