Class Starter - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
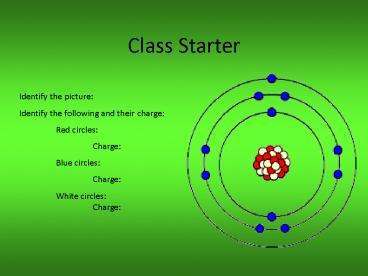
Title: Class Starter
1
Class Starter
Identify the picture Identify the following and
their charge Red circles Charge Blue
circles Charge White circles Charge
2
- The Nature of Matter
- Chapter 2.1
3
Biochemistry Basics
- What is biochemistry?
- ?The study of the chemical substances and vital
processes occurring in living organisms
4
Matter
- Matter
- ?anything that has mass and takes up space
- Atom the smallest unit of matter
- Atoms make up elements
5
Atoms
- Overall charge of an atom is neutral
- Nucleus the center of an atom
- Composed of protons and neutrons
- Protons
- ?positively charged subatomic particle
- Neutrons
- ?neutral/charge-less subatomic particle
6
Atoms
- Electron orbitals areas surrounding nucleus
where the probability of finding an electron is
greatest - ? also called electron clouds, energy
- levels, and electron shells
- Electrons negatively charged subatomic particle
7
Atom Anatomy
8
(No Transcript)
9
Isotopes
- ?Atoms of the same element containing different
numbers of neutrons in the nucleus - Some give off radiation used to
- Trace atoms through a reaction or an organism
- Treat cancer
- Date very old, once living organisms
10
Nonradioactive carbon-12
Nonradioactive carbon-13
Radioactive carbon-14
6 electrons 6 protons 6 neutrons
6 electrons 6 protons 7 neutrons
6 electrons 6 protons 8 neutrons
11
Review
- How is matter and atoms related?
- What are the 3 subatomic particles?
- Where are they located?
- What are their charges?
- What is a benefit to an isotope?
- How many electrons go on each energy level?
12
Periodic Table
- Organized table that shows all of the elements
13
Atomic Number
- Atomic number number at top of each box
?represents the number of protons or electrons in
the atom
14
Atomic Mass
- Atomic Mass
- ?the average weight of all the isotopes of a
specific element - found at the bottom of the box
15
Drawing An Atom
- Step 1 Look at the atomic number and figure out
how many protons are in the nucleus and how many
electrons are floating around
16
Drawing An Atom
- Step 2 Find the atomic mass and subtract from
it the atomic number ? this will give you the
number of neutrons in the nucleus
17
Drawing An Atom
- Step 3 Put the protons and neutrons in the
nucleus - Step 4 Put electrons in orbitals
- 2 electrons can fit in the first orbital
- 8 electrons can fit in the second and third
orbital
18
Drawing An Atom
- Step 4 (Contd) Always fill the electron
orbitals from inside out until all of the
electrons are used - Hint As you are inserting your electrons, make
pairs of electrons in the orbitals
19
Molecules
- Occurs when atoms combine together by a covalent
bond - Covalent bond forms when electrons are shared
between atoms - Ex Water
- ? Bonds are where energy is stored
- Why do they combine?
- To make all outer energy levels full of electrons
20
(No Transcript)
21
Compounds
- A substance composed of two or more atoms of
different elements joined by a chemical bond in
definite proportions
22
Ionic Bond
- Bond that forms when atoms either take electrons
from or give away their electrons to other atoms
23
Ions
- Atoms that have lost or gained electrons
- ?cation positively charged ion lost electrons
- ?anion negatively charged ion gained
electrons - Weaker than covalent bonds
- Hold less energy in the bond
24
Figure 2-3 Ionic Bonding
Section 2-1
Sodium atom (Na)
Chlorine atom (Cl)
Sodium ion (Na)
Chloride ion (Cl-)
Transfer of electron
Protons 11 Electrons -11 Charge 0
Protons 17 Electrons -17 Charge 0
Protons 11 Electrons -10 Charge 1
Protons 17 Electrons -18 Charge -1
25
Figure 2-3 Ionic Bonding
Section 2-1
Sodium atom (Na)
Chlorine atom (Cl)
Sodium ion (Na)
Chloride ion (Cl-)
Transfer of electron
Protons 11 Electrons -11 Charge 0
Protons 17 Electrons -17 Charge 0
Protons 11 Electrons -10 Charge 1
Protons 17 Electrons -18 Charge -1
26
Van der Waals forces
- Attraction between oppositely charged areas of
adjacent molecules - ?weaker than covalent bonds and ionic bonds
- Ex.- Geckos ability to cling to
- walls
27
Chemical Symbol
- Universal system to denote elements in the
periodic table - Example Oxygens symbol is O
28
(No Transcript)
29
Chemical Formula
- Chemical Formula a group of symbols which shows
the number and kind of each atom in a compound - The subscripts found within a formula tells you
the number of atoms of each element in that
compound - ?if there is no subscript, the number of atoms is
then assumed to be one - A number in front of the compound tells you how
many of that compound you have
30
Examples
- H2O2
- 3HCN
- C6H6
- 2C2H6