Neuroplasticity PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title: Neuroplasticity
1
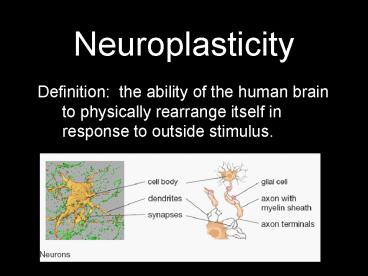
Neuroplasticity
- Definition the ability of the human brain to
physically rearrange itself in response to
outside stimulus.
2
Neuroplasticity
3
EEG
4
PET
5
fMRI
6
fMRS
7
Excellent Book Reference
- Train your Mind Change Your Brain by Sharon
Begley (2007) Ballantine Books - ISBN 978-1-4000-6390-1
8
Findings and Applications
- Dyslexia-
9
Findings and Applications
- Dyslexia- a specific language impairment that
affects 5-17 of the population - Old belief- due to a visual problem such as the
inability to distinguish p and q and b and d - Paula Tallal discovered that it is actually an
auditory problem where the fast sounds of p, b, d
and g cannot be distinguished - Development of Fast ForWord- scans show this
actually changes the brain (Paula Tallal)
10
Findings and Applications
- Neurons dont reproduce but the brain has
neurological stem cells and they DO! This is
called neurogenesis. - Old paradigm- you are born with all the brain
cells you will ever have. WRONG! - Three growth spurts followed by pruning infancy,
preteen or teen years and early 20s. - Pruning is when your brain allows connections and
cells to die off due to lack of use. If you dont
use it, you DO lose it.
11
Findings and Applications
- Stroke victims and constraint-induced movement
therapy (Edward Taub) - This same method can be used to force students to
learn new skills. - Ex. Constraint Game
12
Constraint Game Geology Vocabulary Review
- On two separate cards, write down one noun on
each. - On two other separate cards, write down one verb
each. - On the last two separate cards, write down one
adjective each. - Find a partner, combine and mix up your cards.
- Trade your combined set of cards with another
group. Do not look at the cards. - Pick a card and without using your voice or
writing down your word, somehow communicate it to
your partner and get them to say it. (Charades or
Pictionary).
13
Constraint Game
- Have your partner pick a card and repeat.
- Now pick a second card and this time, get your
partner to say the word by using only your voice.
You may not move your body or draw. (Taboo or
Password) - Have your partner do the same.
- Continue to alternate between not being able to
speak and not being able to move taking turns
until time is called.
14
Neurogenesis and the Teen BrainThe Downside...
- 10-12 yrs frontal lobe growth spurt (frontal
lobes are responsible for judgment, emotional
regulation and control, organization and
forethought) - Repeat of this growth in early 20s.
- Temporal lobes have a growth spurt between 12-16
yrs (these lobes manage language and emotional
control)
15
Neurogenesis and the Teen BrainThe Upside...
- This means that everyone gets a second and third
chance to learn new skills easily such as
language, music, hand-eye coordination, logical
thought and ATTENTION. - Ironically, the students may appear initially
weak in these areas but this is when to emphasize
these skills. - Remember... if you dont use it... you lose it!
(Literally during the neural pruning stage.)
16
Neuroplasticity and the Skill of Paying Attention
- Old belief- Normal attention span is 3-5 minutes
per year of childs age. Doing the math... - 12 years X 5 60 minutes
17
Neuroplasticity and the Skill of Paying Attention
- Reality- Attention is a skill the brain learns so
it varies by culture and experience but only up
to a specific neurological point. We need to
teach the skills to get to that point.
18
Human Set-point for Attention
- Primacy-Recency research shows that pre-teens to
adults have an attentional cycle of about twenty
minutes while younger children have an
attentional cycle of about 6 minutes.
19
What Teachers Need to Consider
- Design lesson plans around attentional cycles.
- Actively teach the skill of paying attention to
reach that set-point.
See block schedule example.
20
Teaching the Skill of Paying Attention
- Explicit teaching of meta-attention in learning
disabled and normal students (Loper, Hallahan and
Ianna 1982) greatly extends attention processes. - In English translation You have to tell the
students you are trying to help them extend their
attention spans and have them buy in. - How do you get them to buy in? Studies show
younger kids prefer rewards and older kids prefer
more interesting materials.
21
Mindfulness, Depression and OCD
- Using scans and evaluations by counselors, people
suffering from depression or OCD had relapses 66
of the time if the were only prescribed drugs but
had a 34 relapse rate when prescribed drugs and
using mindfulness techniques together (Teasdale,
Segal and Williams, 2000).
22
Teaching the Skill of Paying Attention
- Use timers and build speed. (Attention span is
inversely proportional to boredom and
discomfort.) - Make use of their increased need for
socialization and use interactive attention by
working in groups.
CO2 Example from Methods 1
23
Does everyone see why I went through this example?
24
Does everyone see why I went through this example?
- Gets and keeps attention.
- Builds charting skills for NCLB testing.
- Builds speed which increases attentional length.
- Content.
25
Teaching the Skill of Paying Attention
- Work observations skills explicitly (i.e. picture
games, staring contests) during the first few
minutes of administrivia.
Picture game example.
26
(No Transcript)
27
Teaching the Skill of Paying Attention
- Use volunteers to keep students on task.
- Use complex instructions as games or as
additional test questions (i.e. the students are
allowed to ask any question they want but if the
answer is in the instructions on the activity,
then they lose a point).
Complex instruction example.
28
Complex Instructions Example
- Listen carefully...
29
Findings and Applications
- William Greenough discovered that exercise
increases the number of dendritic branches.
However, forced exercise increases stress
hormones that cause neural pruning!! Physical
activity during learning increases retention
Flyswatter activity.
30
Findings and Applications
- Spatial tuning of tactile attention modulates
visual processing within hemifields (Eimer M and
van Velzen, 2002). - Huh? English translation Have your students
act out with their hands what they read. - Scans show that good readers actually see and
hear what they read but poor readers do not.
You have to train the brain to visualize and
acting it out helps directly. - Visualization example
31
Findings and Applications
- The pineal gland in the brain produces melatonin
which induces sleepiness. The pineal gland does
this when it gets dark. - Light intensity greater than 2000 lux is
necessary for melatonin suppression in most
people. - Most classrooms are about 400 lux even before you
dim the lights for the PowerPoint!
32
Findings and Applications
- Poverty penetrates the brain. Poor students can
be identified by their having fewer dendrites and
their exhibiting more anxiety, hypervigilance and
paranoia. This is because stress hormones cause
pruning in some places in the brain and
expansions in others like the amygdala. (The same
pattern is found in soldiers suffering from
post-traumatic stress syndrome.) However,
cognitive therapy can reverse this.
33
Findings and Applications
- Visualizing physical practice causes the same
expansions in the motor cortex (controls
movement) as real physical practice does.
(Pascaul-Leone, 1990s) - Have students practice lab or other physical
activities in their minds before taking a test.
Scores improve significantly. - This also works in physical therapy by decreasing
recovery time and increasing balance.
34
Technology vs. the Brain
- Technology is expanding faster than our ability
to test whether it is effective. - Case in point 2d vs. 3d and the lunar phases
- Informational glut-contributes to short attention
span, actually teaches the brain to ignore
information (TIMSS and textbooks)
35
Technology for the Brain
- Technology is allowing students and teachers to
participate directly in doing real science. - http//marsproject.niu.edu
- http//setiathome.berkeley.edu
- http//stardustathome.ssl.berkeley.edu/