Bilateria PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
The most primitive of all the phyla. Mesoderm is called parenchyma. Has no anus. Nerve system connected to brain. Primitive kidneys. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Bilateral Symmetry mirror images found ... especially the sessile sea-lilies and in annelids known as feather-dusters, etc. ... Annelid worms. Series Circuit ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Phylum Platyhelmenthes (the flatworms) General characteristics Eumetazoa - animals with tissue Bilateria - have bilateral symmetry Head end-cephalization
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... (Radiata): phyla Cnidaria Grade II (Bilateria): all other phyla Division A (Protostomia): Mouth is first opening Subdivision of Protostomes by coelom formation: ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Kingdom Animalia - Diversity Metazoa Parazoa Eumetazoa Radiata Bilateria Where does Tricoplax adhaerens (Phylum Placozoa) belong? Older Phylogenetic Tree ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
A Deuterostomia eredete Protostomia ( ssz j ak) Deuterostomia ( jsz j ak) utols k z s s (utols k z s Bilateria s) a blastoporus sorsa az ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
2. Eumetazoans branch into radiata and bilateria. Symmetry. Cephalization in bilateria. All bilateria have 3 germ layers. 11/26/09. 6. 11/26/09. 7 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... an echinoderm (sea urchin) embryo. Sea urchin development, from ... 47.11 Gastrulation in a sea urchin embryo. 32.8 Body plans of triploblastic bilateria ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The vast majority of animal species belong to the clade Bilateria, which ... Phylum Mesozoa is considered a 'missing link' between protozoa and metazoa. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Flatworms, Mesozoans, and Ribbon Worms Chapter 14 * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Bilateria Most animals have bilateral symmetry. The vast majority of ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
sea stars - sea cucumbers - sea urchins. II. Animal Diversity. C. Bilateria ... filter feeders (Sea Lily), herbivores (sea urchins), predators (sea stars) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Scientific Classification. What's In a Name?? What are some ways you are classified? ... Bilateria dichotomy: Cnidaria (hydra; jellyfish'; sea anemones) & Ctenophora ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Fig. 32-2-3 Zygote Cleavage Eight-cell stage Cleavage Blastula Cross section of blastula Blastocoel Gastrulation ... Cleavage (b) Coelom formation Coelom Key Ectoderm ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Chapter 32 Author: sean reagin Last modified by: administrator Created Date: 5/13/2002 10:56:18 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cartilaginous fish (Class: Chondrichthyes) also efficient paired fins - sharks - skates, rays - ratfish. II. Animal Diversity. 3. Vertebrata. c. Jawed Fishes ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Jellyfish - Anemones. II. Animal Diversity. B. Radiata Cnidarians. 1. Diversity - Hydras ... Jellyfish - Anemones - Corals. II. Animal Diversity. a. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Subkingdom Eumetazoa (all the other phyla) - The Eumetazoa ... animals have an oral (top) and aboral (bottom) side, but no front, back, left or right sides. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Filter food from water pumped through porous bodies nearly all are ... Any imaginary slice through the central axis would divide the animal into mirror ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
An introduction to animal diversity BY Carlos Paez
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Animal Bauplan Symmetry and complexity Chapter 3: Animal Architecture * * * * * * * * * * * * III. Symmetry Radial symmetry: body parts organized about a center axis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Slide 1 Author: ettz Last modified by: Elena Tasheva-Terzieva Created Date: 10/7/2004 10:34:57 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
A team at Celera Genomics sequenced by exon-specific polymerase ... The phylum contains four classes (examples), including jellyfish, sea anemone and hydra ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Animal Physiology
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Animal Physiology By the end of this class you should understand: The system and mechanics of determining how organisms are related How to arrange animals on a ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
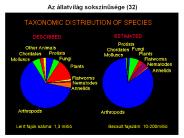
Az llatvil g soksz n s ge (32) Le rt fajok sz ma: 1,3 milli Becs lt fajsz m: 10-200milli Legkor bbi llati fossz li k: Ediacara fauna (600 milli ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 33 Invertebrates
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Animal Evolution I. Animal traits A. Heterotrophic B. Mobile C. Lack cell walls D. Possess nerve and striated muscle D. Reproduces sexually 1.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Practice Questions for Exam 1 Reproduction that occurs when a portion of a parent splits off to form a new individual is a. Asexual b. Budding c. Sexual
