Enlargement of the EU PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 47
Title: Enlargement of the EU
1
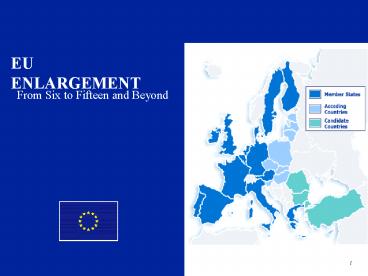
EU ENLARGEMENT
From Six to Fifteen and Beyond
2
From Six To Fifteen
1957
3
From Six To Fifteen
1973
4
From Six To Fifteen
1981
5
From Six To Fifteen
1986
6
From Six To Fifteen
1995
7
From Six to Fifteen and Beyond
2002
8
Tomorrow's Europe
13 December 2002
9
Treaty of the European Union (TEU)
Article 49 of the TEU Any European State which
respects the principles set out in Article 6(1)
may apply to become a member of the
Union. Article 6 of the TEU The Union is founded
on the principles of liberty, democracy, respect
for human rights and fundamental freedoms, and
the rule of law, principles which are common to
the Member States.
10
The Europe Association Agreements
Country Europe Europe Official Agreement
signed Agreement came application for into
force EU Membership Bulgaria March 1993 February
1995 December 1995 Czech Rep. October
1993 February 1995 January 1996 Estonia June
1995 February 1998 November 1995 Hungary December
1991 February 1994 March 1994 Latvia June
1995 February 1998 October 1995 Lithuania June
1995 February 1998 December 1995 Poland December
1991 February 1994 April 1994 Romania February
1993 February 1995 June 1995 Slovakia October
1993 February 1995 June 1995 Slovenia June
1996 February 1999 June 1996 Country Association
Association Official Agreement signed Agreement
came application for into force EU
Membership Turkey September 1963 December
1964 14 April 1987 Malta December 1970 April
1971 16 July 1990 Cyprus December 1972 June
1973 3 July 1990
11
The Copenhagen Criteria
- Political criteriaThe applicant country must
have achieved stability of its institutions
guaranteeing democracy, the rule of law, human
rights and respect for and protection of
minorities. - Economic criteriaIt must have a functioning
market economy, as well as the capacity to cope
with competitive pressure and market forces
within the EU. - Criteria of the adoption of the acquisIt must
have the ability to take on the obligations
related to of membership, including adherence to
the aims of political, economic and monetary
union.
12
The New Europe Integration
EU
EFTA
EU Applicants
13
Accession negotiations Chapters
17. Science and research 18. Education and
training 19. Telecommunications and IT 20.
Culture and audiovisual policy 21. Regional
policy and structural instruments 22.
Environment 23. Consumers and health protection
24. Justice and home affairs 25. Customs union
26. External relations 27. Common foreign and
security policy 28. Financial control 29.
Financial and budgetary provisions 30.
Institutions 31. Other
1. Free movement of goods 2. Freedom of movement
for persons 3. Freedom to provide services 4.
Free movement of capital 5. Company law 6.
Competition policy 7. Agriculture 8. Fisheries
9. Transport policy 10. Taxation 11. Economic
and monetary union 12. Statistics 13. Social
policy and employment 14. Energy 15. Industrial
policy 16. Small and medium-sized
enterprises
14
Towards an Enlarged Europe
- Regular Reports
- The Commission recommends conclusion of
negotiations with ten candidate countries
Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary,
Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, the Slovak
Republic, and Slovenia. - These countries will be ready for membership at
the beginning of 2004. - 2007 indicative date for accession chosen by
Bulgaria and Romania. - Strengthening support for Turkeys pre-accession
preparations.
9 October 2002
15
Bulgaria, Romania, Turkey
- Next steps for Bulgaria and Romania
- 2007 target date to conclude negotiations.
- Detailed roadmaps to complete preparations.
- Judicial and administrative reform.
- Next steps for Turkey
- to fully meet the political criterion.
- Enhanced support from the EU
- Increased financial assistance from 2004.
