Tuberculosis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
Tuberculosis
Description:
tubercle now becomes a solid caseous lesion. Decreased replication in caseous tissue because of anoxia ... liquefaction of the center of the caseous granuloma occurs ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:167
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Tuberculosis
1
Tuberculosis
- the major human respiratory infection throughout
the world - 20 million active cases of TB in the world
- One third of the world population (1.7 billion
persons) are infected with the TB bacillus
2
Characteristics of the organism
- acid-fast bacillus that is not motile, and does
not form spores, nor secrete toxins - intracellular, aerobic, hydrophobic
- reproduces slowly, and requires high levels of
oxygen in order to divide and metabolize
3
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Without oxygen, enters a dormant state, either
inside cells or in extracellular caseous material
in lungs - Able to develop resistant strains (major problem)
through mutations - Resistance differs according to population
characteristics (sanitation, poverty, poor health
care, drug abuse (high rate resistance in NYC)
4
Infectious Process
- Inhaled as droplets into lungsvery few organisms
needed to infect - Bacilli ingested by alveolar macrophages in a
typical phagocytic process - Phagocytosis faultythe organisms actually
survives inside the phagolysome - Host kills infected macrophagesproducing caseous
tissue
5
Infectious Process
- a constant battle between host defenses and the
evasive properties of the microorganism in TB
cannot grow and divide in caseous tissuesbut
liquefied cavity in middle does provide an
environment for TB bacilli to divide
6
Lesions
- Exudative and Proliferative
- Exudative inflammatory lesions heavily
infiltrated with polymorphonuclear leukocytes,
monocytes, and lymphocytes and producing a
fibrinous exudate - Proliferative Clssic granulomatous lesions
7
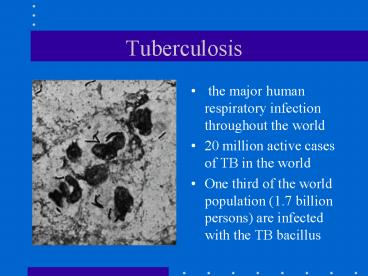
Lesions
- Tubercles seen on xray under microscope rings
of macrophages other inflammatory cells
surrounding infected cells. Caseous (solid
cheese-like material) in middle
8
Stages of Infection
- Stage I (day 1 to 7 after infection)
- resident alveolar macrophages attack organisms
through phagocytosis - Bacilli may be killed at this point, arresting
the disease - Or Bacilli released from macrophages, which
starts Stage II
9
Stages
- Stage II (days 7 to 21 ) symbiosis
- Macrophages from blood enter lung tissue
- Tubercles form
- Living bacilli divide and grow in number
10
Stages
- Stage III
- bacterial growth slowed because of both
cell-mediated immunological activities delayed
type hypersensitivity responses - tubercle now becomes a solid caseous lesion
- Decreased replication in caseous tissue because
of anoxia - Many tubercles become sterile..calcified and
fibrotic - Others may contain living organisms in suspended
animation
11
Stages
- Stage IV
- liquefaction of the center of the caseous
granuloma occurs - This allows organisms to receive enough 02 to
start dividing again - Ineffective immune response to huge numbers of
microorganisms produced - Cavitation occurs, releasing organisms
12
Stages
- Primary infection occurs in the lungs, and may
produced calcified tubercle (95 of cases
arrested here) - Most often, does not cause acute Sx, but develops
insidious infection or sets stage for future
secondary infection - Secondary (post-primary)infection most common
form of TB in adults
13
Immunology of TB
- After macrophages ingest TB bacilli, process and
present to T cells in association with MHC II - IL-1 released, T cells recruited
- Th-1 cells stimulated, release pro-inflammatory
cytokines which stimulate resting resident
macrophages - Macrophages continue to release cytokines into
lung - Th-2 cells, NK cells, and neutrophils also
recruited into lung
14
Immunology
- Positive tuberculin test is a delayed
hypersensitivity reactionmay take 10 weeks after
infection before it becomes positive - False positives and negatives are possible
15
Clinical Presentation
- Sx almost always are pulmonary cough,
hemoptysis, chest pain - Systemic Sx include fatigue, weight loss, fevers,
night sweats, these symptoms probably due to
cytokinesespecially TNF-alpha
16
Treatment
- Clinical presentation
- Positive skin test with negative chest X-ray
- Household contacts of patients with active TB
- Active TB with negative sputum smear and culture
- Therapy
- isoniazid prophylactic therapy (300 mg per day)
for 6-12 months - isoniazid and rifampin therapy for 4 months
- Initial phase isioniazid, rifampin,
pyrazinamide for 2 mos. Then isoniazid and
rifampin for 4 mos. Minimal length of treatment
is 6 mos. - Initial phase isioniazid, rifampin, and
pyrazinamide for 2 mos. Followed by isoniazid and
rifampin for 4 mos.. - Patients who have failed therapy or have relapsed
- Repeat susceptibility testing for resistance.
- Retreatment with an initial daily phase of
isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol,
and streptomycin for 2 mos followed by the same
drugs minus streptomycin for an additional 1 mo,
then 5 mos of therapy with isonizaid, rifmaopin,
and ethambutol given 3 times per week or daily.
17
Treatment
- Patients with positive cultures
- Patients who have failed therapy or have relapsed
- isioniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide for 2 mos
isoniazid and rifampin for 4 mos. - Repeat susceptibility testingRetreatment with
isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol,
and streptomycin for 2 mos 5 mos of isonizaid,
rifmaopin, and ethambutol given 3 times per week
or daily.
18
website
- http//www.cpmc.columbia.edu/resources/tbcpp/extre
s.html - For resource information on tuberculosis