SNAP OPTICS PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title: SNAP OPTICS
1
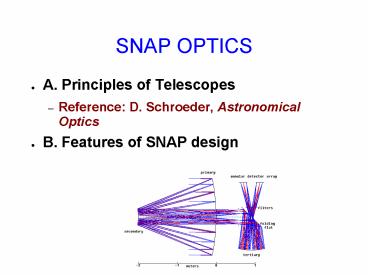
SNAP OPTICS
- A. Principles of Telescopes
- Reference D. Schroeder, Astronomical Optics
- B. Features of SNAP design
2
Two descriptions
- Geometric Optics
- Ray Tracing
- Physical Optics
- Diffraction (wave properties)
3
Fundamental Laws of Optics
?1
?i
?o
n1
n2
?2
?i ?o
n1sin ?1 n2sin ?2
Mirror
Snell's Law (Lenses)
4
Simple Lens
5
Simple Designs
Newtonian (parabolic mirror)
Cassegrain (hyperbolic secondary)
Perfect images on-axis
6
Aberrations
- Spherical
- On-axis
- Symptom Light from edge of mirror has different
focus from center - Cause Spherical mirror or lens
- Cure Parabolic Primary
Aberrations are reduced by adjusting surface
shapes, element spacings, other free parameters
in a design.
7
Aberrations
- Coma
- Off-axis, limits useful field of view
- Symptom Light from edge of mirror has offset
focus from center - Cause Parabolic Primary
- Cure Hyperbolic Primary Secondary mirror
(Ritchey-Chretien)
8
Aberrations
- Astigmatism
- Off-axis, limits useful field of view
- Symptom Light from top, bottom of mirror have
offset focus from left, right - Cause
- Cure Corrector lens or extra mirror
9
Additional Aberrations
- Distortion
- Can't map a sphere onto a plane
- Field Curvature
- Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration (lenses only)
- Latitudinal Chromatic Aberration (lenses only)
10
SNAP Design
Features 1. Three mirrors, all conics (no 6th
order) 2. Intermediate image plane allows
insertion of folding flat 3. Flat focal plane 4.
Focal Length 21783 mm Focal ratio 10.9
Scale 9.398 arcsec/mm FOV 0.75 degrees
CCD PIXEL SIZE 0.1"
11
Fundamental of PhysicalOptics
Exit pupil is image of primary mirror as seen at
the focal plane.
Image intensity at focal plane is Fourier
transform of wavefront error f integrated over
exit pupil.
Perfect exit pupil (f0) Intensity J1(v)/v
where vpr/(f?)
Airy disk 1st dark ring at r1.22?/D SNAP
0.063" for B filter
12
SNAP Diffraction
Wavefront error r 283 mm
Exit Pupil
Image (closeup)
Image (wide field)
13
PSF (Point Spread Function)factors
- Optical Design (aberrations and diffraction)
- Fabrication errors
- Surface roughness
- Optics cleanliness
- Collimation
- Atmospheric seeing (ground only)
- Filter characteristics (ghosting)
- Detector characteristics
14
SNAP Focal Plane
15
Optical Design Software
- Windows
- Zemax
- Oslo (Free, useful version available!)
- Code V
- Linux/Unix
- trace (snap.fnal.gov gt calibrations)