16
The formal steps
2003
Enhanced pre-accession assistance for Romania and
Bulgaria. 9th April - European Parliament
assent 16th April - Signature of the Treaty in
Athens with Laeken 10 Ratification -
Parliamentary / referenda EU has 25 members End
of 2004 - Commission report and recommendation on
Turkey's progress
1st May 2004
17
Candidate countries GDPin 1999 2000
Source Eurostat PPP Purchase Power Parity
18
CYPRUS
Area 9,251 km² Population 759,100
inhabitants Capital Nicosia Others towns
Limassol, Larnaca Language Greek, Turkish,
English Currency Cypriot pound
- Cyprus is a Republic with a presidential system
of government. Under the 1960 Constitution,
executive power is vested in the President of the
Republic, elected by universal suffrage for a
five-year term of office. - The President exercises executive power through
a Council of Ministers and the Government
Spokesman appointed by him. - Each Minister is the head of his Ministry and
exercises executive power of all subjects within
that Ministry's domain. - The political system of Cyprus is unicameral.
- Its legislative chamber is made up of 80 members
(56 Greek Cypriot and 24 Turkish Cypriot) - Judicial power is held by the Supreme Court and
district tribunals
19
CYPRUS
Area 9,251 km² Population 759,100
inhabitants Capital Nicosia Others towns
Limassol, Larnaca Language Greek, Turkish,
English Currency Cypriot pound
- Foreign Policy
- Cyprus is located in a strategically important
position with respect, among other things, to the
neighboring Middle East. - Cyprus has been a member of the United Nations
since 1960, part of the non-aligned nations
movement since 1960, a Council of Europe member
since 1961 and of OSCE and WTO since 1975 and
1995 respectively - The economy of Cyprus is weakened by its
internal division and by its dependence upon
tourism - The services sector accounts for 75 of the GDP,
industry for 19.9, and farming for 4.6.
According to European Commission forecasts,
Cyprus' GDP should rise by 2 in 2003
20
CZECH REPUBLIC
Area 78,860 km2 Population 10,269,726
inhabitants Capital Prague Language Czech
Currency Czech crown
- The Czech Republic was instituted on 1 January
1993 after the dissolution of Czechoslovakia. - It is a Parliamentary Republic divided into 14
regions, including the city-region of Prague. The
bicameral Parliament is endowed with legislative
powers and is made up of a Lower House of 200
elected members (universal suffrage). - Elections (majority voting system) take place
every 4 years. - The Senate is made up of 81 members whose term of
office is 6 years (every two years, there is an
election involving one third of the Senate). - After the June 2002 election, the Czech
Republic's government was made up of a
center-left coalition of social democrats (CSSD),
the People's Party (KDU-CSL) and the Freedom
Union-Democratic Union (US?DEU). This coalition
controls 101 of the 200 Lower House seats.
21
CZECH REPUBLIC
- Foreign Policy
- The Czech Republic has been a NATO member since
12 March 1999. Among the priorities announced by
the present Government in its Programme of 5
August 2002 was full integration with the
European Union, which it is to join on 1 May
2004. - Other goals are to play an active role in NATO,
the struggle against terrorism, developing its
relations with neighboring countries, and
strengthening regional collaboration. - Economy
- The economy of the Czech Republic is stable and
multifaceted. Trade with EU countries (above all,
Germany) and tourism have both increased over the
last few years. Half the national income is
generated by the services sector. The metallurgy,
automobile, machinery and arms industries
generate 41 of the GDP (farming, 4).
Privatization of many sectors is under way
(telecommunications, banks and energy), and this
has encouraged foreign investment. According to
European Commission forecasts, the Czech
Republic's GDP should rise by 2.8 in 2003.
Area 78,860 km2 Population 10,269,726
inhabitants Capital Prague Language Czech
Currency Czech crown
22
HUNGARY
Area 93,029 km² Population 10,174,853
inhabitants Capital Budapest Language
Hungaria Currency Forint
- Hungary is a Parliamentary Republic.
- Its 1989 Constitution gives legislative power to
a unicameral parliament (National Assembly -
Országgyulés), made up of 386 members elected for
a four-year term of office (uninominal voting, in
part proportional, two-round election system,
ballot). - Following the April 2002 general election,
Hungary has been governed by a centre-left
coalition made up of the Socialist Party (MSzP,
with 178 seats - the relative majority) and the
Alliance of Free Democrats (SzDSz, a liberal
party). The coalition has 198 seats. The
opposition is headed by FIDESz, the conservative
party of former Prime Minister Victor Orban who
governed Hungary during the previous legislature.
