Single Slit Diffraction - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Single Slit Diffraction
Description:
For the converse, no phase change occurs! See full discussion in the text book. Newton's Rings ... For the converse, no phase change occurs! Non-Glare Lenses ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:403
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Single Slit Diffraction
1
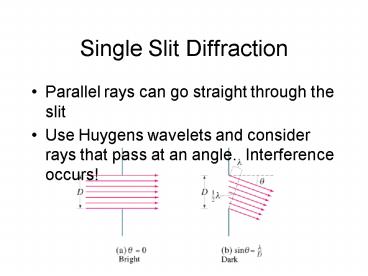
Single Slit Diffraction
- Parallel rays can go straight through the slit
- Use Huygens wavelets and consider rays that pass
at an angle. Interference occurs!
2
Single Slit Diffraction
- Keep looking for combinations that are either
half a wavelength or a full wavelength apart
3
Single Slit Interference
4
Diffraction Grating
- Many slits close together gives maxima that are
sharper and thinner
5
Diffraction Grating
6
Spectroscopy
Look at the first spectrum maximas. Can
accurately measure the wavelengths from the size
of the angle using dsin? m? where m 1. We
know different substances have different spectra,
so we can identify by these spectra.
7
Thin Films
We can have constructive and destructive
interference depending on whether the difference
in path length is a wavelength or half a
wavelength. Since this will occur at different
distances for different colors, they will spread
by angle to get the maxima.
8
Newtons Rings
A beam of light reflected by a material index of
refraction is greater than that of the material
in which it is traveling changes phase by half a
cycle. For the converse, no phase change occurs!
See full discussion in the text book.
9
Newtons Rings
A beam of light reflected by a material index of
refraction is greater than that of the material
in which it is traveling changes phase by half a
cycle. For the converse, no phase change occurs!
10
Non-Glare Lenses
We want the rays reflected from the front of the
coating and the back of the coating to be a half
wavelength apart so they interfere destructively.
Clearly wavelength dependent, so only perfect at
one color, but close enough at others.
11
Interferometry
Use a half-silvered mirror so half the light is
reflected and half is transmitted. Moving the
mirror will constructive or destructive
interference. The pattern changes from one to
the other upon movement of a quarter wavelength
of the light. Enables very sensitive distance
measurements.
12
Polarization
- Refers to the orientation of the electric field
vector. - For normal light sources, the field direction is
random since we have a multitude of individual
atoms involved in the creation of the light - Any atoms light emission depends on the atoms
orientation and that is random
13
Polarization
- Some materials have a unique property of only
transmitting light with a particular orientation
of the electric field vector - These materials are called polarizers
14
Polarization
15
Polarization
A polarizer is light a slit that would allow the
rope to vibrate only with vertical polarization,
but not with horizontal polarization.
16
Polarization
Unpolarized light has the electric field vector
pointing in all possible orientations.
17
Polarization
- Resolve any arbitrary electric field vector into
components parallel and perpendicular to the
direction of polarization of the material.
18
Polarization
- Split the unpolarized light into parallel and
perpendicular components - Only the parallel is transmitted (half the
original)
19
Polarization
20
Polarization
- Light gets dimmer with each pass
21
Polarization
- Light reflecting from non-metallic surfaces tends
to get polarized in the plane parallel to the
surface - Polaroid sunglass block rays that are
horizontally polarized, and thus reduce glare
from light reflected from the pavement
22
Brewster Angle