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
1. First key branch was between eumetazoan(tissues) and parazoan(no tissues) ... Coelom formation. Fate of blastopore. 9/13/09. 8. 9/13/09. 9. 9/13/09. 10. 9/13/09. 11 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Hydras - Jellyfish - Anemones - Corals. II. Animal Diversity. B. Radiata ... Hydra and jellies alternate between polyp and medusa stages; coral and anemones ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Phylogeny and Systematics Author: Nancy Wheat Last modified by: NANCY WHEAT Created Date: 2/11/2006 3:37:02 AM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Evolution in the Fossil Record and Molecular Clocks
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... (4,500 species) Ectoprocts A brachiopod Brachiopoda (335 species) Rotifera (1,800 species) A rotifer (LM) A ctenophore, or comb jelly Ctenophora ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
El concepto de la vida animal Presentaci n 2 No est basado en ning n cap tulo del libro de texto Dr. Robert J. Mayer Arzuaga UPR en Aguadilla
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Evolution 26.16 Our changing view of biological diversity 26.1 Some major episodes in the history of life. Note that molecular ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Introduction to Kingdom Animalia. Defining Animals. 1. Animals are multicellular, ... 2. Animals generally store their carbohydrate reserves as glycogen ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... protostome Table 33.2 Classes of Phylum Platyhelminthes Figure 33.10 Anatomy of a planarian Figure 33.12 Anatomy of a ... Nematoda Roundworms ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Fig. 26-3 Species: Panthera pardus Genus: Panthera Family: Felidae Order: Carnivora Class: Mammalia Phylum: Chordata Kingdom: Animalia Archaea Domain: Eukarya
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Body Plan of Cnidarians. Nematocysts Capture Prey. Cnidarian Life Cycle ... Summary of Cnidarian Characteristics. Radial symmetry. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Geografia Agr ria Agricultura e com rcio mundial de alimentos Professor: Ricardo Ribeiro Revolu o tecno-cient fica A biotecnologia se aprofundou na intera o ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Slide 1 ... Evo.....
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Reproductive system is not well understood: Only female reproductive organs have been identified. ... Pigs become infected by eating grubs.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
GROUPED INTO ABOUT 35 PHYLA. MOST ARE AQUATIC. MOST FAMILIAR PHYLUM CHORDATA ... ECHINODERMATA (SEA URCHIN) EXCEPTION. GERM LAYERS ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
To introduce you to several characteristics found in animals and the range of ... Pisces (fishes) Amphibia frogs newts etc (smooth skin) Reptiles lizards ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Outline Evolutionary Relationships Acoelomates (sort of ) Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nemertea Gnathiferans Phylum Rotifera Phylum Acanthocephala
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... Evolution of nervous systems * Why study the evolution of nervous systems Curiousity May provide fundamental insights into nervous system function and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
coelom. 6. Broad Groupings of Kingdom Animalia. 7. Key Transitions ... Coelom poses circulation problem. solved by circulatory system. open circulatory system ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
ANIMALIA Domain Eukarya, Kingdom Animalia Linnaeus classification: 2 Kingdoms (mid-1700s) Whittaker classification: 5 Kingdoms (1959) http://coralreefwatch.noaa.gov/ ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL DIVERSITY Chapter 32 Our Kingdom We are Animals Animals Are Species-rich Morphologically diverse lineage of multicellular organisms on the tree ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Figure 32.0 Coral Reef. Figure 32.1 Early embryonic development (Layer 1) ... Figure 32.3 One hypothesis for the origin of animals from a flagellated protist ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
These animals are also triploblastic they have three embryonic germ layers. Organ-system level of organization more division of labor among their organs.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Phylogeny of basal animal groups (character mapping) Choanoflagellates ... 2. For the 'alternative phylogeny,' dashes at the same level imply the need for ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
INTRODUCTION TO THE ANIMAL KINGDOM Common Patterns and Development in Animals What Are Animals? Animals are multicellular Eukaryotic Heterotrophic by ingestion ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Animal Evolution The Basics Animals = multicellular, heterotrophic Life history: Sexual w/ flagellated sperm/nonmotile egg Development: cleavage, blastula, gastrula ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Slide 1 ... Evo.....
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download