- The parliamentary spectrum also contains the
Hungarian Democratic Forum, a FIDESz ally. The 5
threshold requirement bars the extreme right wing
party, MIEP, from participating in parliamentary
activities.
23
HUNGARY
- Foreign Policy
- Hungary has been a NATO member since 1999, and in
2002 concluded negotiations for joining the
European Union, signing the Accession treaty in
Athens on 16 April 2003 and will join the EU on 1
May 2004. - Considerable attention has been paid to
relations with the Hungarian minorities in
neighbouring countries (1.6 million in Romania,
600,000 in Slovakia, 300,000 in Serbia-Voivodina,
and 200,000 in the Ukraine).Hungary has been a
UNO member since 1955, and has been a Council of
Europe and OECD member since 1992 and 1996,
respectively. - Economy
- The Hungarian economy is healthy, and its 2002
performance was found to be satisfactory both in
terms of GDP growth and from the employment point
of view. The Hungarian government is now
concentrating on the economic policies necessary
for progress toward the euro zone which, it is
hoped, Hungary will be joining in 2007. The
national income is generated for the main part by
the services sector (62 of the total figure)
industrial concerns in the fields of metallurgy,
building, chemicals (above all, pharmaceutical),
food, and automobile motors account for 34 of
the GDP (farming stands at 4). According to
European Commission forecasts, Hungary's GDP
should rise by 3.7 in 2003.
Area 93,029 km² Population 10,174,853
inhabitants Capital Budapest Language
Hungaria Currency Forint
24
ESTONIA
Area 45,227 km² Population 1,366,959
inhabitants Capital Tallin Language Estonian
Currency Estonian crown
- The Constitution of Estonia dates from 1992
- Estonia is a Parliamentary Republic the President
of which is elected every five years by a
unicameral Parliament (Riigikogu). - Parliament is made up of 101 members elected
every four years (proportional system), and a 5
splinter party threshold applies for those
wishing to take part in parliamentary activities - The Centre Party won 25.4 of the votes, the new
group, Res Publika won 24.6 and the Reform Party
of the retiring Premier, Siim Kallas, won 17.7. - During the last elections, the Estonian United
People's Party representing the Russian
population, gained only 2.24 of the votes and
therefore was not able to enter Parliament. The
Slavic-speaking minorities (Russians, Ukrainians,
Belorussians) make up 32.07 of the population
(438,308 inhabitants). - Like the other two Baltic countries, Estonia
gained independence only during the two interwar
decades, and then, again, in 1991, just months
before the fall of the Soviet Union A new
Constitution was(1992),
25
ESTONIA
Area 45,227 km² Population 1,366,959
inhabitants Capital Tallin Language Estonian
Currency Estonian crown
- Foreign Policy
- In 1995, Estonia officially applied to become a
member of the European Union, concluding
negotiations in December 2002. Membership is
planned for 1 May 2004. - In November 2002, the North Atlantic Council
Summit in Prague extended an invitation to
Estonia and six other countries to join NATO.
Estonia is to officially join the alliance in May
of 2004. - Economy
- Among transition economies Estonia's is one of
the most advanced, having developed rapidly and
acquired a liberal tax system. Indeed, Estonia
may be considered one of the most rapidly growing
European continental markets. It has taken the
lead (also as a result of its geographic
position) in the competition in central and
eastern Europe for foreign investments. The
services sector plays a leading role, and
accounts for 66 of the country's GDP. The
rubber, wood, metallurgy, textiles, transport and
telecommunications equipment industries generate
29 of the national income, and farming accounts
for 6. According to European Commission
forecasts, Estonia's GDP should increase by 4.9
in 2003.
