The Hyperuricemia Cascade - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
The Hyperuricemia Cascade
Description:
Uric Acid, Hyperuricemia, and Gout _____ Uric acid (urate) end product of purine degradation – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:536
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Hyperuricemia Cascade
1
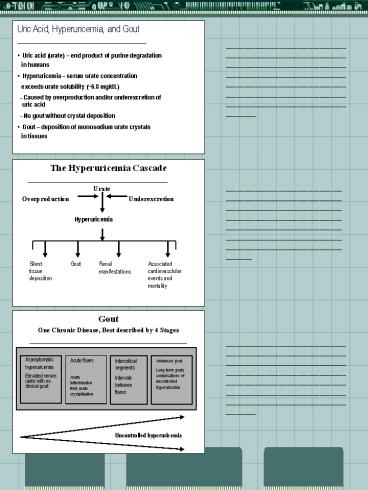
- Uric Acid, Hyperuricemia, and Gout
- __________________________________________________
__ - Uric acid (urate) end product of purine
degradation - in humans
- Hyperuricemia serum urate concentration
- exceeds urate solubility (6.8 mg/dL)
- - Caused by overproduction and/or
underexcretion of uric acid - - No gout without crystal deposition
- Gout deposition of monosodium urate crystals
- in tissues
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- The Hyperuricemia Cascade
- _________________________________________
-
Urate - Overproduction
Underexcretion
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________
Hyperuricemia
Silent tissue deposition
Gout
Renal manifestations
Associated cardiovasclular events and mortality
- Gout
- One Chronic Disease, Best described by 4 Stages
- ______________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia Elevated serum urate
with no clinical gout
Acute flares Acute inflammation from urate
crystallization
Intercritical segments Intervals between flares
Advanced gout Long-term gouty complications of
uncontrolled hyperuricemia
Uncontrolled hyperuricemia
2
How Silent Tissue Deposition Causes Acute
Flares ___________________________________________
_________ 1. Hyperuricemia leads to
extracellular accumulation of
urate 2. Urate crystals form 3.
Urate crystals deposit in joint(s)
4. Inflammatory process initiated 5.
Acute flare
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________
- Clinical manifestations
- Of an Acute Gout Flare
- ___________________________________________
- . Abrupt onset severe joint inflammation,
- often at night
- - Warmth, swelling, erythema, and pain
- - Fever may occur
- . Untreated initial attacks subside over 3-10
days - . 90 of first initial attacks are
monoarticular - - 50 podagra
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- Sites of Acute Flares
- ___________________________________________
- 1. 90 of gout patients eventually experience
- podagra
- - Acute flare in the first
metatarsophalangeal - (MTP) joint
- 2. Gout can also occur in other joints,
bursae, and tendors
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
3
- Intercritical Segments
- _____________________________________________
_ - Asymptomatic intervals between flares
- - Gout clinically inactive
- Disease, if untreated, may continue to advance
- - Intercritical segments may shorten over time
- - Crystals may still be found in asymptomatic
joints - - Uncontrolled hyperuricemia continues to
increase body - urate stores
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- Advanced Gout
- ________________________________
- . Uncontrolled hyperuricemia increases tissue
- urate stores
- . Deposition may progress to
- - Chronic arthritis
- - Radiographic changes
- - Development of tophi
- . Acute flares continue
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________
- Advanced Gout
- Chronic Arthritis and Acute Flares
- _______________________________________________
- . Chronic arthritis
- - Joints are persistently uncomfortable,
stiff, and swollen - Intensity of pain is often less than acute flares
- . Acute flares may still occur
- - Polyarticular involvement may develop
- - Attacks become additive and ascending
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
4
Advanced Gout Tophaceous Deposits ________________
_______________________________ . Solid urate
deposits in tissue - Irregular, destructive
nodularities produced . Risk factors include -
Long duration of hyperuricemia - High serum
urate levels - Long periods of active,
untreated gout
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- Diagnosing Gout
- _______________________________________________
- . History and physical
- . Synovial fluid analysis
- . Serum urate not a reliable measure
- - May be normal at the time of flare
- Urinary uric acid excretion increased
- during acute flares
- - May be elevated with joint symptoms
- from other causes
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- Risk Factors for the
- Development of Gout
- ______________________________________________
- . Male gender
- . Female gender postmenopause
- . Advanced age
- . Drugs
- - Diuretics, low-dose aspirin (ASA),
cyclosporine - . Hypertension
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
5
Risk Factors for the Development of Gout
(contd) _________________________________________
___ . Transplant . High alcohol intake -
Highest with beer, followed by liquor - No
increased risk with wine . High body mass index .
