Database Systems - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Database Systems
Description:
the attribute names Ai of R. the domain Di (datatype format) for each Ai ... CREATE DOMAIN gender_dom CHAR(1) CHECK (VALUE IN ('F', 'f', 'M', 'm')); SQL Schema ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:20
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Database Systems
1
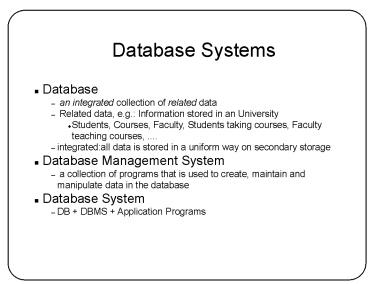
- Database Systems
- Database
- an integrated collection of related data
- Related data, e.g. Information stored in an
University - Students, Courses, Faculty, Students taking
courses, Faculty teaching courses, .... - integratedall data is stored in a uniform way on
secondary storage - Database Management System
- a collection of programs that is used to create,
maintain and manipulate data in the database - Database System
- DB DBMS Application Programs
2
- Database System Organization
- A Simplified View
Users
DBS
Application Programs
Query and transaction Processing
Management of Stored Data
DBMS
Meta-data
Database
3
- Databases vs File Systems
- What is wrong with a File System?
- Data Integration and Data Sharing
- Features of DBMS that cannot be provided with a
file system - Data Consistency
- Controlled Redundancy
- Program-Data Independence
- Integrity Enforcement
- Concurrency Control
- Backup and Recovery
- Security and Privacy
- Multiple views of Data
4
- Additional Advantages
- Performance
- Expandability/Flexibility
- Reduced Applicaiton Development Time
- Enforcement of Standards
- Economies of Scale
- The Price You Pay !!
- High initalcost
- High overhead
- Not special purpose
- When is DBMS Inappropriate?
- Database is small and has simple structure
- applications are simple and special-purpose
- applications with real-time requirements
- concurrent, multi-user access to data is not
needed
5
- The Three Levels of Abstraction
- Internal Level
- describes the physical storage structure of the
DB - Conceptual Level
- describes the structure of the whole DB
- hides storage and implementationdetails
- External Level
- point of view of users
Logical and Physical Data Independence
6
- Data Modeling / Database Design
- Database Design
- is the activity of specifying the schema of a
database in a given data model - Database Schema
- is the structure of a database that
- captures data types, relationships, constriants
on the data - is independent of any application program
- changes infrequently
- Database instance or state
- the actual data in the database at a given time
- Data Model
- a set of primitives for defining the structure of
a DB - a set of operations for specifying the retrievals
and updates on a DB - relational, hierarchical, network,
object-oriented, .....
7
- Relational Model (Codd 1970)
- The most popular implementation model
- simplest, has the most uniform data
structures,has a formal mathematical model,
powerful query languages (relational algebra),
existence of 4th generation languages - but, not suitable for some applications
- Everything is represented by relations
- Formally Given sets D1, D2, ....Dn (not
necessarily distinct), a relation R ? D1 X D2 X
...X Dn - Di 's are the domains and n is the arity
(degree) of R - elements of R are called tuples
- number of tuples in R is the cardinality of R
8
Relational Model (continued)
- relational data model helps to view a relation as
a table - each row represents a tuple (record)
- each column represnts an attribute (field)
- Observe the following properties
- no two rows are identical
- the ordering of tuples is unimportant
- the ordering of columns is important
PART
Part PName Color Weight
P1 Nut Red 12
P2 Bolt Blue 17
P3 Screw Green 16
9
- Relation Schema
- A relation scheme R specifies
- the attribute names Ai of R
- the domain Di (datatype format) for each Ai
- datatype is a set of atomic data values
- no attribute is set-valued (1st Normal
Form or, 1-NF) - no attribute is composite
- format is the specification of the
representationof a data values - A collection of relation schema used to represent
the information in the database is the database
scheme - A relation instance r of R (denoted r(R)) is the
set of tuples that compose the relation at a
given intance, i.e. the current values. - cardinality r(PARTS) 3, the arity PARTS 4
- In general, R gt 0, r(R) ? 0
10
- Keys
- Let R be a realtion schema and K ? R
- K is a superkey of R if it can uniquly identify
any tuple in any r(R). There are no tuples t and
t' such that tK t'K - K is a candidate key if K is a minimal superkey.