26
LATVIA
Area 64,589 km² Population 2,345,768
inhabitants Capital Riga Language Lettish
Currency Lat
- Latvia regained its independence in August 1991
following the collapse of the Soviet Union. - It is a Parliamentary Republic whose President is
elected by parliament for a four-year term of
office. The country's unicameral Parliament
(Saeima) is made up of 100 members elected every
four years (proportional system universal
suffrage 5 parliamentary threshold). After the
general election of October 2002, Einars Repse
formed a centre-right government with the First
Party of Latvia (7.6), the Farmers and Greens
Alliance (9.5) and the Fatherland and Freedom
Party (5.4). The party of outgoing Prime
Minister Andris Berzins ("Latvia's Way") and the
Social Democratic Party fell below the 5
threshold
27
LATVIA
Area 64,589 km² Population 2,345,768
inhabitants Capital Riga Language Lettish
Currency Lat
- Foreign Policy
- The Association Treaty with the EU was signed in
1995 and accession negotiations were concluded in
2002. Latvia is to become a member of the EU on 1
May 2004. - Following the signing of the Washington
Charter(1998), between the United States and the
Baltic States, the NATO Summit in Prague of
December 2002 invited Latvia and six other
countries to join the alliance, and Latvia will
officially become a member in May 2004. Latvia's
political and commercial relations with the other
Baltic states are good, and there has been an
improvement in relations with the Russian
Federation. There has been friction over the fact
that Latvia has been most selective in its
policies regarding citizenship and voting rights
for the large Slavic-speaking community.
28
LATVIA
Area 64,589 km² Population 2,345,768
inhabitants Capital Riga Language Lettish
Currency Lat
- Economy
- Due to the fact that it had gradually increased
exchanges with European Union countries, Latvia
managed to avoid the worst of the consequences of
the Russian economic crisis of 1998. Most
companies and banks have been privatized. Latvia
joined the World Trade Organization (WTO) in
February 1999. The country is struggling with its
national budget deficit, and this is one of its
most serious problems. The predominant services
sector accounts for 70 of the GDP 26 of the
national income is generated by industrial firms
that produce buses, cars, radios and washing
machines, as well as textiles, electronic and
pharmaceutical products (farming accounts for
5). According to European Commission forecasts,
Latvia's GDP should rise by 5.5 in 2003
29
LITHUANIA
Area65,300 km2 Population 3,475,586
inhabitants Capital Vilnius Language
Lithuanian, Polish, Russian Currency litas
Lithuania is the largest of the three Baltic
Republics, having declared independence from the
USSR on 11 January 1990. According to the terms
of the Constitution (approved by referendum in
1992), Lithuania is a Parliamentary Republic.
The president is elected every five years
(universal suffrage). The unicameral Parliament
(Seimas) is elected every 4 years. The electoral
system is mixed. Half of the 141 members are
elected by single-member constituencies and the
other half by proportional system. Since July
2001, Algirdas Mykolas Brazauskas has headed a
centre-left coalition supported by the Social
Democratic Party (the winners of the election)
and the New Union Party (social liberals).
30
LITHUANIA
Foreign Policy EU membership negotiations were
concluded in December 2002 in Copenhagen, and
Lithuania is to become a member of the EU on 1
May 2004. The NATO Summit in Prague of November
2002 invited Latvia and six other countries to
join the alliance. Lithuania is to officially
become a member of NATO in May 2004. Other
priorities for the government are developing
cooperation with other Baltic countries and - on
a bilateral basis - entering into a strategic
partnership with Poland. It also wishes to
improve relations with the Russian
Federation. Economy Despite the drawbacks of its
binding commercial ties with Russia and the
economic crisis of 1998, Lithuania's GDP growth
rate in 2002 increased more rapidly (5.9) than
in the other Baltic countries. However, the
unemployment rate remains high (13 in 2002). The
services sector accounts for 61 of the GDP 31
of the national income is produced by industrial
production of television equipment, optical
products, refrigerators and furniture, as well as
the shipbuilding, oil refining and food
industries farming accounts for 7. According to
European Commission forecasts, Lithuania's GDP
should rise by 4.5 in 2003.