Diet high in meat and seafood
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
Synovial Fluid Analysis Compensated Polarized
Light Microscopy _________________________________
_________ . Gold standard to confirm gout .
Urate crystals identified by - Needle and rod
shapes - Strong negative birefringence .
Crystals intracellular during attacks
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- The Importance of a
- Differential Diagnosis
- _____________________________________________
- Think about gout before diagnosing other
- diseases with different and/or less specific
therapies - - Pseudogout-Calcium - Rheumatoid
arthritis (RA) - pyrophosphate . Nodules
potentially - deposition
confused with - disease (CPPD) tophi
- . Chrondrocalcinosis - Osteoarthritis
- . Rhomboid-shaped - Septic arthritis
- crystal -
Cellulitis - - Psoriatic Arthritis
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
6
Differential Diagnosis Example CPPD ______________
_______________________________ . Clinically
similar to gout - Acute attacks of inflammation
in joints . Crystals different under compensated
polarized light - Weakly positively
birefringent - Rhomboid, rods, squares or
irregular
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
The Treatment Goals for Gout _____________________
__________________________ 1. Rapidly terminate
the acute flare 2. Protect against further
flares - Reduce the chance of
crystal-induced inflammation 3. Treat
the hyperuricemia and prevent disease
progression - Long-term correction of the
metabolic cause - Sufficient lowering of
serum urate depletes total body urate pool
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- 1.Termination of the Acute Flare
- _____________________________________________
- . Control crystal-induced inflammation and pain
- and resolve the flare
- - Not cure for gout
- . Resolves the symptom
- . Urate crystals remain in the joint
- . Serum urate should NOT be
lowered - during flare
- - Choice of medication not as critical as
- . Rapid initiation of therapy
- . Appropriate duration of therapy
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
7
Termination of the Acute Flare Considerations
for Agent Selection ______________________________
_________________ Agent
Considerations NSAIDs .
Contraindicated in peptic ucler disease, GI
bleeds, history
of aspirin or NSAID-Induced asthma, renal
dysfunction
. Interaction with warfarin
(consider COX-2) Colchicine . Not effective
late in the flare
. Contraindicated in dailysis patience
. Use with caution with
renal or hepatobillary dysfunction,
active infection, gt 70 years
of age . Drug
interactions with cyclosporine, statins,
macrolides . Use
of IV formulation controversial and should be
used with
extreme caution IV use can cause local tissue
necrosis Corticosteroids And ACTH .
Worsening of glycemic control in diabetics
. May need to add
other anti-inflammatories or use
moderate-to-high doses
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________________
2.Protection Against Further Flares ______________
_________________________________ . Colchicine
0.5-1 mg/day or low-dose NSAIDs - Decrease
frequency and severity of flares - Prevent
disease flares associated with initiation
of urate-lowering therapy . Homeostatic
mechanisms mobilize deposited crystals . Will
not stop destructive aspects of gout
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- 3.Treating Hyperuricemia and
- Preventing Disease Progression
- _____________________________________________
- . Lowering urate to lt6 mg/dL allows depletion of
- - Total body urate pool
- - Deposited crystals
- . Therapy should be lifelong and continuous
- - Otherwise, symptoms (eg, acute flares,
tophi) recur - . Available urate-lowering agents for gout
- - Uricosuric agents (probenecid, losartan
mild, - fenofibrate mild
- - Xanthine oxidase inhibitor (allopurinol)
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
8
Advantages to Existing Arsenal Of Urate-lowering
Agents ___________________________________________
__ Agent
Advantage Uricosurics . Reverses most
common physiologic
abnormality in gout
- 90 of patients are underexcretors of uric
acid Allopurinol . Effective in both
overproducers and
underexcretors .
Single daily dose .
Can be efficacious in patients with renal
insufficiency
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
Limitations to Existing Arsenal of Urate-lowering
Agents ___________________________________________
___
Allopurinol Uricosurics Renal function an
issue v
v Drug interaction
v v Target serum
urate not always achieved v
v Potentially fatal hypersensitivity
syndrome v Nonselective enzyme inhibition
v Risk of nephrolithiasis
v Multiple daily
dosing
v
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- Therapeutic Challenges Warrant
- New Agents to Treat Gout
- _____________________________________________
- . Serum urate not always lowered to lt6 mg/dL
- . Treatment gaps exist in patients with
- - Renal insufficiency
- - Allergies
- - Allopurinol intolerance
- - Drug interactions
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
9
Why the Increased Epidemiology of
Gout? ____________________________________________
_ . Increased prevalence of risk factors and
comorbidities - Longevity - Diuretic and
aspirin use - Hypertension . Dietary trends .
