Development and Aging PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 60
Title: Development and Aging
1
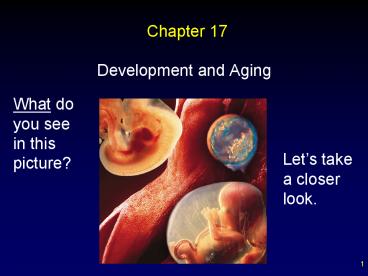
Chapter 17
- Development and Aging
What do you see in this picture?
Lets take a closer look.
2
(No Transcript)
3
Outline
- Fertilization
- Pre-Embryonic and Embryonic Development
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy and Birth
- Development after Birth (including Aging)
4
Fertilization
- Steps of fertilization (Conception).
- Several sperm penetrate corona radiata.
- Several sperm attempt to penetrate zona
pellucida. - One sperm enters egg and nuclei fuse, producing a
zygote. - Eggs plasma membrane and zona pellucida change
to prevent polyspermy.
5
Fertilization
6
Occurrence of Pregnancy
- When a zygote begins dividing, it is termed an
embryo (pre-embryo). - Developing embryo travels down oviduct and
eventually implants in endometrium.
(Implantation / pregnancy) - Presence of human gonadotropic hormone (HCG) in
the blood confirms pregnancy. - If implantation does not occur, a woman never
knows fertilization took place.
7
Human Development before Implantation
8
- Following implantation, the placenta
- originates from maternal and fetal
- tissues.
- Placenta then produces human chorionic
- gonadotropin (HCG) which maintains the
- corpus luteum in the ovary until the
- placenta begins its own production of
- progesterone and estrogen.
- Physical signs of pregnancy include no
- menstruation, increased urination,
- morning sickness, increased size of
- breasts, and darkening of areolae.
9
Pre-Embryonic and Embryonic Development
- Processes of development.
- Cleavage - Cell division without growth.
- Growth - Increase in size of cells.
- Morphogenesis - Shaping of embryo.
- Differentiation - Cells take on specific
structure and function.
10
Extraembryonic Membranes
- Membranes that extend out beyond the embryo.
- Amnion - Provides fluid environment for
developing embryo and fetus. - Yolk sac - First site of red blood cell
formation. - Allantois - Contributes to cardiovascular system.
- Chorion outermost membrane, develops from the
trophoblast, contributes to the placenta.
11
Extraembryonic Membranes
12
Pre-Embryonic and Embryonic Development
- Stages of development.
- Morula - Solid mass of cells resulting from
cleavage. - Blastocyst (Blastula) - Ball of cells formed from
morula. - Embryonic disk - Inner mass of cells of
blastocyst. - Gastrula - Embryo composed of three tissues.
- Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm.
- These are the foundation of the body systems
(Germ Layer Theory).
13
Early Developmental Stages
14
Pre-Embryonic and Embryonic Development
- Stages of development.
- Neurula - Nervous system develops from ectoderm
located just above the notochord. - Involves induction as one tissue influences the
development of another tissue.
15
Primitive Streak and Neurula
16
(No Transcript)
17
Germ Layer Theory of Organ System Development
18
Embryonic Development
- Embryonic development occurs from the second week
to the eighth week. - Fetal development occurs from the third month
through the ninth month. - See Table 17.1 Human Development (in text) for
a summary of key events during the 9 months of
pregnancy.
19
Embryonic Development
- Immediately after fertilization, the embryo
divides and develops into a blastocyst
(Blastula). - Bounded by a layer of cells (trophoblast) that
becomes the chorion. - Implantation completed by the end of the second
week. - Embryo is a gastrula by the end of the third
week. - Placenta is forming by end of fourth week.
20
Embryonic Development
21
Embryonic Development
- By the end of the second month, all organs have
appeared and the placenta is fully functioning. - Embryonic development complete.
22
Five-Week-Old Embryo
23
Fetal Circulation
- The umbilical cord stretches between the placenta
and the fetus and contains the umbilical arteries
and veins. - Placenta functions
- Exchange of gases and nutrients between maternal
and fetal blood takes place in the umbilical
arteries. - Umbilical vein carries blood and oxygen away from
the placenta to the fetus. - Produce hormones to maintain pregnancy (estrogen,
progesterone, HCG)
24
Fetal Circulation and the Placenta
25
(No Transcript)
26
(No Transcript)
27
Science Focus
- Cloning Humans Can It Be Done?