Area65,300 km2 Population 3,475,586
inhabitants Capital Vilnius Language
Lithuanian, Polish, Russian Currency litas
31
MALTA
Area316 km2 Population 394,641
inhabitants Capital Valletta Language
Maltese, English Currency Maltese lira
Malta - whose territory includes the island of
Malta, the islands of Gozo and Comino, and other
minor islands - is a Parliamentary Republic, with
a unicameral Parliament. It was a British colony
from 1800 until its independence on 21 September
1964. The Republic was proclaimed on 13 December
1974. The Chamber of Representatives is made up
of 65 members elected every five years. This
single member constituency system permits a
plurality premium. The last general election was
called by the government after the referendum
result favouring EU membership, and took place on
12 April 2003. The Nationalist Party held on to
the government with 51.8 of the votes, while the
Labour Party took 47.5.
32
MALTA
Area316 km2 Population 394,641
inhabitants Capital Valletta Language
Maltese, English Currency Maltese lira
Foreign Policy Malta is a member of various
international organizations and institutions
including the United Nations, OSCE, the
Commonwealth and the Council of Europe. It is now
making preparations to join the European Union on
1 May 2004. Negotiations for EU membership, which
had begun in 1990, were interrupted by the Labour
government, which insisted on strict neutrality
for this island country. The nationalists took up
negotiations once more in 1998 and campaigned for
membership up to the referendum approval of EU
membership. Economy Malta's main resources are
its favorable geographic position and an
efficient labour force. The Republic of Malta
produces only 20 of its food needs, has little
water and no energy sources of its own. Its
economy therefore depends on international trade,
tourism and manufacturing72 of the GDP is
generated by the services sector. The industry
sector (electronics, food, textiles and tobacco)
accounts for 26 of the national income, and
farming for 3. According to European Commission
forecasts, Malta's GDP should rise by 3.1 in
2003.
33
POLAND
Area 312,685 km2 Population 38,632,453
inhabitants CapitalWarsaw Language Polish
Currency zloty
Poland - the largest and most populous of the
states on the way towards EU membership - is a
Parliamentary Republic based on the Constitution
of 1997. Poland's President is elected every 5
years (universal suffrage ballot system). The
bicameral Parliament is elected every 4 years.
The Lower House (Sejm) is made up of 460 members
elected by proportional system (5 threshold for
parties 8 for blocks). The Senate (Senat) is
made up of 100 elected members (majority voting
system). The political ticket made up of the
Democratic Left Alliance (SLD) and Union of
Labour (UP) won the general election of 23
September 2001 with 41.04 of the votes. The
government is formed with the Peasants Party
(PSL) (8.98). The coalition fell apart in March
2003, as a result of PSL criticism of the
conditions for joining the European Union, and
Miller then became leader of a minority
government. The opposition is made up of groups
known as Civic Platform (12.68 of the votes
obtained during the last election), Self-Defence
(10.02), Law and Justice (9.5) and the League
of Polish Families (7.87). Blocked by the 5
threshold was Solidarnosc Electoral Action, the
party of former Prime Minister Jerzy Buzek.
34
POLAND
Area 312,685 km2 Population 38,632,453
inhabitants CapitalWarsaw Language Polish
Currency zloty
Foreign Policy Negotiations with EU began in
1998 and were concluded in December 2002 during
the Copenhagen Summit, and on 1 May 2004, Poland
will become a member of the Union. Poland has
been a member of NATO since March 1999. Regional
cooperation is intense with the Czech Republic,
Slovakia and Hungary (Visegrad Group) and with
the Baltic countries (Council of Baltic Sea
States). Warsaw is also keenly interested in
improving relations with Russia and the other
neighboring countries. Economy In recent years
Poland has been pursuing an intense policy of
economic liberalization, which led to
considerable GDP growth between 1993 and 2000
this was followed, however, by a downturn in 2001
and 2002. The tertiary sector generates 61 of
the national income the manufacturing sector
generates 35 of the GDP (the main divisions are
chemical, foods, iron metallurgy and glass
processing) but the farming sector (4 GDP) has
encountered problems on the road to development
due to low investments. According to European
Commission forecasts, Poland's GDP should rise by
2.5 in 2003.
35
SLOVAKIA
Area49,035 Km² Population 5,379,455
inhabitants CapitalBratislava LanguageSlovak
Currency Slovak crown
Slovakia is a democratic Parliamentary republic,
founded on 1 January 1993, following the
peaceable dissolution of Czechoslovakia. The
unicameral Parliament, known as the National
Council, is made up of 150 members elected every
four years by universal suffrage. The
proportional voting system is accompanied by a
threshold ruling requiring parties to obtain more
than 5 electoral support in order to be seated.
