Antidiuretic Hormone ADH - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 34
Title:
Antidiuretic Hormone ADH
Description:
Breathe faster to get rid of excess carbon dioxide if pH is too low ... GI ( stool, stoma, drains, tubes ) Insensible: sweat. exhaled. PG ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:531
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Antidiuretic Hormone ADH
1
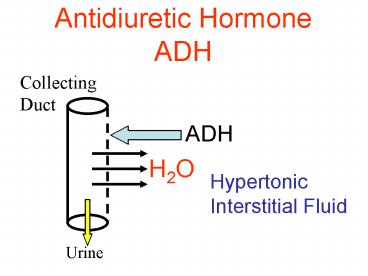
Antidiuretic HormoneADH
Collecting Duct
Hypertonic Interstitial Fluid
Urine
2
Calcitonin
Calcium
3
Estrogen
Calcium
4
Parathormone
Calcium
5
Blood pH 7.4(7.35-7.45)
- Blood pH regulated by
- 1. Kidneys
- 2. Lungs
- 3. Buffers in blood
6
H Secreted HCO3- Resorbed
Blood
H
Kidney Nephron
Urine
HCO3-
7
Kidneys Regulate pH
- Excreting excess hydrogen ions, retain
bicarbonate - if pH is too low
- Retaining hydrogen ions, excrete bicarbonate
- if pH is too high
8
Lungs Regulate pH
- Breathe faster to get rid of excess carbon
dioxide if pH is too low - Carbon dioxide forms carbonic acid in the blood
- Breathe slower to retain carbon dioxide if pH is
too high
9
Carbon Dioxide and Acid
CO2 H2O H2CO3 H HCO3-
10
More Carbon Dioxide More Acid Lower pH
- Breathing slower will retain CO2 , pH will
- decrease (more acid)
- Breathing faster will eliminate more CO2 pH will
- increase (less acid)
11
Blood pH Drops to 7.3How does the body
compensate?
- Breathe faster to get rid of carbon dioxide
- eliminates acid
12
Blood pH Increases to 7.45How does the body
compensate?
- Breathe slower to retain more carbon dioxide
- retains more acid
13
The role of ADH
- ADH urinary concentration
- ADH secreted in response to ?
osmolality - secreted in response to ? vol
- ADH acts on DCT / CD to reabsorb water
- Acts via V2 receptors aquaporin 2
- Acts only on WATER
14
Calculation of osmolality
- Difficult measure add all active osmoles
- Easy sodium x 2 urea glucose
- Normal 280 - 290 mosm / kg
15
Fluid shifts in disease
- Fluid loss
- GI diarrhoea, vomiting, etc.
- Renal diuresis
- Vascular haemorrhage
- Skin burns,sweat
- Fluid gain
- Iatrogenic
- Heart / liver / kidney failure
16
Prescribing fluids
- Crystalloids
- 0.9 saline - not normal !
- 5 dextrose
- 0.18 saline 0.45 dextrose
- Others
- Colloids
- Blood
- Plasma / albumin
- Synthetics eg gelofusion
17
The rules of fluid replacement
- Replace blood with blood
- Replace plasma with colloid
- Resuscitate with crystalloid or colloid
- Replace ECF depletion with saline
- Rehydrate with dextrose
18
How much fluid to give ?
- What is your starting point ?
- Euvolaemia ? ( normal )
- Hypovolaemia ? ( dry )
- Hypervolaemia ? ( wet )
- What are the expected losses ?
- What are the expected gains ?
19
Signs of hypo / hypervolaemia
- Signs of
- Volume depletion Volume overload
- Postural hypotension
Hypertension - Tachycardia Tachycardia
- Absence of JVP _at_ 45o
Raised JVP / gallop rhythm - Decreased skin turgor Oedema
- Dry mucosae Pleural effusions
- Supine hypotension Pulmonary oedema
- Oliguria Ascites
- Organ failure Organ failure
20
What are the expected losses ?
- Measurable
- urine ( measure hourly if necessary )
- GI ( stool, stoma, drains, tubes )
- Insensible
- sweat
- exhaled
21
- Electrolyte (Na, K, Ca) Steady State
- Amount Ingested Amount Excreted.
- Normal entry Mainly ingestion in food.
- Clinical entry Can include parenteral
administration.
22
Case 1
- A 62 year old man is 2 days post-colectomy. He is
euvolaemic, and is allowed to drink 500ml. His
urine output is 63 ml/hour - 1. How much IV fluid does he need today ?
- 2. What type of IV fluid does he need ?
23
Case 2
- 3 days after her admission, a 43 year old woman
with diabetic ketoacidosis has a blood pressure
of 88/46 mmHg pulse of 110 bpm. Her charts show
that her urine output over the last 3 days was
26.5 litres, whilst her total intake was 18
litres - 1. How much fluid does she need to regain a
normal BP ? - 2. What fluids would you use ?
24
Case 3
- An 85 year old man receives IV fluids for 3 days
following a stroke he is not allowed to eat. He
has ankle oedema and a JVP of 5 cms his charts
reveal a total input of 9 l and a urine output of
6 litres over these 3 days. - 1. How much excess fluid does he carry ?
- 2. What would you do with his IV fluids ?
25
Case 4
- 5 days after a liver transplant, a 48 year old
man has a pyrexia of 40.8oC. His charts for the
last 24 hours reveal - urine output 2.7 litres
- drain output 525 ml
- nasogastric output 1.475 litres
- blood transfusion 2 units (350 ml each)
- IV crystalloid 2.5 litres
- oral fluids 500 ml
26
Case 4 cont
- On examination he is tachycardic his supine BP
is OK, but you cant sit him up to check his
erect BP. His serum Na is 140 mmol/l. - How much IV fluid does he need ?
- What fluid would you use ?
27
Case 5
- 30yo girl
- SOB, moist cough, chest pain
- ESKD
- Very little urine output
- Has missed dialysis last 3 sessions
28
Case 5
- What next?
- Current weight 78kg
- IBW 68kg
- JVP twitching her ear
- No peripheral oedema
- Coarse crackles to mid zones
- BP 240/110
- P 100
- Gallop rhythm
- 4cm of liver in RUQ
29
Case 5
- Assessment
- Acute significant overload
- Probably about 10kg
30
Case 6
- 55yo lady
- Presents to dialysis for her routine session
- BP 78/30
- History of dizziness for the last 6 hours
- Current weight 58kg
- IBW 59kg
31
Case 6
- P 120
- Chest clear
- HS dual
- No oedema
- Admits to 24hours of diarrhoea
- Thirsty
- No JVP visible
32
Case 6
- Dehydrated
- Volume constricted
- Hypotensive due to decreased circulating fluid
volume - Resuscitation?
33
The End
34
Acknowledgements
- Paddy Gibson 4th year teaching ppt 2009
- Robert Harris Fluid Balance ppt 2009
- Heather Laird-Fick Fluid and electrolyte
disorders ppt 2009 - JXZhang Lecture 14 ppt 2009
- Dennis Wormington fundamentals of fluid
assessment ppt 2009