Functional Groups PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title: Functional Groups
1
Functional Groups
2
Functional Groups
- Functional group - a specific arrangement of
atoms in an organic compound, that is capable of
characteristic chemical reactions. - The symbol R is used to represent any carbon
chains or rings (i.e. the REST of the compound)
3
Functional Groups
- Most organic chemistry involves substituents
- often contain O, N, S, or P
- also called functional groups- they are the
chemically functional part of the molecule, and
are the non-hydrocarbon part
4
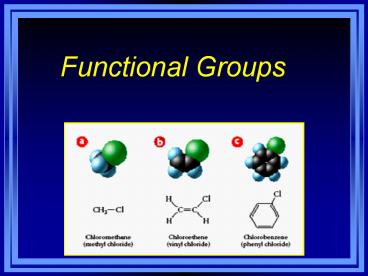
Halogen Substituents
- Halocarbons - class of organic compounds
containing covalently bonded fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, or iodine - General formula R-X (X halogen)
- CH3-I Iodomethane
- CH3CH2Br Bromoethane
5
Alcohols
- Alcohols - a class of organic compounds with an
-OH group - The -OH functional group in alcohols is called a
hydroxyl group thus R-OH is the formula - How is this different from the hydroxide ion?
(covalent bonding with the carbon- not ionic with
a metal like bases)
6
Alcohols
- Naming
- drop the -e ending of the parent alkane name add
ending of -ol, number the position of OH - The one carbon alcohol, CH3-OH is called methyl
alcohol or methanol
7
Alcohols
8
Alcohols
- Phenols - compounds in which a hydroxyl group is
attached directly to an aromatic ring (benzene).
9
Properties of Alcohols
- Much like water, alcohols are capable of hydrogen
bonding between molecules - they will boil at a higher temp. than alkanes and
halocarbons with a comparable number of atoms
10
Properties of Alcohols
- Alcohols are derivates of water the -OH comes
from water, and are somewhat soluble - the longer carbon chain the more non-polar the
molecule which makes it less soluble in water.
11
Properties of Alcohols
- Many aliphatic alcohols used in laboratories,
clinics, and industry - Isopropyl alcohol (2-propanol) is rubbing
alcohol used as antiseptic, and a base for
perfume, creams, lotions, and other cosmetics - Ethylene glycol (1,2-ethanediol) - commonly sold
as antifreeze
12
Properties of Alcohols
- Glycerol (1,2,3-propanetriol) - used as a
moistening agent in cosmetics, foods, and drugs
also a component of fats and oils - Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) CH3CH2OH used in the
intoxicating beverages also an important
industrial solvent
13
Properties of Alcohols
- Denatured alcohol- means it has been made
poisonous by the addition of other chemicals,
often methyl alcohol (methanol, or wood alcohol).
We use denatured alcohol in lab!!!! - As little as 10 mL of methanol has been known to
cause permanent blindness, and 30 ml has
resulted in death!
14
Ethers
- An ether is a class of organic compounds in which
oxygen is bonded to 2 carbon groups - R-O-R is formula
- Naming? The two R groups are alphabetized, and
followed by ether
15
Ethers
- Diethyl ether is the one commonly called just
ether - was the first reliable general anesthetic
- dangerous- highly flammable, also causes nausea
- ethers are fairly soluble in water
16
Aldehydes and Ketones
- An oxygen can also be bonded to a single carbon
by a double bond - The CO group is called the carbonyl group
- it is the functional group in both aldehydes and
ketones
17
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Aldehydes - carbonyl group always joined to at
least one hydrogen (meaning it is always on the
end!) - -e ending replaced by -al, such as methanal,
ethanal
18
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Ketones - the carbon of the carbonyl group is
joined to two other carbons (meaning it is never
on the end) - ending of one such as propanone, 2-pentanone,
3-pentanone
19
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Neither can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds,
thus a much lower b.p. than corresponding
alcohols - wide variety have been isolated from plants and
animals possible fragrant odor or taste many
common names
20
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Benzaldehyde
- Cinnamaldehyde
- Vanillin
- Methanal (the common name is formaldehyde)
- 40 in water is formalin, a preservative
21
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Propanone (common acetone) is a good solvent
miscible with water in all proportions - why is it a good substance used in nail-polish
removers? (a powerful solvent-able to dissolve
both polar nonpolar)
22
The Carboxylic Acids
- A Carboxyl group has a carbonyl group (CO)
attached to a hydroxyl group (-OH) formula
R-COOH - weak acids (ionize
