Antigen recognition is mediated by specific antigen receptors - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
Antigen recognition is mediated by specific antigen receptors
Description:
Antigen recognition is mediated by specific antigen receptors ... CELL LYSIS. Uses of Monoclonal Antibodies. Diagnostic agents (histology, immunoassays) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:97
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Antigen recognition is mediated by specific antigen receptors
1
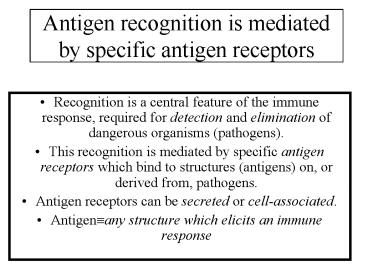
Antigen recognition is mediated by specific
antigen receptors
- Recognition is a central feature of the immune
response, required for detection and elimination
of dangerous organisms (pathogens). - This recognition is mediated by specific antigen
receptors which bind to structures (antigens) on,
or derived from, pathogens. - Antigen receptors can be secreted or
cell-associated. - Antigen?any structure which elicits an immune
response
2
Receptors for antigen in the immune system
- Signalling receptors
- B-cell (immunoglobulin)
- T-cell receptors
- Substantial somatic diversification of receptors
within the individual - Antigen display receptors
- MHC Class I and II
- Limited diversity, all of which is inherited as
part of polymorphism in the species
3
Immunoglobulin properties
- Need to study homogeneous, pure protein
- Myelomas-tumours of plasma cells
- Monoclonal antibodies
4
HYBRIDOMAS TO MAKE MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
LYMPHOCYTE
HYBRIDOMA
MYELOMA
5
A prototype antibody molecule
Light chain
Disulfide bonds
Heavy chain
6
ENZYME DIGESTION OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS
Fragment antigen-binding
Fragment crystallisable
Papain
Pepsin
7
IMMUNOGLOBULIN-THE BASIC UNIT
8
Structure of an immunoglobulin molecule (2)
9
Hypervariable regions in the antibody
sequence Complentarity determining regions
10
A V-REGION
11
ANTIBODY FUNCTION
ANTIGEN BINDING
CDRs
Complementarity determining regions
EFFECTOR FUNCTION (business end)
12
ANTIBODY CLASSES AND SUBCLASSES (ISOTYPES)
- CLASSES
- IgM, IgG, IgD, IgA, IgE
- SUBCLASSES
- IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4
13
IMMUNOGLOBULIN CLASSES-THE BASIC SUBUNITS
MONOMER PENTAMER MONOMER
DIMER MONOMER
MONOMER WHEN ACTING
AS B-CELL RECEPTOR FOR ANTIGEN
14
THE PENTAMERIC IgM MOLECULE
FIRST LINE OF DEFENCE LOW AFFINITY-HIGH AVIDITY
15
DIMERIC IgA
Protection of the mucosa
16
AFFINITY AND AVIDITY
17
A typical antibody molecule
Antigen binding region
Fc region interacts with innate effector
mechanisms and greatly amplifies them
Fc region
18
Fc Receptors
- High affinity-Ig pre-bound to receptor
- Waits for antigen to come along.
- IgG, IgE
- Low affinity- receptor not normally occupied.
- only occupied after antibody has become complexed
to antigen (useful in phagocytosis) - IgG, IgA, IgE
19
Role for IgE on mast cells and basophils
High affinity receptor for IgE
antigen
Antigen comes to the mast cell which already has
IgE attached to its receptor
20
Role for IgE and eosinophils
eosinophil
Low affinity receptor
antigen
Antibody coated antigen comes to the cell
21
(No Transcript)
22
Immunoglobulins-properties
23
Immunoglobulins-properties
24
Protective effects of antibody
Opsonisation and antibody-dependent destruction
25
ANTIBODY CAN BLOCK BINDING AND ENTRY OF VIRUSES
INTO CELLS
26
Interaction between innate and adaptive immunity.
The complement system
27
(No Transcript)
28
COMPLEMENT ACTIVATION ON A CELL SURFACE
INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS CHEMOTACTIC
FACTORS OPSONISATION CELL LYSIS
C5 C6 C7 C8 C9
29
Uses of Monoclonal Antibodies
- Diagnostic agents (histology, immunoassays)
- Experimental probes for cell biology
- Therapeutic agents
- What are the advantages over polyclonal
antibodies raised by immunisation of larger
animals?
30
Therapeutic Monoclonal antibodies for killing
lymphocytes
31
CD52 is strongly expressed on lymphocytes and not
on blood stem cells
CD52
lymphocytes
STEM CELLS
MYELOID CELLS
PLATELETS
RED CELLS
32
ANTIBODY FUNCTION
ANTIGEN BINDING
CDRs
Complementarity determining regions
EFFECTOR FUNCTION (business end)
33
HUMANISATION OF ALEMTUZUMAB (ANTIBODY ENGINEERING)
ANTIGEN BINDING
CDRs
EFFECTOR FUNCTION (business end)
34
ALEMTUZUMAB-THE FIRST HUMANISED THERAPEUTIC
ANTIBODY
Riechmann, L. Clark, M., Waldmann, H., Winter,
G. 1988 Reshaping human antibodies for therapy.
Nature 332, 323-327.
35
The first administration of humanised CAMPATH-1H
(ALEMTUZUMAB)
Hale, G. Clark, M.R., Marcus, R., Winter, G.,
Dyer, M.J.S., Phillips, J.M., Riechmann, L.
Waldmann, H. 1988 Remission Induction in
Non-hodgkin Lymphoma with Reshaped Human
Monoclonal Antibody CAMPATH-1H Lancet II,
1394-1399
36
(No Transcript)
37
90 reduction in relapse rate after Alemtuzumab.
Alemtuzumab treatments
Months before and after Alemtuzumab
Correct as of 31 December 2003
38
ANTIBODIES
- RECEPTORS FOR ANTIGEN ON B-CELLS
- WHEN SECRETED IMMUNOGLOBULIN ANTIBODIES
- ONE B-CELL MAKES ONLY ONE ANTIBODY
- HYBRIDOMAS THROUGH CELL FUSION
- MONOCLONAL ANTIOBODIES
- ANTIBODY ENGINEERING
- THERAPEUTICS AND DIAGNOSTICS
- EXPERIMENTAL PROBES