There is no K' ? K such that K' is also a
superkey of r(R) - A primary key is one of the candidate keys,
remaining candidate keys are alternate keys - E.g. CLASS (Course, Prof, Sched, Room)
- Identify superkeys, candidate keys
Key is a property of a relation schema but is not
of a relation
11
- Relational Database Schema
- A database schema is a set of relation schemas
and a set of integrity constraints - Integrity constraints
- structural
- key constraints uniqueness of keys
- entity integrity constraint no primary key value
can be null - referential integrity constraint
- semantic
12
- Referential Integrity Constraints
- In the relational model, the only way an entity
can reference another entity is through the value
of the primary key of the second entity - A foreign key (FK) is a set of one or more
attributes of a relation R1 that forms a primary
key (PK) of another relation R2 - This means
- the attributes in FK have the same domain as the
primary key attributes of R2 - the value of FK in any tuple t1 of r(R1) is
either null or matches with a value of PK for
some tuple t2 in r(R2), i.e., t1FK t2PK
SSN EName DNO
EMP
Each employee must belong to some department
DEPT
DNO DName Mgr
13
Referential Integrity Constraints (continued)
- we say attributes FK of R1 reference or refer to
the relation R2 - Referential integrity constraints can be defined
for the same relation, i.e., tuples may refer to
another tuple in the same relation
SSN EName DNO SUPERSSN
EMP
14
Relational Query Languages
- Query languages allow manipulation and retrieval
of data from a database - Relational model supports simple, powerful query
languages - strong formal foundation based on logic
- allows for optimization
- Two mathematical languages form the basis for rel
languages (e.g., SQL) and for implementation - Relational Algebra More operational, useful for
representing execution plans - Relational Calculus Lets users describe what
they want, rather than how to compute it
(non-operational, declarative) - Basic operations
- selection, projection, cross-product,
set-difference, union, intersection, join,
division
15
- SQL
- SQL (Structured Query Language) is the query
language for the System R developed at IBM San
Jose Astraham, Gray, Lindsay, Selinger .. - SQL is now the query language for IBM's DB2 and
the de-facto standard on most commercial RDBMS - SQL is a comprehensive language providing
statements for data definition, query and update.
Hence it is both DDL and DML - SQL allows to create views, it can be embedded in
a general-purpose programming language (C or
PASCAL) - SQL has one basic statement for retrieving data
from the database the SELECT statement - SELECT ltattribute listgt
- FROM lttable listgt
- WHERE ltconditiongt
- Standards
- SQL or SQL1 (ANSI 1986)
- SQL2 or SQL-92 (ANSI 1992)
- SQL3 underway extends SQL with OO and other
concepts
16
- SQL Data Types
- Numeric
- Integers of various ranges INTEGER (or INT),
SMALLINT - Real numbers of various precision FLOAT, REAL,
DOUBLE PRECISION - Formatted numbers DECIMAL(i,j) or DEC(i,j) or
NUMERIC(i,j) - Character Strings
- Fixed length n CHAR(n) or CHARACTER(n)
- Variable length of maximum n VARCHAR(n) or CHAR
VARYING(n) (default n 1) - Bit strings
- Fixed length n BIT(n)
- Varying length of maximum n VARBIT(n) or BIT
VARYING(n)
17
- SQL Data Types (continued)
- Date Time SQL2
- DATE (10 positions) YYYY-MM-DD
- TIME (8 positions) HHMMSS
- TIME(i) defines i decimal fractions of seconds
- (81i positions) HHMMSSddd...d
- TIME WITH TIME ZONE includes the displacement
from standard universal time zone 1300 to
-1259 (6 additional positions)
HHMMSS/-HHMM - TIMESTAMPdate, time with 6 fractions of seconds
and optional time zone - INTERVAL Year/Month or Day/TIME
18
- DDL
- DDL is used to define the (schema of) database
- to create a database schema
- to create a domain
- to create, drop. alter a table
- to create, remove an index defunct in SQL2
- to create or drop a view
- to define integrity constraints
- to define access privileges to users (Oracle
CONNECT, RESOURCE, DBA) - to GRANT or REVOKE privileges ON/TO object/user
- SQL2 supports multiple schemas
- CREATE SCHEMA name AUTHORIZATION user
- CREATE SCHEMA EMPLOYEE AUTHORIZATION atluri
19
- Create Domain
- CREATE DOMAIN name_dom AS VARCHAR(30)