slightly) - Named by replacing -e with -oic and followed by
the word acid - methanoic acid ethanoic acid
23
Carboxylic Acids
- Abundant and widely distributed in nature, many
having a Greek or Latin word describing their
origin - acetic acid (ethanoic acid) from acetum, meaning
vinegar - Many isolated from fats are called fatty acids
24
The Esters
- Esters formula RCOOR
- Condensation reaction
- carboxylic acid alcohol ? ester water
- usually a trace of mineral acid added as catalyst
(because acids are dehydrating agents) - many esters have pleasant, fruity odors- banana,
pineapple, perfumes
25
Esters
- Although polar, they do not form hydrogen bonds
thus, much lower b.p. than the hydrogen-bonded
carboxylic acids they came from
26
Esters
- Naming? It has 2 words
- remove the -ic acid, add -ate
27
Functional Group Review
28
Polymers
- Polymers are giant molecules, not small like the
ones studied earlier in this chapter - examples are plastics
- Polymer- large molecule formed by the covalent
bonding of smaller molecules called monomers
29
Polymers from Monomers
30
Addition Polymers
- An addition polymer forms when unsaturated
monomers react to form a polymer - ethene will form polyethylene
- polyethylene is easy to clean, chemically
resistant- milk bottles, plastic wrap,
refrigerator dishes
31
High Density Polyethylene
32
Addition Polymers
- Polypropylene is a stiffer polymer, used in
utensils and containers - Polystyrene is formed from styrene
(phenylethene), and is a poor heat conductor
(styrofoam Dow Chemical) - molded coffee cups and picnic coolers, insulates
homes - Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) used for pipes in
plumbing
33
Addition Polymers
- Polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE, or teflon DuPont)
is very resistant to heat and chemical corrosion - found on nonstick cookware coating on bearings
and bushings used in chemical reactors
34
Condensation Polymers
- Condensation polymers are formed by the
head-to-tail joining of monomer units - usually accompanied by the loss of water from the
reacting monomers, and forming water as a product
35
Condensation Polymers
- Ex polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- Dacron ( DuPont), Fortrel ( Wellman),
Polyesters permanent press clothing, tire cords - Sheets of polyester called Mylar ( DuPont), used
as magnetic tape in tape recorders and computers,
as well as balloons - Nylon carpet, fishing line, hosiery
36
Condensation Polymers
- Examples
- aromatic rings form Nomex ( DuPont), which is a
poor electrical conductor makes parts for
electrical fixtures flame resistant clothing for
race car drivers flame resistant building
materials - Kevlar ( DuPont) strong and flame resistant
37
Plastic container code system.
38
What Do the Numbers Mean?
- 1 -- PETE (Polyethylene terephthalate)
- PET (or PETE) is used in the production of soft
drink bottles, peanut butter jars... - PET can be recycled into fiberfill for sleeping
bags, carpet fibers, rope, pillows...
39
What Do the Numbers Mean?
- 2 -- HDPE (High-density polyethylene)
- HDPE is found in milk jugs, butter tubs,
detergent bottles, motor oil bottles... - HDPE can be recycled into flower pots, trash
cans, traffic barrier cones, detergent bottles...
40
What Do the Numbers Mean?
- 3 -- V (Polyvinyl chloride)
- PVC is used in shampoo bottles, cooking oil
bottles, fast food service items... - PVC can be recycled into drainage and irrigation
pipes...
41
What Do the Numbers Mean?
- 4 -- LDPE (Low-density polyethylene)
- LDPE is found in grocery bags, bread bags, shrink
wrap, margarine tub tops... - LDPE can be recycled into new grocery bags...
42
What Do the Numbers Mean?
- 5 -- PP (Polypropylene)
- PP is used in most yogurt containers, straws,
pancake syrup bottles, bottle caps.... - PP can be recycled into plastic lumber, car
battery cases, manhole steps...
43
What Do the Numbers Mean?
- 6 -- PS (Polystyrene)
- PS is found in disposable hot cups, packaging
materials (peanuts), and meat trays... - PS can be recycled into plastic lumber, cassette
tape boxes, flower pots...
44
What Do the Numbers Mean?
- 7 -- Other
- This is usually a mixture of various plastics,
like squeeze ketchup bottles, "microwaveable"
dishes...
45
Timeline of Plastics
1862 First man-made plastic 1866 Celluloid
makes its debut 1891 Rayon is discovered 1907
Bakelite is invented 1913 Cellophane causes
the plastics craze
46
Timeline of Plastics
1926 PVC is invented 1933 Polyethylene is
discovered 1933 Saran makes its debut 1938
Teflon is discovered 1939 Nylon stockings hit
market 1957 Here comes velcro