Improved survival from comorbidities .
Limitations in treatment
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
Why Worry About Gout? Gout May be a Signal
for Unrecognized Comorbidities ___________________
_________________ Comorbidities associated with
hyperuricemia . Renal manifestations
. Heart failure . Obesity
. Hyperlipidemia . Metabolic
syndrome . Hypertension . Diabetes
mellitus . Cardiovascular
disease
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- Summary
- _____________________________________________
- . Gout needs to be
- - Accurately diagnosed
- - Recognized as a chronic disease with 4
stages - - Treated separately for
- . Terminating acute flares
- . Controlling chronic hyperuricemia
and tissue - deposition
- . Potentially exciting new therapies are under
- development
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
10
Teaching Points __________________________________
___________ Hyperuricemia is linked to
comorbidities . Obesity
. Hyperlipidemia .
Metabolic syndrome . Hypertension
. Diabetes mellitus . Renal
disease . Heart failure
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
Teaching Points __________________________________
__ Risk factors for hyperuricemia and gout
. Heredity .
Transplanation . Male gender
- Cyclosporine .
Postmenopause . High alcohol intake
. Advanced age - Liquor, Beer
. Medications . High
body mass index . Diet
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- Teaching Points
- _____________________________________________
- . Gout can manifest in any joint
- - 1st MTP only 50 of the time
- . During the flare
- - Urate may be normal 50 of the time
- - Promptly initiate agents for termination
- . After the flare
- - Consider urate-lowering agents with
prophylaxis - . Risk / Benefit assessment
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
11
Treatment Goals 1.Termination of the Acute
Flare ________________________________ .
Anti-inflammatory medication to suppress
crystal-induced inflammation - Not a cure for
gout . Resolves the symptoms .
Urate crystals remain in the joint . For
efficiency, choice of medication not as
critical as . Appropriate dose of
therapy . Appropriate duration of
therapy
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
Treatment Goals 2. Anti-inflammatory Therapy to
Prevent Further Flares __________________________
_________________________________ . Colchicine
0.6 mg qd/bid or low-dose NSAIDs - Decrease
frequency and severity of flares - Can decrease
disease flares associated with initiation of
urate-lowering therapy - May not stop
destructive aspects of gout . Safety of chronic
NSAIDs vs colchicine - Colchicine lower GI,
neuromuscular - NSAID upper GI, renal, HTN,
Na retention
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
- Hyperuricemia and Gout
- _____________________________________________
- . Laboratory defined hyperuricemia is NOT the
same - as biologically defined hyperuricemia
- . Virtually all patients with gouty arthritis
have - biologicall defined hyperuricemia
- - Urate deposites in tissues when gt6.8 mg/dL
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
12
Imaging ____________________________________ .
Radiographic changes of gout are seen in up to
50 of patients . Most common involved joint is
the first MTP joint, other toes, ankles,
hands . Bone mineralization is initially normal
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
Imaging (continuing) _____________________________
______________________________ . Finding include
soft-tissue tophi (containing birefringent
monosodium urate crystals) . Punched-out erosious
with siderotic borders and overhanging
edges . Preservation of the joint space . Good
bone denstity (unlike RA)
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
X-Ray ____________________________________________
__
13
Treatment Goals 3.Urate-lowering Therapy to
Prevent Flares and Disease Progression ___________
_________________________ . Lowering urate to lt6
mg/dL - Tophus reabsortion and uric acid
excretion . Therapy should be lifelong and
continuous - Symptoms ( eg, acute flares,
tophi) recur if stopped . Available
urate-lowering agents for gout - Uricosuric
agents ( probenecid, losartan mild,
fenofibrate mild - Xanthine oxidase
inhibitor (allopurinol)
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________
Conclusion _______________________________________
____________________ . Gout is a chronic disease
caused by the deposition of urate crystals
resulting from hyperuricemia . Uncontrolled
hyperuricemia can cause significant joint
manifestations . Hyperuricemia is associated with
other prevalent comorbidities hypertension,
obesity, hyperlipidemia, and insulin
resistance . Anti-inflammatory agents control the
symptoms of gout, but treating the disease may
require lowering the serum urate - Assess
the risks and benefits . When administering
urate-lowering therapy, the defined serum
urate is 6 lt mg/dL
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
________________________________