The Microscopic View - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 7
Title:
The Microscopic View
Description:
Some of the gas molecules will eventually strike the condensed phase and condense back into it. ... If the intermolecular forces between molecules are: ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:17
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Microscopic View
1
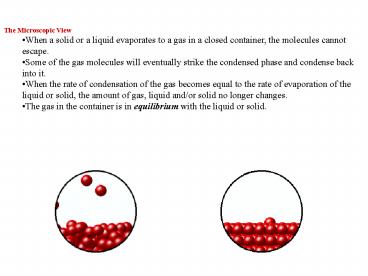
- The Microscopic View
- When a solid or a liquid evaporates to a gas in a
closed container, the molecules cannot escape. - Some of the gas molecules will eventually strike
the condensed phase and condense back into it. - When the rate of condensation of the gas becomes
equal to the rate of evaporation of the liquid or
solid, the amount of gas, liquid and/or solid no
longer changes. - The gas in the container is in equilibrium with
the liquid or solid.
2
- Factors That Affect Vapor Pressure
- Surface Area the surface area of the solid or
liquid in contact with the gas has no effect on
the vapor pressure.
- Types of Molecules the types of molecules that
make up a solid or liquid determine its vapor
pressure. If the intermolecular forces between
molecules are - relatively strong, the vapor pressure will be
relatively low. - relatively weak, the vapor pressure will be
relatively high.
3
- Temperature at a higher temperature, more
molecules have enough energy to escape from the
liquid or solid. At a lower temperature, fewer
molecules have sufficient energy to escape from
the liquid or solid.
4
Vapor Pressure Suppose we have a closed container
into which we pour some water. As soon as we add
the water we check a pressure gauge connected to
the container. We let the container sit for a
while and then we check the pressure again. What
might the pressure guage indicate? As the water
evaporates the pressure exerted by the vapor
above the liquid increases, until at some point,
the pressure reaches a constant value, the vapor
pressure of the substance
5
The molecular basis of vapor pressure The kinetic
energy of the molecules at the surface of a
liquid varies over a range of values
- Some of the molecules have enough kinetic energy
to overcome the attractive forces between the
molecules - The weaker the attractive forces, the greater the
fraction of molecules with enough kinetic energy
to escape - The greater the fraction of molecules which can
escape the liquid, the greater the vapor pressure
- Not only can water molecules leave the surface,
but molecules in the vapor phase can also hit and
go into the water - Initially, there are no molecules in the vapor
phase and the number of molecules in the vapor
which are rejoining the water is zero - As time goes on there are more molecules in the
vapor phase and the number of a vapor molecule
striking the water increases - At some point in time the number of vapor
molecules rejoining the water equals the number
leaving to go into the vapor phase - an equilibrium has been reached, and the pressure
has stabilized at the characteristic vapor
pressure of the substance
6
- What if molecules in the interior of the liquid
decides to leave the liquid phase and go into the
vapor phase? -
- This interior bubble will rapidly collapse if the
external pressure is greater than the vapor
pressure - If the external pressure is equal to, or lower
than the vapor pressure, then the bubble will
remain or expand and the liquid boils
7
Vapor Pressure
- The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature
at which its vapor pressure equals atmospheric
pressure. - The normal boiling point is the temperature at
which its vapor pressure is 760 torr.