Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title:
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7
Description:
Cell signaling. Activate gene expression ... Movement of molecules across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:56
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7
1
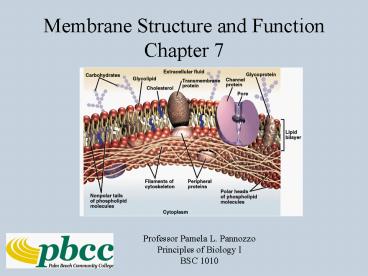
Membrane Structure and FunctionChapter 7
Professor Pamela L. Pannozzo Principles of
Biology I BSC 1010
2
Phospholipid Bilayer
3
Plasma Membrane
4
(No Transcript)
5
Membrane Fluidity
6
Proteins Within the Membrane
- About 2 of the molecules found in plasma
membrane - 50 of its weight since they are large
- Float within the lipid bilayer, may be fixed
- Different proteins for different cells
- General Types
- Integral proteins pass through the membrane
- Peripheral proteins adhere to
- membrane surface
7
Membrane Proteins Do a Lot
8
Membrane Protein Functions (cont)
9
Membrane Carbohydrates
10
Extracellular Matrix
- Tissue strength
- Attach cells
- Cell signaling
- Activate gene expression
- Structural polysaccharides (create gelresist
compression) - Proteoglycans
- Glycosaminoglycans
- Chitin
- Structural proteins (bone, cartilage, connective
tissue) - Collagen, elastin
- Adhesive proteins (connect cells)
- fibronectin
11
Membrane Sidedness
12
Membrane Transport Movement Through the Cell
Membrane
13
Plasma Membrane
- Regulates transport of molecules across cell
boundaries - Cell functions as an open system
14
Selective Permeability
- Cell functions as open system
- Types of molecules
- Small hydrophobic molecules--hydrocarbons, CO2,
O2 - Small hydrophilic molecules--water, ions, polar
molecules - Large molecules proteins, polysaccharides
15
Diffusion
- Movement of solutes in solution across a membrane
- Movement from an area of higher concentration to
lower concentration - Concentration gradient
- Difference between two sides of a membrane
- Passive transport
- Requires no energy
16
Diffusion
17
Diffusion (cont)
18
Osmosis
- Movement of water molecules across a membrane
- Special case of Diffusion
- Passive transport
- Direction of movement determined by total solute
concentration on either side of the membrane - Isotonic solutions with equal solute
concentrations - Hypertonic greater solute concentration
- Hypotonic lower solute concentration
- Cell shrinkage (crenation) or swelling (lysis)
19
Osmosis
20
Osmosis (cont)
21
Facilitated Diffusion
- Movement of hydrophilic molecules across a
membrane with the help of transport proteins - Passive transport
- Movement from higher to lower concentration
22
(No Transcript)
23
Active Transport
- Movement of molecules across a cell membrane
against their concentration gradient - Mechanisms
- Ion pumps
- Coupled transport
- Transport proteins act as pumps
- Conformational shape change
- Requires energy
- ATP phosphorylates transport protein
- Dephosphorylation restores original conformation
24
Ion Pumps
25
Coupled Transport
26
Endocytosis
- Bulk (active) tranport, requires energy
- Movement of large molecules into a membrane by
formation of a vesicle - Types
- Phagocytosis
- Pinocytosis
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis
27
Phagocytosis
28
Pinocytosis and Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
29
Receptor Mediated Endocytosis EM
30
Exocytosis
- Movement of large molecules out of a membrane
through formation of a vesicle - Examples
- Secretion of insulin by pancreas
- Secretion of mucus by salivary glands
- Secretion of chemical signals by nerve cells