The President of the Slovak Republic is elected
every five years by universal suffrage. The
country is divided into eight regions and 79
provinces. Since the September 2000 elections,
Slovakia has been governed by a centre-right
coalition, headed by the Slovak Democratic and
Christian Union of Prime Minister, Dzurinda
(SDKU, 28 seats) and supported by three other
parties.
36
SLOVAKIA
Area49,035 Km² Population 5,379,455
inhabitants CapitalBratislava LanguageSlovak
Currency Slovak crown
Foreign Policy The protocols for accession to
NATO were signed on 26 March 2003 and the treaty
for membership in the European Union was signed
in Athens on 16 April 2003. Economy Over the
last few years, Slovakia has managed to overcome
many of the problems encountered in its efforts
to modernize the economy. Most of the
privatization schemes have been completed. Banks
have attracted the participation of important
foreign investors, and foreign investment in
general is increasing. Economic growth in
Slovakia in 2001-2002 exceeded even the most
optimistic forecasts, despite the general
slowdown. The economy's weak point, however, is
the high unemployment rate (18.5 in 2002). The
services sector accounts for 61 of the GDP. 34
of national revenue is derived from the
metallurgic, food, chemical, paper, textiles and
optics industries, and 5 from agriculture.
According to European Commission forecasts,
Slovakia's GDP should grow by 3.7 in 2003.
37
SLOVENIA
Area 20,273 Km2 Population 1,994,026
inhabitants (2001) Capital Ljubljiana Language
Slovenian (90) (Italian and Hungarian in some
areas) CurrencyThaler
- Slovenia broke away from Yugoslavia in 1991.
- It is a Parliamentary Republic, with a Parliament
is composed of the Chamber of Deputies, a
legislative body composed of 90 members elected
every four years, and the State Council, a
consultative body renewed every five years and
composed of 40 members representing local
councils in addition to professional and
socio-economic interests. - The President of the Republic is elected every
five years. Janez Drnovsek became President as a
result of the last presidential elections in
December 2002. He had already been leader of the
Liberal Democratic Party (LDS) and Prime Minister
for extended periods from 1992 onwards. Since
December 2002 the Government has been led by the
former Finance Minister, Anton Rop. The wide
coalition supporting his government is the same
that backed the previous legislation and remains
centred on Drnovsek and Rop's Liberal-Democratic
Party (LDS), whose main ally is the Union of
Social Democrats (ZLSD) these parties are joined
by the Slovenian People's Party (SLS), the
Pensioners' Party (DeSUS) and other movements
such as the Young People's Party (SMS).
38
SLOVENIA
Area 20,273 Km2 Population 1,994,026
inhabitants (2001) Capital Ljubljiana Language
Slovenian (90) (Italian and Hungarian in some
areas) CurrencyThaler
- Foreign Policy
- Slovenia has succeeded in becoming a respected
member of the Partnership for Peace and the
Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC). In 1998
and 1999 Slovenia was a member of the UN Security
Council. In the first half of 2004 Slovenia will
become a full member of the EU (1 May) and of
NATO. - Economy
- During its process of transition towards a
fully-fledged market economy, in recent years
Slovenia has seen stable growth in the main
macro-economic indicators (even inflation,
despite its relatively high levels, is gradually
falling). This has allowed the country to become
more competitive and thus to prepare itself for
accession to the European Union. Some structural
reforms still remain to be completed, such as
those regarding the process of privatization and
the drafting of strategies to attract further
foreign investments. Despite a cyclical economic
slow-down in 2001-2002, Slovenia has managed to
maintain an average annual growth of 3. The
services sector remains the main GDP contributor,
accounting for 61 of the total. The metallurgic,
electronics, textiles, chemical and wood
industries account for 36 of the nation's
income, and agriculture for 3. According to
European Commission forecasts the GDP should
increase by 3 in 2003
39
UNEMPLOYMENT
40
GDP (billion euro)
41
Per Capita GDP euros (2001)
42
Growth Rate
43
Inflation
44
Debt/GDP (2001)
45
DEFICIT/GDP
46
(No Transcript)
47
(No Transcript)