Raoults Law, Nonvolatile Solute - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
Raoults Law, Nonvolatile Solute
Description:
Ethanol and Hexane. polar and nonpolar molecules don't mix ... Would you expect an ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and methanol (CH3OH) mixture to be an ideal solution? ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1026
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Raoults Law, Nonvolatile Solute
1
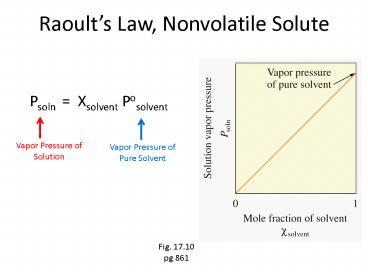
Raoults Law, Nonvolatile Solute
- Psoln Xsolvent Posolvent
Vapor Pressure of Solution
Vapor Pressure of Pure Solvent
2
Raoults Law, Two Volatile Components
- Components A and B in an ideal binary solution
- Ptotal PA PB XA PoA XB PoB
Remember XA XB 1
3
Two Volatile Components
Ideal solution A-A, B-B and A-B
interactions very similar (two molecules very
similar) ?Hsoln 0 Kind of like ideal gases.
Fig. 17.11 pg 863
4
Nonideal Solutions
Negative Deviation from Raoults Law Solvent and
solute have high attraction ?Hsoln is large,
negative (ex. hydrogen bonding occurs) A-B
stronger than A-A and B-B Tendency of solvent
molecules to escape is lowered
Fig. 17.11 pg 863
5
Nonideal Solutions
Positive Deviation from Raoults Law Solvent and
solute repel slightly ?Hsoln is positive A-B
weaker than A-A and B-B Increased tendency of
solvent molecules to escape
Fig. 17.11 pg 863
6
Examples
- Negative Deviation
- Acetone and Water solution
- (attractive H-bonding)
7
Example Question
- Would you expect an ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and
methanol (CH3OH) mixture to be an ideal solution?
- No, hydrogen bonding interactions cause a
negative deviation from Raoults law.
8
Boiling Point Elevation
- A solution has a lower vapor pressure than the
pure solvent (Psoln Xsolvent Posolvent) - Therefore, a solution has a ________ boiling
point than the pure solvent!
higher
9
(No Transcript)
10
Boiling Point Elevation
- We previously calculated change in vapor pressure
(Psoln Xsolvent Posolvent) - Now we calculate change in boiling point
Table 17.5
11
Example from Email
- What is the boiling point of a solution (1atm)
that was prepared by dissolving 20.0g of urea in
100.0g of water? - urea MW 60.07 g/mol
- water Kb 0.51 C kg/mol
12
Freezing Point Depression
- Solute molecules disturb solid-liquid equilibrium
and lower the freezing point
Figure 17.13 pg 866
13
Freezing Point Depression
- Adding salt to roads depresses the freezing
point, helping turn ice into water
14
Freezing Point Depression
- ?T is positive, even though temperature is lowered
15
Example from Email
- What mass of glucose must be added to 1.0 L of
water to produce a solution that freezes at -1.0
C? - glucose MW 180.2 g/mol
- water Kf 1.86 C kg/mol