- CREATE DOMAIN project_dom AS CHAR(20)
- CREATE DOMAIN dept_dom AS VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT
'none' - CREATE DOMAIN city_dom CHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL
- CREATE DOMAIN hour_dom FLOAT DEFAULT 0
- CREATE DOMAIN gender_dom CHAR(1)
- CHECK (VALUE IN ('F', 'f',
'M', 'm'))
20
- SQL Schema
EMP(Name,SSN,DNO,BirthPlace) DEPT(DName,DNO,MGRS
SN) PROJECT(PName,PNO,PLocation,DNum)
WORKSON(ESSN,PNO,Hours) CREATE SCHEMA
'COMPANY' CREATE TABLE EMP (
EName name_dom NOT NULL, SSN CHAR(9) NOT
NULL, DNO INTEGER NOT NULL,
BirthPlace city_dom, PRIMARY KEY(SSN),
FOREIGN KEY (DNO) REFERENCES DEPT (DNO) )
21
- Constraints
- Constraints on attributes
- NOT NULL constraint
- DEFAULT value allows the specification of default
value (without the default clause, the default
value is NULL) - PRIMARY KEY (attribute-list)
- UNIQUE (attribute list) allows the specification
of alternative key - FOREIGN KEY (key) REFERENCES table (key)
- Enforcement of Time Constraints
- Immediate
- Deferrable (until commit time)
- Actions if a referential integrity constraint is
violated (referential triggered actions) - SET NULL
- CASCADE (propagate action)
- SET DEFAULT)
- Qualifying actions by the triggering condition
ON DELETE and ON UPDATE - FOREIGN KEY (DNO) REFERENCES DEPT (DNO)
- ON DELETE SET DEFAULT ON UPDATE CASCADE
22
- Naming of the Constraints
Keyword CONSTRAINT may be used to name a
constraints Helpful in modifying or dropping the
constraint CREATE TABLE EMP (
EName name_dom NOT NULL, SSN CHAR(9) NOT
NULL, DNO INTEGER NOT NULL,
BirthPlace city_dom, CONSTRAINT Emp_PK
PRIMARY KEY(SSN), CONSTRAINT Emp_FK
FOREIGN KEY (DNO) REFERENCES DEPT (DNO) )
23
- System Catalog (Dictionary)
- Dictionary stores a set of tables that describe
the database - Base Relations (tables)
- possible attributestable-name, creator,
of-tuples, tuple-length, of- attributes, .. - Attributes of Relations (columns)
- possible attributes table-name, attribute-name,
format, order, key. ,, - Indexes
- possible attributes table-name, index-name,
key-attribute, .. - Authorization
- Integrity
- In Oracle, the dictionary is made up of
tablespaces (one or more physical files) SYSTEM,
USERS, TEMP, APPLICATIONS
24
DROP Command
- DROP command can be used to remove
- a schema
- DROP SCHEMA Company CASCADE
- DROP SCHEMA Company RESTRICT
- CASCADE option removes everything tuples,
tables, domains, ... - RESTRICT option removes the schema if it has no
elements in it - a table
- DROP TABLE EMP CASCADE
- DROP SCHEMA EMP RESTRICT
- CASCADE option removes the table and all
references to it - RESTRICT option removes the table if it is not
referenced
25
- ALTER Command
- The ALTER allows to
- alter the domain of an attribute
- ALTER TABLE Student
- ALTER GPA NUMBER(4,2)
- set or drop default value of an attribute
- ALTER TABLE Student
- ALTER GPA DROP DEFAULT
- ALTER TABLE Student
- ALTER GPA SET DEFAULT 0.00
- add a new attribute to a relation
- ALTER TABLE Student
- ALTER Admission DATE
- drop an attribute (not in SQL1)
- ALTER TABLE Student
- DROP GPA CASCADE/RESTRICT
26
- The Select Statement
- The general form of a SELECT statement
- SELECT ltattribute listgt
- FROM lttable listgt
- WHERE ltconditiongt
- GROUP BY ltattribute listgt
- HAVING ltconditiongt
- ORDER BY ltattribute,ASC/DESC pairgt
27
- Relational Operators in SQL
- Projection
- SELECT A,B
- FROM R
- Selection
- SELECT
- FROM R
- WHERE F
- Product of two tables A X B
- SELECT R.?, S.?
- FROM R, S
28
More Queries
- Query List the names of all employees that work
in CS - SELECT ? Name
- FROM EMP
- WHERE Dept CS
- Renaming of attributes
- SELECT ? Name AS CSName
- FROM EMP
- WHERE Dept CS
- SELECT DISTINCT BirthPlace
- FROM EMP
- (UNIQUE is not valid any more in SQL2)
29
Some More ..
- Give the number of all employees in the CS
Department - SELECT ? COUNT(?)
- FROM EMP
- WHERE Dept CS
- Give the number of employees in each department
- SELECT ? Dept, COUNT(?)
- FROM EMP
- GROUPBY Dept
- Give the names of the departments that have more
than 50 employees. Also list the number of
employees in those departments - SELECT ? Dept, COUNT(?)
- FROM EMP
- GROUPBYDept
- HAVING COUNT(?) gt 50
- More SQL Built-in Functions
- SUM, AVG,MAX,MIN (List the employee names who
make more than the average salary of all
employees)