Appendicular Skeleton - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 46
Title:
Appendicular Skeleton
Description:
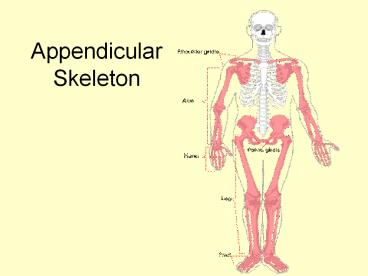
Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of the limbs and bones that anchor the limbs to the axial skeleton. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:93
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Appendicular Skeleton
1
Appendicular Skeleton
2
Appendicular Skeleton
- The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones
of the limbs and bones that anchor the limbs to
the axial skeleton. - Pectoral girdle scapula, clavicle.
- Upper limbs humerus, radium, ulna, carpals,
metacarpals, phalanges. - Pelvic girdle coxal bones.
- Lower limbs femur, tibia, fibula, patella,
tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges.
3
Figure 7.42
4
Pectoral Girdle
- Clavicles collar bones that attach the sternum
to the shoulder anteriorly. - Scapulae shoulder blades with two processes.
- Acromion process tip of the shoulder.
- Coracoid process attaches to the clavicle and
provides attachments for muscles. - Glenoid fossa articulates with the humerus.
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
Upper limb
- Humerus upper arm bone, articulates with the
glenoid fossa of the scapula
9
(No Transcript)
10
1
2
3
4
5
8
6
9
7
11
Upper limb cont.
- Radius thumb side of the forearm, articulates
with the capitulum of the humerus and the radial
notch of the ulna - Ulna longer bone of the forearm, olecranon and
coronoid processes articulate with the humerus
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
Hand
- Carpal bones eight small bones of the wrist.
- Metacarpal bones five bones, the framework of
the palm. - Phalanges finger bones, three in each finger
(proximal, middle, distal phalanx), two in the
thumb.
16
(No Transcript)
17
Figure 7.47
18
Pelvic Girdle
- Coxal bones two hips bones composed of three
fused bones. - Ilium superior part of the coxal bone.
- Ischium lowest portion of the coxal bone.
- Pubis anterior part of the coxal bone. The two
pubic bones joint at the symphysis pubis.
19
Figure 7.49
Iliac crest
(bone) Pubis
Obturator foramen
20
(No Transcript)
21
Figure 7.49
22
(No Transcript)
23
Superior iliac notch
Inferior iliac notch Pubic tubercle
Lesser sciatic notch
24
Male and Female Pelvis
- Female iliac bones are more flared. Hips are
wide - female pubic arch angle is greater.
- The sacral curvature is shorter and flatter.
25
- greater distance between the ischial spines and
tuberosities in the female. - The differences create a wider pelvic cavity in
all diameters - Larger pelvic brim
26
WHY???
27
Figure 7.51
28
Lower Limb
- Femur thigh bone, longest bone
- Patella kneecap, located in a tendon, femur,
tibia, and patella form the knee joint - Tibia shinbone, lateral malleolus forms the
ankle - Fibula slender bone lateral to the tibia, not
part of the knee joint
29
Figure 7.52
30
Linea aspera (posterior)
Popliteal surface
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
(No Transcript)
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
- Osgood schlatter disease
- Swelling of bony projection of tibia below knee
- Due to over use of thigh muslces
- More common in teens b/c of rapid bone growth
38
(No Transcript)
39
(No Transcript)
40
(No Transcript)
41
Foot
- Tarsal bones seven small bones in the ankle. The
calcaneus (heel bone) is the largest, located
below the talus. - Metatarsal bones elongated bones that form the
arch of the foot. - Phalanges each toe has three except the great
tow which has two.
42
1
2
3
4
5
43
Figure 7.55
44
- Tarsus and metatarsus arranged and bound by
ligaments to form arch - Plantar fascitis flat foot fallen foot
- Weakened tissue, constant or heavy weight applied
to foot
45
Life-Span Changes
- Calcium levels fall through life and the skeleton
loses strength. - Osteoclasts outnumber osteoblasts.
46
Life-Span Changes
- By age 35, everyone loses bone mass. Women lose
bone mass faster between menopause and age
seventy. - Trabecular bone is lost before compact bone.