28
Fetal Development
- At the beginning of the third month, head growth
begins to slow and the body increases in length. - Ossification centers appear in bones.
- Sex can be determined sometime in the third month.
29
Three-to-Four Month-Old Fetus
30
Fifth through Seventh Months
- Mother begins to feel fetal movement.
- Wrinkled skin covered by fine hair, lanugo, is
covered by a greasy substance vernix caseosa. - Lungs lack surfactant so if baby is born
prematurely it will have to be on a respirator
(respiratory distress syndrome).
31
Six-Month-Old-Fetus
32
Eighth and Ninth Months
- Fetus usually rotates so head is pointed down
toward cervix. - Fetus is now about 530 mm in length and weighs
about 3,400 g. - Full-term babies have the best chance of
survival. - Breech birth (rump first) may require a
cesarean section.
33
(No Transcript)
34
Development of Male and Female Genitals
- Sex of an individual is determined at the moment
of fertilization. - Gonads arise from indifferent tissue that can
develop into ovaries or testes, depending on the
action of hormones. - In the absence of a Y chromosome and in the
presence of two X chromosomes, ovaries develop
instead of testes.
35
Development of Male and Female Genitals
- Abnormal Development of Genitals
- XY female syndrome / XX male syndrome
- Due to misplaced SRY gene (sex
determining region of the Y). - Ambiguous Sex Determination
- androgen insensitivity syndrome
- male pseudohermaphroditism.
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
HEALTH FOCUS
- Preventing Birth Defects
39
(No Transcript)
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
Pregnancy and Birth
- Major changes that take place in the mothers
body during pregnancy are due to placental
hormones - 1. The uterus relaxes.
- 2. The pulmonary values increase.
- 3. Other effects incontinence, edema, varicose
veins, pregnancy-induced diabetes, striae
gravidarum (stretch marks), increase in
melanocyte activity.
43
Birth
- False-labor (Braxton Hicks contractions)
preliminary contractions that occur periodically
but lasting less than 30 seconds. - True labor is marked by uterine contractions that
occur regularly every 15-20 minutes and last for
40 seconds or more. - Positive feedback control.
- Parturition is the technical term for giving
birth to an offspring.
44
Birth
- Stage 1.
- Mucous plug may be expelled from cervical canal
called bloody show before stage 1 technically
begins. - Cervical canal slowly disappears called
effacement (taking up the cervix). - Breaking of the water
- Cervix dilates completely.
45
(No Transcript)
46
Birth
- Stage 2.
- Babys head descends into the vagina.
- Episiotomy?
- Baby is delivered.
47
(No Transcript)
48
- Stage 3.
- Placenta delivered, usually within 15 minutes.
- Called the afterbirth.
49
(No Transcript)
50
Stages of Parturition
51
Female Breast and Lactation
- Female breast contains 15-20 lobules, each with a
milk duct beginning at the nipple and ending in
alveoli. - In pregnancy, breasts enlarge as ducts and
alveoli increase in number and size. - Milk usually not produced during pregnancy.
- Prolactin (lactogenic hormone) suppressed due to
increase in estrogen and progesterone. - Suckling stimulates release of oxytocin.
52
Female Breast Anatomy
53
Development after Birth
- Development is a lifelong process into adulthood,
after which aging occurs. - Gerontology is the study of aging.
- Aging encompasses progressive changes that
contribute to an increased risk of infirmity,
disease, and death. - Theories.
- Genetic in Origin.
- Whole-Body Process.
- Extrinsic Factors.
54
(No Transcript)
55
Effect of Age on Body Systems
- Skin.
- Skin becomes less elastic due to changes in
elastic fibers. - Processing and transporting.
- Heart shrinks due to a reduction in cardiac
muscle. - Blood pressure gradually increases.
- Liver not as efficient in metabolizing drugs.
- Blood supply to kidneys reduced.
56
Effect of Age on Body Systems
- Integration and coordination.
- Few neural cells of the cerebral cortex are lost
during the aging process. - Reaction time slows.
- Loss of skeletal muscle mass not uncommon.
- Reproductive system.
- Females undergo menopause (Ch. 16).
- Male androgen levels fall between ages 50-90, but
sperm produced until death.
57
(No Transcript)
58
BIOETHICAL FOCUS
- Maternal Health Habits
59
Outline
- Fertilization
- Pre-Embryonic and Embryonic Development
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy and Birth
- Development after Birth (including Aging)
60
(No Transcript)